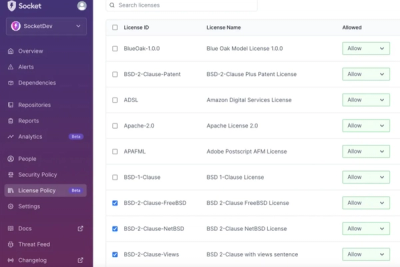
Product
Introducing License Enforcement in Socket
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
This package has been designed to facilitate browsing and retrieving content from the Public Media Platform (PMP) API. It makes it easy to generate signed requests and browser hypermedia resources returned by the PMP API.
For more information about PMP, read the documentation <https://github.com/publicmediaplatform/pmpdocs/wiki>_
This application has been created at KBPS Public Broadcasting in San Diego by Erik Aker and it has been licensed under GPL v2.
py3-pmp-wrapper has been written for Python3.3 and Python3.4. It is not compatible with Python2.7 and below. All references below to installing this application refer only to Python versions 3.3 and 3.4.
To install py3-pmp-wrapper with pip <https://pip.pypa.io>_, just run
this in your terminal::
$ pip install py3-pmp-wrapper
or, with easy_install <http://pypi.python.org/pypi/setuptools>_::
$ easy_install py3-pmp-wrapper
py3-pmp-wrapper is on GitHub, where the code is
available <https://github.com/KPBS/py3-pmp-wrapper>_.
You can clone the public repository::
$ git clone https://github.com/KPBS/py3-pmp-wrapper
Once you have a copy of the source, you can embed it in your Python package, or install it into your site-packages easily::
$ python setup.py install
.. _quickstart:
After the application has been installed, you can create a Client object:
>>> from pmp_api.pmp_client import Client
>>> client = Client("https://api-pilot.pmp.io")
With a working client, you will need to authenticate using your client-id and client-secret
>>> client.gain_access(CLIENT-ID, CLIENT-SECRET)
Now you're ready to make requests:
>>> home_doc = client.home() # Get homedoc
>>> random_request = client.get("https://Some/arbitrary/endpoint?params=someparam")
>>> random_request
<Navigable Doc: https://Some/arbitrary/endpoint?params=someparam>
>>> client.document # Most recent result is saved here
<NavigableDoc: https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs?params=someparam>
The Client will automatically sign all requests and it should renew your
access token if it expires.
Using the fetched document's navigation object, the Client can follow
navigation, if it's present:
# If the document defines a 'next' navigation element, we can follow it
>>> client.next()
<NavigableDoc: https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs?guid=SOME_GUID&offset=10>
>>> client.prev() # Same as above, returns None if nothing there...
>>>
>>> client.last() # requests 'last' page of results as given by document
>>> client.first() # requests 'first' page of results as given by document
We can also go back or forward, like a browser, re-requesting the previous
document:
>>> client.document
<NavigableDoc: https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs?params=someparam>
>>> client.back() # This issues a new request; does not pull from cache
<NavigableDoc: https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs?guid=SOME_GUID>
>>> client.forward() # same as `back`
<NavigableDoc: https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs?params=someparam>
Most of the useful navigation is done via urn, the primary method for
accessing content, and the Client object provides a query method for use with
a urn. For example, let's look at urn:collectiondoc:query:docs, which
contains information for querying documents.
>>> document = client.query('urn:collectiondoc:query:docs',
params={"tag": "samplecontent",
"profile": "story"})
<NavigableDoc: https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs?guid=SOME_GUID>
To really get interesting information back, we need to have some way of
managing it. For this reason, the Client object returns NavigableDoc
elements. These have a number of methods and properties, which should make it
easier to extract information from the document.
>>> document = client.query('urn:collectiondoc:query:docs',
params={"tag": "samplecontent",
"profile": "story"})
<NavigableDoc: https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs?guid=SOME_GUID>
>>> document.links
{'item': [{'href': 'https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs/SOMEGUID ...
>>> client.document.items
[{'attributes': {'valid': {'to': '3014-07-29T18:08:11+00:00', 'from': ...
>>> document.querylinks
[{'rels': ['urn:collectiondoc:query:users'], 'href-template': ...
In order to get interesting results back, we generally want to issue queries,
but it can be tough to know how to make queries. The NavigableDoc object can
help with that.
>>> document.template('urn:collectiondoc:query:docs')
'https://api-pilot.pmp.io/docs{?guid,limit,offset,tag,collection,text,searchsort,has,author,distributor,distributorgroup,startdate,enddate,profile,language}'
In addition, we can find options associated with the urn:
>>> document.options('urn:collectiondoc:query:docs')
{'rels': ['urn:collectiondoc:query:docs'], 'href-template': ...
What if we want to know which urns are listed at a particular endpoint? We
must ask the document for its query_types:
>>> for item in document.query_types():
... print(item)
('Query for users', ['urn:collectiondoc:query:users'])
('Query for schemas', ['urn:collectiondoc:query:schemas'])
('Access documents', ['urn:collectiondoc:hreftpl:docs'])
('Query for documents', ['urn:collectiondoc:query:docs'])
etc.
Finally, you can always retrieve all of the results inside a document by
accessing its collectiondoc attribute. This will return a dictionary of all
values contained in the document:
>>> document.collectiondoc
{ALL-The_Data ...}
This should cover most use-cases for browsing PMP API content.
FAQs
Python3 Wrapper Interface for Public Media Platform API
We found that py3-pmp-wrapper demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
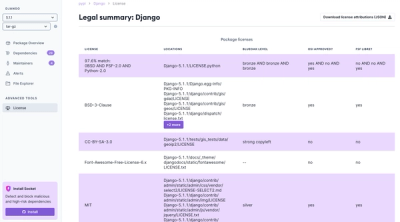
Product
We're launching a new set of license analysis and compliance features for analyzing, managing, and complying with licenses across a range of supported languages and ecosystems.
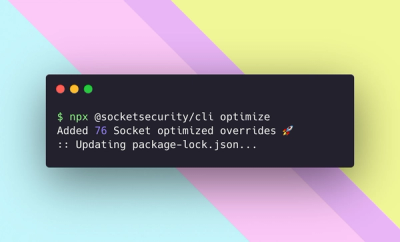
Product
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.