
Security News
Another Round of TEA Protocol Spam Floods npm, But It’s Not a Worm
Recent coverage mislabels the latest TEA protocol spam as a worm. Here’s what’s actually happening.
python-prtree
Advanced tools
python_prtree is a python/c++ implementation of the Priority R-Tree (see references below), an alternative to R-Tree. The supported futures are as follows:
PRTree2D, PRTree3D and PRTree4D (2D, 3D and 4D respectively)insert and erase
insert method can be passed pickable Python objects instead of int64 indexes.query and batch_query
batch_query is parallelized by std::thread and is much faster than the query method.query method has an optional keyword argument return_obj; if return_obj=True, a Python object is returned.rebuild
rebuild.This package is mainly for mostly static situations where insertion and deletion events rarely occur.
You can install python_prtree with the pip command:
pip install python-prtree
If the pip installation does not work, please git clone clone and install as follows:
pip install -U cmake pybind11
git clone --recursive https://github.com/atksh/python_prtree
cd python_prtree
python setup.py install
import numpy as np
from python_prtree import PRTree2D
idxes = np.array([1, 2])
# rects is a list of (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
rects = np.array([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5],
[1.0, 1.5, 1.2, 3.0]])
prtree = PRTree2D(idxes, rects)
# batch query
q = np.array([[0.5, 0.2, 0.6, 0.3],
[0.8, 0.5, 1.5, 3.5]])
result = prtree.batch_query(q)
print(result)
# [[1], [1, 2]]
# You can insert an additional rectangle by insert method,
prtree.insert(3, np.array([1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0]))
q = np.array([[0.5, 0.2, 0.6, 0.3],
[0.8, 0.5, 1.5, 3.5]])
result = prtree.batch_query(q)
print(result)
# [[1], [1, 2, 3]]
# Plus, you can erase by an index.
prtree.erase(2)
result = prtree.batch_query(q)
print(result)
# [[1], [1, 3]]
# Non-batch query is also supported.
print(prtree.query([0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0]))
# [1, 3]
# Point query is also supported.
print(prtree.query([0.5, 0.5]))
# [1]
print(prtree.query(0.5, 0.5)) # 1d-array
# [1]
import numpy as np
from python_prtree import PRTree2D
objs = [{"name": "foo"}, (1, 2, 3)] # must NOT be unique but pickable
rects = np.array([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5],
[1.0, 1.5, 1.2, 3.0]])
prtree = PRTree2D()
for obj, rect in zip(objs, rects):
prtree.insert(bb=rect, obj=obj)
# returns indexes genereted by incremental rule.
result = prtree.query((0, 0, 1, 1))
print(result)
# [1]
# returns objects when you specify the keyword argment return_obj=True
result = prtree.query((0, 0, 1, 1), return_obj=True)
print(result)
# [{'name': 'foo'}]
The 1d-array batch query will be implicitly treated as a batch with size = 1.
If you want 1d result, please use query method.
result = prtree.query(q[0])
print(result)
# [1]
result = prtree.batch_query(q[0])
print(result)
# [[1]]
You can also erase(delete) by index and insert a new one.
prtree.erase(1) # delete the rectangle with idx=1 from the PRTree
prtree.insert(3, np.array([0.3, 0.1, 0.5, 0.2])) # add a new rectangle to the PRTree
You can save and load a binary file as follows.
# save
prtree.save('tree.bin')
# load with binary file
prtree = PRTree('tree.bin')
# or defered load
prtree = PRTree()
prtree.load('tree.bin')
Note that cross-version compatibility is NOT guaranteed, so please reconstruct your tree when you update this package.
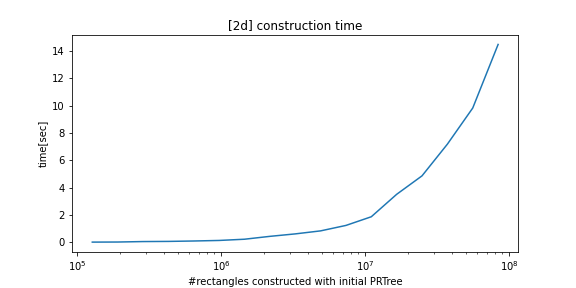
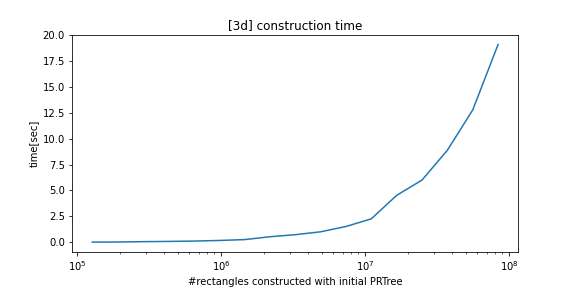
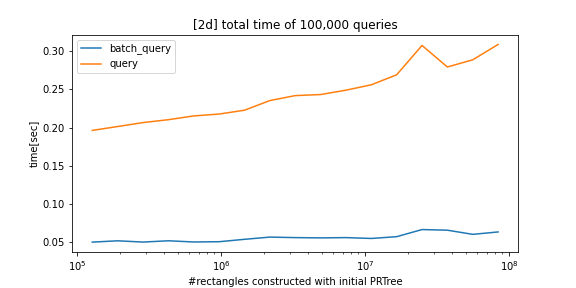
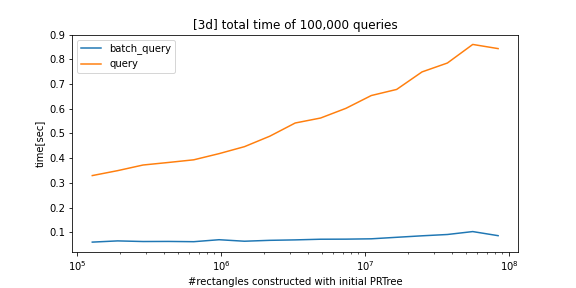
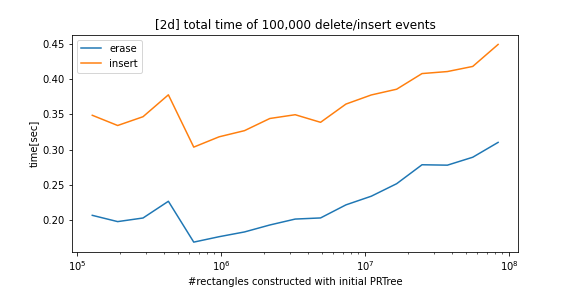
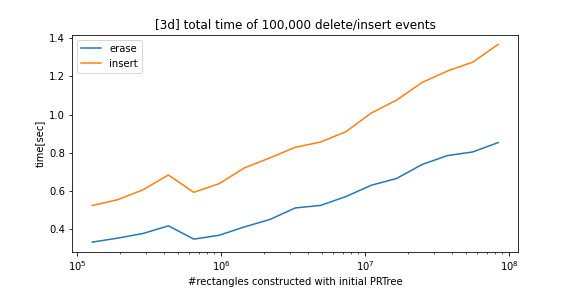
python-prtree>=0.7.0BREAKING CHANGES:
Bug Fix Details:
The bug occurred when two bounding boxes were separated by a very small gap (e.g., 5.39e-06). When converted from float64 to float32, the values would collapse to the same float32 value, causing the intersection check to incorrectly report them as intersecting. This has been fixed by implementing a precision-matching approach: float32 input uses pure float32 for speed, while float64 input uses a two-stage filter-then-refine approach (float32 tree + double-precision refinement) for correctness.
python-prtree>=0.5.8python-prtree>=0.5.7python-prtree>=0.5.3python-prtree>=0.5.2You can use pickable Python objects instead of int64 indexes for insert and query methods:
python-prtree>=0.5.0python-prtree>=0.4.0The Priority R-Tree: A Practically Efficient and Worst-Case Optimal R-Tree Lars Arge, Mark de Berg, Herman Haverkort, and Ke Yi Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD '04), Paris, France, June 2004, 347-358. Journal version in ACM Transactions on Algorithms. author's page
FAQs
Python implementation of Priority R-Tree
We found that python-prtree demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Recent coverage mislabels the latest TEA protocol spam as a worm. Here’s what’s actually happening.

Security News
PyPI adds Trusted Publishing support for GitLab Self-Managed as adoption reaches 25% of uploads

Research
/Security News
A malicious Chrome extension posing as an Ethereum wallet steals seed phrases by encoding them into Sui transactions, enabling full wallet takeover.