
Research
/Security News
10 npm Typosquatted Packages Deploy Multi-Stage Credential Harvester
Socket researchers found 10 typosquatted npm packages that auto-run on install, show fake CAPTCHAs, fingerprint by IP, and deploy a credential stealer.


Kirill Boychenko
October 10, 2025
The Contagious Interview operation continues to weaponize the npm registry with a repeatable playbook. Since our July 14, 2025 update, we have identified and analyzed more than 338 malicious packages with over 50,000 cumulative downloads.
25 of these packages remain live on the npm registry at the time of writing. We have submitted takedown requests to the npm security team and petitioned for suspension of the associated publisher accounts.
In this latest wave, North Korean threat actors used more than 180 fake personas tied to new npm aliases and registration emails, and ran over a dozen command and control (C2) endpoints (see IOCs). Their tooling has evolved from direct BeaverTail malware droppers to HexEval, XORIndex, and encrypted loaders. Each executes at install or import, reconstructs obfuscated BeaverTail in memory, then typically fetches the InvisibleFerret backdoor for persistence. New malicious packages appear weekly, including this week.
The pattern is wave-based and iterative. The threat actors ship typosquatted packages, tweak the loader code, and scale distribution across new aliases.
Targets include Web3, cryptocurrency, and blockchain developers, as well as technical job seekers approached with recruiting lures, leading to multi-stage compromise and financial loss.
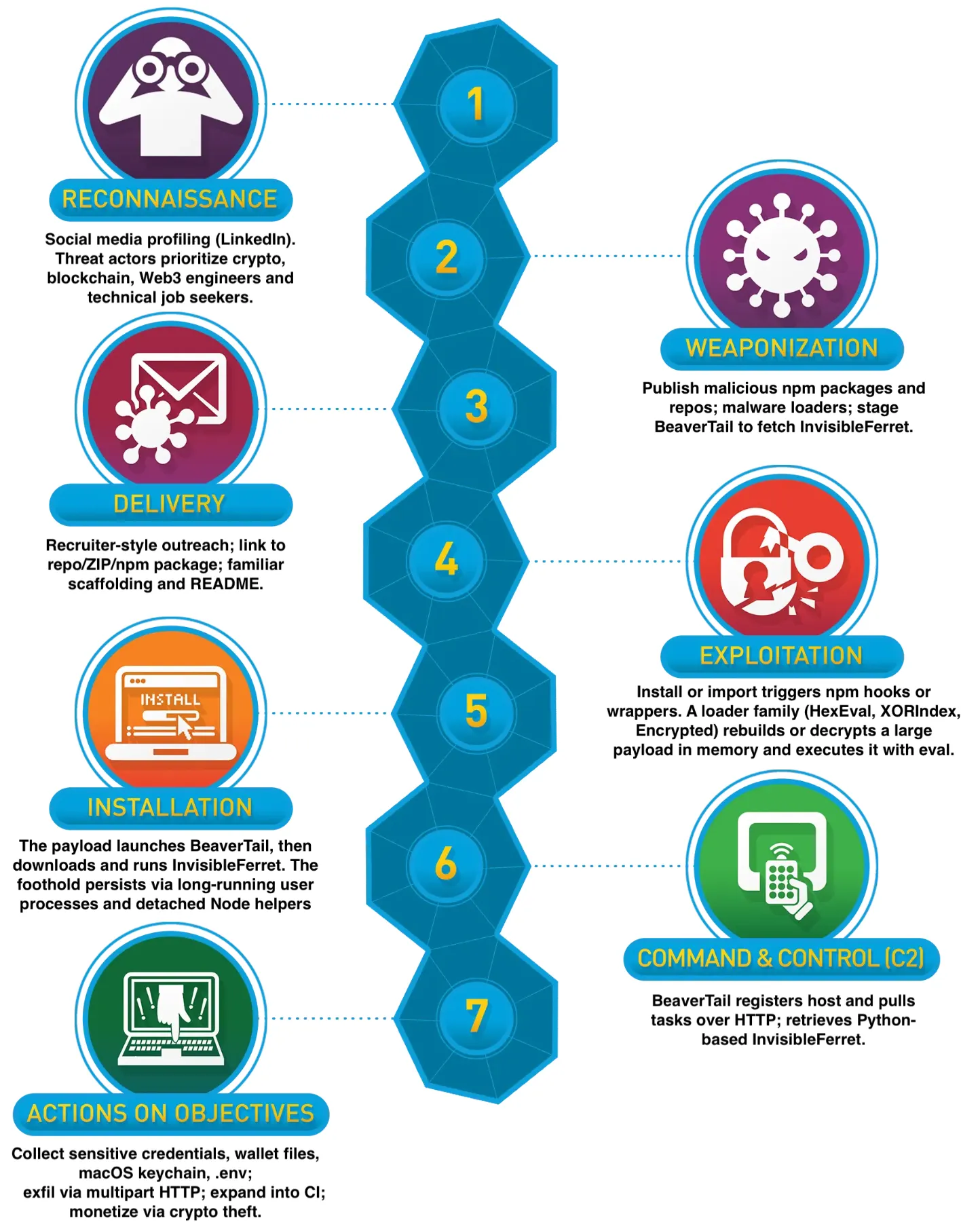
Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain framework mapped to the current Contagious Interview campaign. Reconnaissance on LinkedIn, weaponization with published malicious packages, delivery via recruiter lures, exploitation by malware loaders that execute in memory, installation of BeaverTail and the InvisibleFerret backdoor, C2 over web protocols, then actions on objectives that establish initial access, and steal sensitive credentials and wallet keys.
The campaign opens with focused reconnaissance. Threat actors approach targets on social media, most often LinkedIn, posing as recruiters or hiring managers. They screen for technical fit and financial upside, prioritizing cryptocurrency and blockchain developers, Web3 engineers, and technical job seekers. The objective is to compromise machines that are likely to hold credentials, private keys, tokens, and other monetizable secrets.
A recent victim account on LinkedIn illustrates this stage. A software engineer received a “job opportunity” message, was given a repository for a quick assignment, and found an innocuous dependency named eslint-detector that contained an encrypted, obfuscated payload. The lure targeted a Web3 and crypto profile, relied on routine dependency installation, and used a polished company persona. What looked like a part of the recruitment assignment was a staged malware delivery.
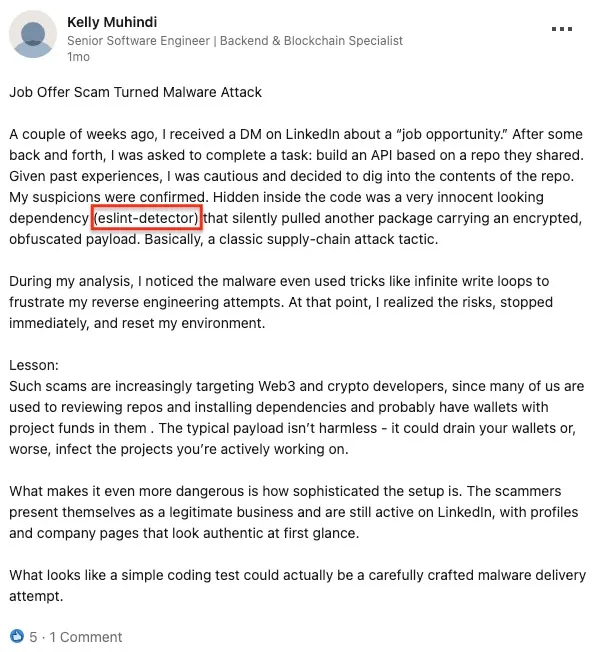
LinkedIn victim report of a job-offer lure that delivered a malicious npm package, eslint-detector, which silently fetched an encrypted payload, illustrating Contagious Interview reconnaissance and supply chain delivery tactics.
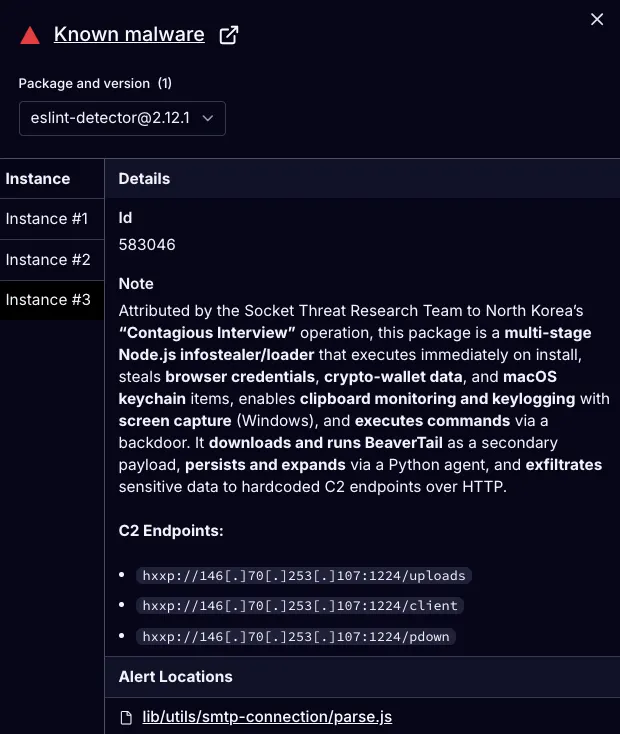
Socket AI Scanner’s analysis of the malicious eslint-detector package highlights install-time execution of a multi-stage infostealer/loader, theft of browser credentials and crypto-wallet data, macOS Keychain access, clipboard monitoring and Windows keylogging with screen capture, remote command execution, BeaverTail download with Python-based persistence (i.e. InvisibleFerret staging), and HTTP exfiltration to hardcoded C2 endpoints.
We continue to see weekly upload bursts, rapid re-uploads after takedowns, and iterative changes to loaders and postinstall scripts. Independent and excellent research by Kieran Miyamoto on the DPRK Research blog (https://dprk-research.kmsec.uk/) also corroborates this pattern and closely tracks the campaign’s weekly cadence across the npm registry.
Over 335 malicious packages in this wave align with the documented Contagious Interview techniques that combine job-seeker social engineering with open source supply chain abuse, notably npm typosquats, brand impersonation, and obfuscated loaders that fetch the second and third-stage malware and backdoors. Threat actors’ objective is developer endpoint access, CI/CD persistence, and ultimately cryptocurrency theft and strategic espionage across blockchain, Web3, and broader tech firms.
Over 335 names cluster around everyday dependencies that interview candidates and working developers install on autopilot, especially in the Node/Express stack. We see close misspellings and plausible add-ons of staples like express, dotenv, body-parser, validator, cors, helmet, morgan, nodemailer, and nodemon. Examples include epxreso/epxresso/epxressoo (Express), dotevn (dotenv), boby_parser (body-parser), vaildator (validator), cors-validator (cors), http-helmet (helmet), morgan-logger (morgan), nodemailer-helper (nodemailer), and nodemon-pkg (nodemon). As some victims report, play on deadline pressure in fake job interview assignments (“just run npm install”) turn routine setup into initial access.
Beyond server basics, the current wave targets what developers touch constantly during quick prototypes: frontend/framework and toolchain surface area (e.g., react-router, tailwindcss, next, vite, webpack, eslint, prettier). We see lookalikes such as react-router-html, react-redirect-router, nextjs-babel-toastify, numerous [vite]-prefixed lookalikes like vite-plugin-react-ping and the near-duplicate vvite-plugin-react-ping, plus vitejs-plugin-react-refresh and webpack-css-branch-loader.
When it comes to crypto hiring, the Web3 kits are also targeted: ethers.js is typosquatted as ethrs.js and ethres.js; web3.js is typosquatted as we3.js and wb3.js; and there are systematic typosquats of truffle (e.g., truffel), ganache (e.g., ganacche), and foundry (e.g., foudry), as well as hardhat-themed packages like hardhat-deploy-notifier and hardhat-deploy-notification. We also see brand impersonation such as metamask-api. The typosquatted names mirror what candidates are most likely to search, typo, or accept in a template.
Targets often receive a series of interview messages followed by a link to a code repository. Cloning and running the project executes an initialization script on first use, which starts the malware chain. Some victims also receive links to documents or forms on common productivity platforms (e.g. Google Docs), setting up a “take home” task that delivers the payload.
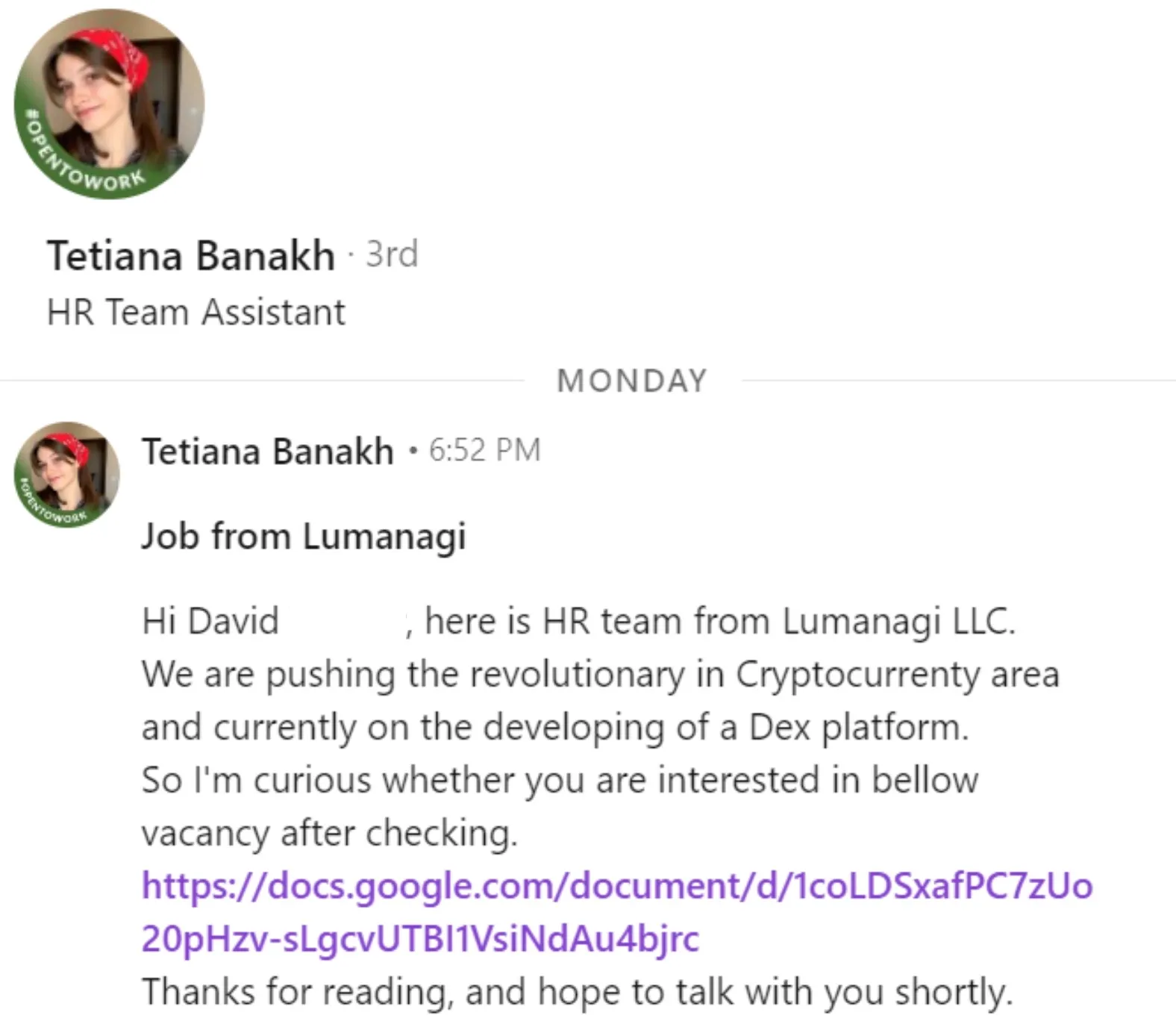
LinkedIn DM lure directing the target to a Google Docs link, a stage-one tactic that establishes a hiring pretext, pivots off-platform, and sets up delivery of a coding test with malicious dependency.
Additionally, we found that threat actors registered email addresses to look like recruiter/HR or “tech” personas that would resonate with developers and job-seekers. We see (1) recruiting/business veneer, e.g. bob.berg.business@gmail[.]com, soft.business0987@gmail[.]com, astroglobal.work@gmail[.]com, jiayingzhang.contact@gmail[.]com; (2) developer/engineering cues, e.g. goldenrhynodev@gmail[.]com, luis.fernando.dev1214@gmail[.]com, sean_tech208@hotmail[.]com, stromdev712418@gmail[.]com, ryon_dev_3@outlook[.]com; and (3) crypto/Web3 flavor, e.g. jackson.tf7.eth@gmail[.]com. These match how threat actors in Contagious Interview campaigns build plausible recruiting identities while keeping infrastructure disposable.
Exploitation begins the moment threat actor code executes on the target machine. In this campaign, execution is user-driven, not a vulnerability exploit. Install or import triggers threat actor logic via npm lifecycle hooks such as postinstall, through entry points that run code at module load, or via small cross-platform wrappers. Three loader families (described in more detail below) implement this pivot from delivery to code run.
A note on the exploitation of npm registry mechanisms by Contagious Interview threat actors. In the current wave of the npm ecosystem infiltrations, we found cases highlighting some gaps in account-level enforcement on the npm registry that threat actors are targeting for abuse. For example, the threat actors’ alias anarenhsaihan published two malicious packages: jito-components, which has since been removed and replaced by a security holding page, and components-flexibility, which remains live at the time of writing. Both packages serve as loaders for the BeaverTail malware.
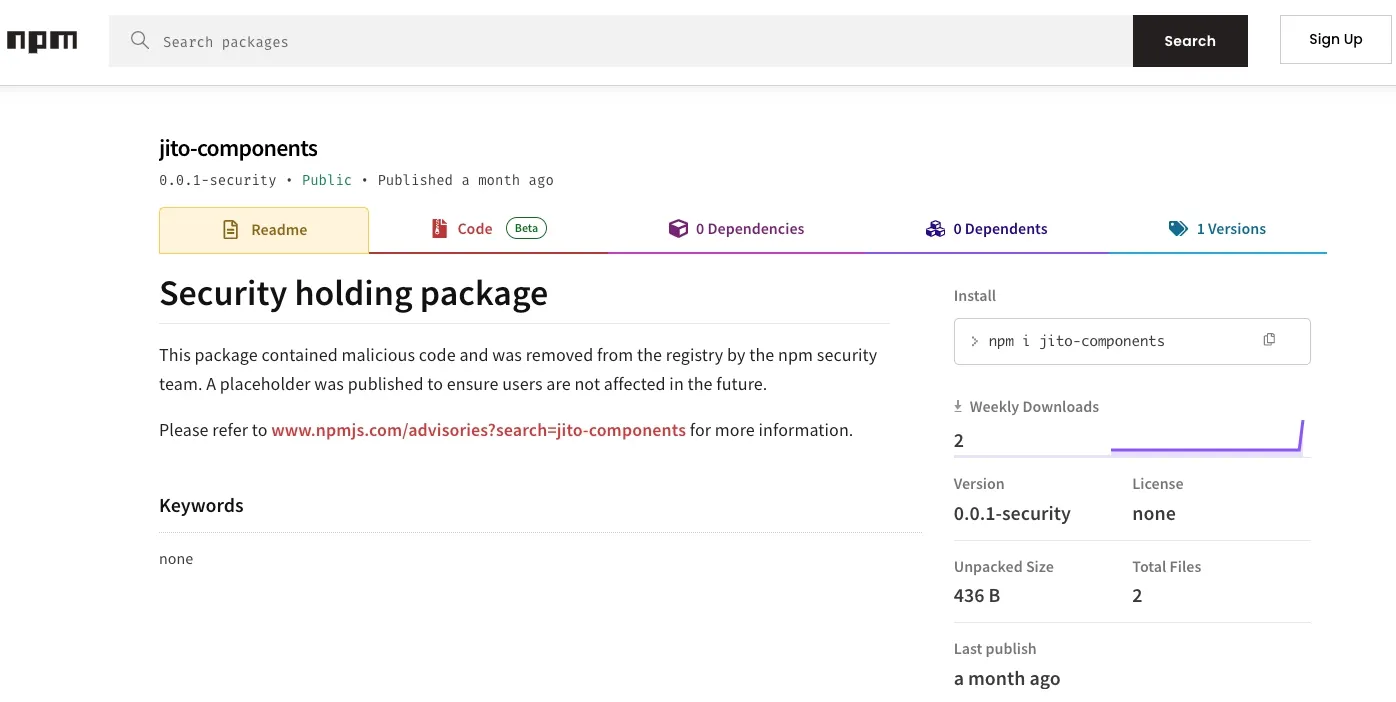
The npm registry marks jito-components as a security holding package after detecting malicious code, replacing the original with placeholder version 0.0.1-security to block installs and protect users.
Despite the jito-components package being flagged and removed by the npm security team, the threat actor’s account was not suspended. This allowed the same alias to publish a second malicious package under the guise of a legitimate UI styling utility.
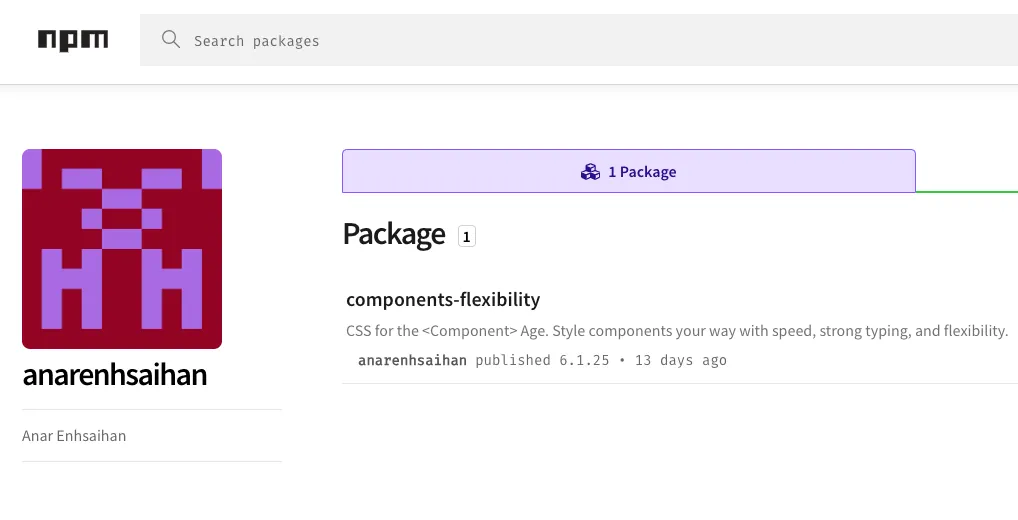
npm account anarenhsaihan with a live package, components-flexibility, indicating the alias remains active and able to publish after the jito-components takedown.
Cleaning up the ecosystem is not a trivial task, especially against advanced persistent threat (APT) actors. Contagious Interview is not a cybercrime hobby, it operates like an assembly line or a factory-model supply chain threat. It is a state-directed, quota-driven operation with durable resourcing, not a weekend crew, and removing a malicious package is insufficient if the associated publisher account remains active.
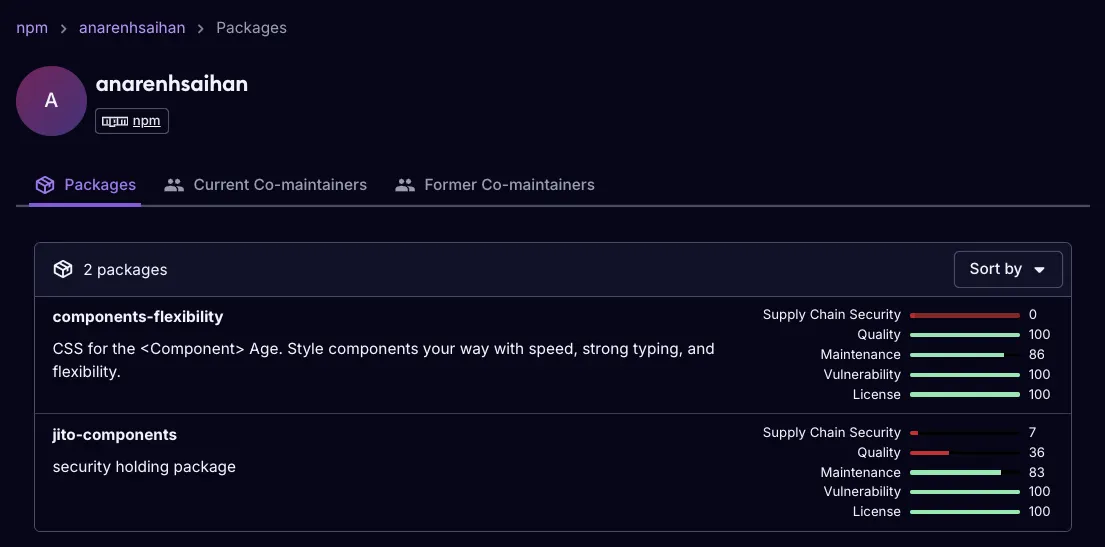
Socket AI Scanner’s view of the npm alias anarenhsaihan shows jito-components replaced with a security holding package while components-flexibility remains live. Our analysis of components-flexibility highlights install-time loader behavior, in-memory execution via eval, and delivery of BeaverTail malware.
Contagious Interview packages install like nesting dolls, a small loader runs first, reconstructs BeaverTail in memory, then BeaverTail drops and fetches the InvisibleFerret backdoor. Earlier waves relied on two families of loaders. HexEval stores stage-two as long hex strings, decodes them at runtime, and evaluates the plaintext with eval, which transfers control to BeaverTail. XORIndex hides strings and code as XORed byte tables and rebuilds them with simple index math before executing the result. Both approaches avoid leaving a readable second stage on disk, and both appear across hundreds of malicious packages.
Recent wave added encrypted loaders. The goal is obfuscation versus cryptographic safety. The malicious packages with encrypted loaders ship a small module that imports Node’s crypto, fixes the algorithm to AES-256-CBC, and hardcodes both the key and the initialization vector (IV). The ciphertext, a large hex blob, is stashed elsewhere in the package, sometimes in a file named LICENSE. At install or import, the module reads that blob, decrypts it, converts it to UTF-8, and evaluates the plaintext in process.
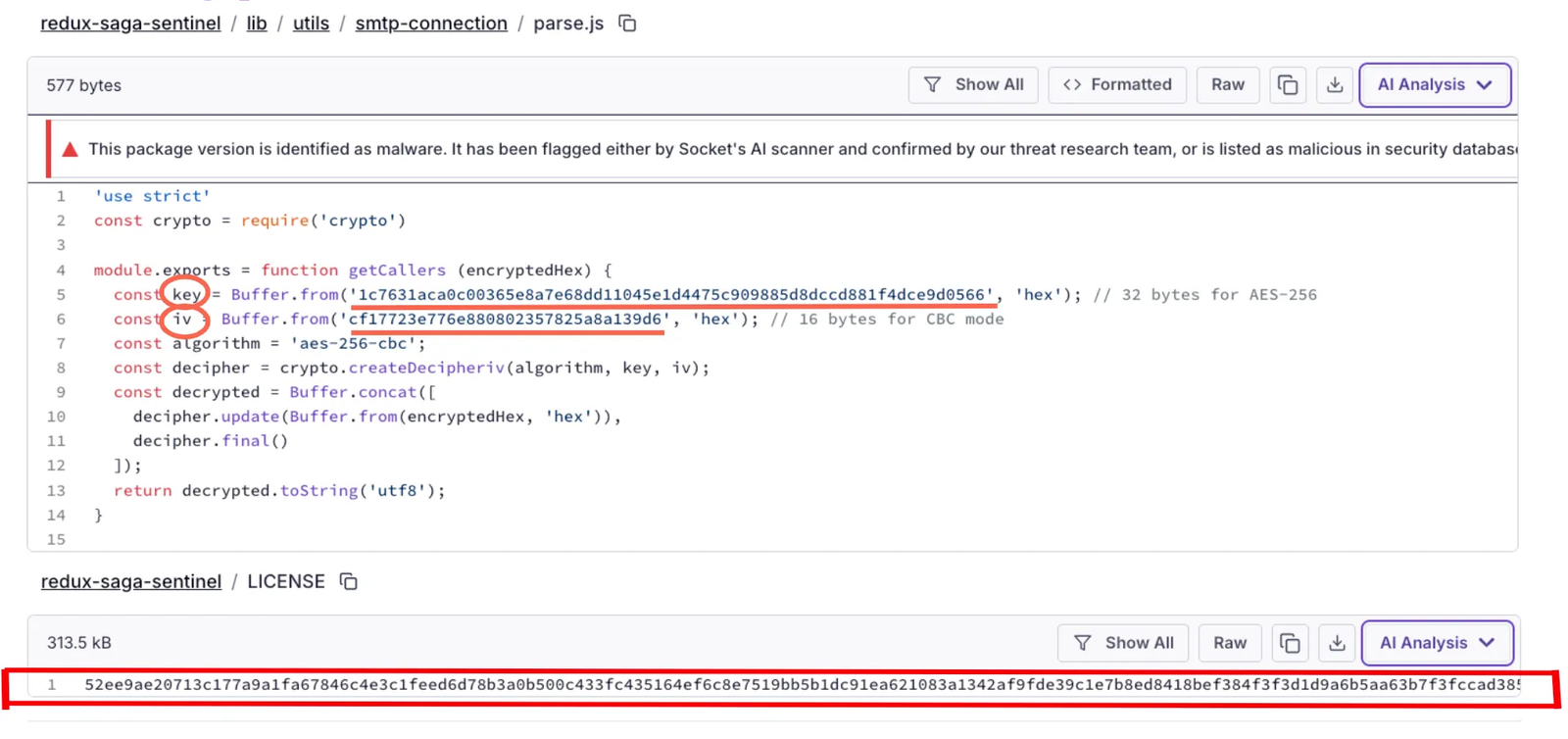
Socket AI Scanner’s analysis of the malicious redux-saga-sentinel package highlights an encrypted loader split across two files. The top file, lib/utils/smtp-connection/parse.js, imports Node crypto and hardcodes an AES-256-CBC key and IV. The bottom file, LICENSE, stores the large hex ciphertext. At runtime, parse.js decrypts the LICENSE blob to plaintext JavaScript and executes it, enabling in-memory loader execution within the same package.
The below CyberChef panel shows how defenders can reproduce decryption: convert the hex ciphertext to raw bytes, apply AES-256-CBC with the embedded key and IV, and recover the stage-two JavaScript. The recovered body remains obfuscated, but deobfuscation confirms BeaverTail, based on its file and wallet targeting, control-flow patterns, and the handoff logic for launching the InvisibleFerret backdoor.
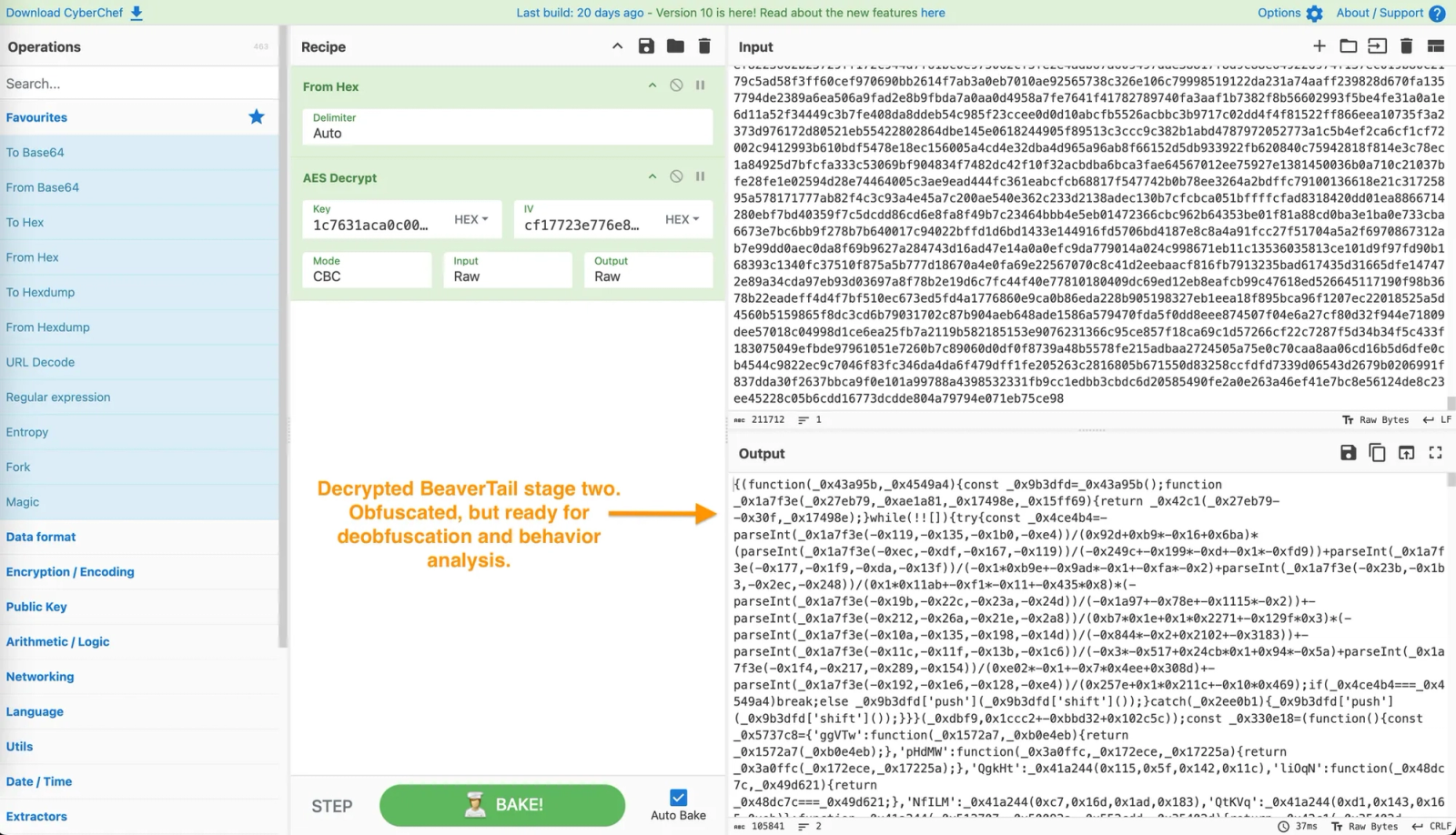
CyberChef reproduces the decrypt of the package’s encrypted loader. Converting the hex ciphertext and applying AES-256-CBC with the embedded key and IV recovers BeaverTail stage-two JavaScript in the Output pane, still obfuscated but ready for deobfuscation and behavior analysis.
Operationally, installation means a long-running foothold rather than a guaranteed autorun. The loader starts BeaverTail, which fetches and launches InvisibleFerret. With BeaverTail active and InvisibleFerret staged, the malware is ready to register the host and begin tasking, which leads directly into Stage 6.
BeaverTail establishes C2 over HTTP(S) and sometimes WebSocket, registers the host, fetches tasking, and stages InvisibleFerret, a cross-platform Python backdoor for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
The campaign blends raw IP C2 with platform C2. Fixed IPs on commodity VPS providers act as backends, while front-end beacons often use legitimate hosting such as *.vercel.app to blend into developer traffic. URIs are deliberately plain and work-adjacent, with paths such as /api/ipcheck, /process-log, and /apikey that masquerade as health checks or logging hooks, so a quick glance by a developer or code reviewer raises little suspicion. Infrastructure recycles across waves with small mutations. Threat actors reuse domain patterns and URL shapes, periodically switch between raw IPs and platform subdomains, and reappear on non-standard ports, historically including port 1224 and in this wave additional high ports, to evade simple egress filters.
Monetization and follow-on objectives focus on cryptocurrency theft and maintaining persistent access for further compromise. There is no vetted dollar total for this specific campaign, but independent reporting estimates that North Korea-linked threat actors have already stolen $2 billion in 2025 and approximately $1.34 billion in 2024. The social engineering workflow described here, fake recruiter personas that push candidates into running take-home assignments or “tests”, aligns with tactics Reuters reported across the crypto sector in 2025. Stolen assets typically move through layered mixers, cross chain swaps, and lower visibility networks, with investigators observing multi hop flows across Bitcoin, Ethereum, BTTC, and Tron.
The campaign’s trajectory points to a durable, factory-style operation that treats the npm ecosystem as a renewable initial access channel. Across waves, we document a steady push of new malware loader variants, including recent encrypted loaders.
We anticipate more loader riffs that split decryption and staging across files to defeat static scans, continued reuse of URL shapes and hosting platforms for cover traffic, and rapid re-uploads after takedowns, especially when publisher accounts remain active.
Account suspensions help, but they are not sufficient, since accounts can be created on a whim. Registries should adopt layered controls: suspend and revoke tokens for confirmed malicious publishers; require re-verification with 2FA and provenance signing; apply pre-publish and prefetch screening to quarantine high-risk uploads; throttle suspicious velocity and namespace churn; and cluster related aliases by shared infrastructure, email patterns, and code templates so enforcement follows the operator, not the name.
Defenders should harden the points where this campaign succeeds: pull requests, installs, and CI. Treat every npm install as code execution and block risky behavior before it reaches developer machines or pipelines. Shift left by scanning code and PRs in real time; require a clean report before merge and vet external libraries for provenance, maintainer trust, and pinned versions.
Socket’s security tooling is purpose-built to address these challenges. The Socket GitHub App provides real-time PR scanning, flagging suspicious or malicious packages before merge. The Socket CLI surfaces red flags during installs and lets teams enforce allow/deny rules, blocking risky behaviors such as postinstall scripts, unexpected network egress, decrypt-and-eval loaders, or native binaries. Socket Firewall blocks known malicious packages before the package manager fetches them, including transitive dependencies, by mediating dependency requests; use it alongside the CLI for behavior-level gating. The Socket browser extension alerts users to suspicious packages while browsing. Socket MCP extends protection into AI-assisted coding, detecting and warning on malicious or hallucinated packages before they are introduced through LLM suggestions. Integrating these tools into development pipelines will help proactively detect and prevent malware, reducing exposure to Contagious Interview-style supply chain attacks.
135[.]181[.]123[.]177138[.]201[.]50[.]5144[.]172[.]105[.]235144[.]172[.]112[.]106146[.]70[.]253[.]10723[.]127[.]202[.]24923[.]227[.]202[.]244http://fashdefi[.]store:6168/defy/v7https://0927[.]vercel[.]app/api/ipcheckhttps://api[.]npoint[.]io/b964566497d98298d32chttps://ip-check-server[.]vercel[.]app/api/ip-check/208https://json-project-hazel[.]vercel[.]app/apikey/QWERTYU890T12HMLhttps://log-server-lovat[.]vercel[.]app/api/ipcheck/703https://process-log[.]vercel[.]app/api/ipcheckhttps://process-log-update[.]vercel[.]app/api/ipcheckalchmey-sdkalert-codestreamerasync-chaibabel-cli-ganachebind-errorbingo-abstract-transportbingo-logbingo-loggerbingo-prettyboby_parserbtrez-loggercase-sensitive-pathschai-utilschartable-utilschecking-ipchecking-ipschunk-loggercolorful-buttonscommon-js-supportcommon-logifycomponents-flexibilityconfig-logcookie-loggercookie-loggerscookie-loggocookie-parsingcookies-loggercors-validatorcross-sessionddok-escapesdisplay-notificationsdotevndragon0905-vite-tsconfig-assistantemittery-upepxresoepxressoepxressooerr-notificationerror-analysiserror-fallbackerror-loggerjseslint-config-detectoreslint-detectoreslint-loggereslint-plugin-react-purifyeslint-ts-vieweslint-validation-clieslints-loggereth-node-utilsetherresethres.jsethrs.jsexpress-prismaexpress-xmlrequestfile-uploading-advancefiligrean-iconfiligren-iconfiligron-iconfiliogrean-icofinancial-utilsflowhintflowicoflowmintfoudryfoundaryfoundreyfoundrifrontend-cronfunc-analysfunc-analystfunc-analysisfunc-loggerfundrygad-loggerganacganaccheganachaganacheeganachhegannachegatepassglow-admingnachgridmindhardhat-deploy-notificationhardhat-deploy-notifierhashsentinelhttp-err-notificationhttp-helmethttp-req-loggerhttpresloghttpreqloghusky-eshusky-loggericon-seaip-checkersip-checkingip-checksitem-boxjito-componentsjnscriptjs-notifiersjson-configsjson-confsjson-log-streamjson-weqjokenjson-webhooksjsonlise-confjsons-loggerjsonstylizerlayzrlog-tasklog4actionlogger-cookielogger-extjslogger-pinologging-winstonlogflow-jsonlogin-tokenizerlovable-cilovable-clilovable-cookie-loggerlovable-cookies-loggerlovable-jslovable-loggerlovable-loggerslovable-reactlovable-tsluma-glow-dbmatrix-chartsmega-compressmetamask-apimiddleware-loggersmongodb-cdmongodb-cimongodb-ornmongose-cimongose-climorgan-loggermotionflowmongoose-cimuxfluxmy-tttnext-plugin-uni-i18nnextjs-babel-toastifynode-log-confignode-log-streamnode-logflownode-logger-sdknode-loggerxnode-notificationsnode-nvm-sshnode-orm-loggernode-vite-confignode-winstonnode-winston-loggernodeapi-jsonnodemailer-helpernodemon-pkgnodelog-litenodespodenotification-clientsnotification-displayernotification-layernotifications-clientnotifications-layernotifications-logorbital-ledgerparse-loggerparser-sessionparser-tsonpino-nodepixzenpreset-logprepare-configprettier-utilspretty-format-settingproc-log-cmdproc-log-errorprocess-loadqrcode-pretty-reactquery-loggerrandlyrc-loggerreact-babel-purifyreact-context-stylizerreact-copackreact-content-providerreact-dhtmlreact-dropzone-logreact-eslint-typereact-fs-cofnigreact-fs-configreact-hook-eslintreact-icons-loaderreact-lovablereact-miltonreact-outcome-error-alertreact-propreact-repackreact-redux-stylizerreact-redirect-routerreact-router-htmlreact-router-purifyreact-stylizerreact-tediterreact-thunk-logreact-toast-uireal-socket-rtrecharts-smartredux-eslint-sagaredux-lint-sagaredux-saga-devtoolredux-saga-guardredux-saga-helpredux-saga-inspectorredux-saga-sentinelredux-saga-validatorredux-thunk-actionredux-toolkit-rtsrequest-guardrequest-krakenrequest-sentryrouter-kitrtk-logrtk-loggerrtk-servicertk-sleeprtk-wakesafe-winstonsensitive-paths-focussession-loggersessionfiysessions-loggersimple-icon-makersome-promisestake-configstream-loggersstrictorsuccgdesstai1wind-configs-viewertailwind-beauty-icontailwind-book-icontailwind-class-overridestailwind-classname-overridestailwind-classes-overridestailwind-color-icontailwind-computer-icontailwind-config-overridestailwind-config-settingtailwind-configstailwind-configs-viewertailwind-cup-icontailwind-desktop-icontailwind-glass-icontailwind-icontailwind-icon-animatetailwind-mouse-icontailwind-mui-modaltailwind-nbr-icontailwind-next-icontailwind-react-icontailwind-react-muitailwind-round-icontailwind-scrollbar-showtailwind-scrollmenutailwind-style-componentstailwind-style-overridestailwind-supabasetailwind-theme-colorstailwindcss-animatexstailwindcss-animatorstailwindcss-color-icons-litetailwindcss-config-overridestailwindcss-remotiontheta-tv-chartstjsontypetrsliptrufleetruffeltsleepuidraftismuxliftuxlinevaildatorviamvite-audit-pluginvite-auditlogvite-babel-plugin-es6-promisevite-binding-jsvite-chunk-toolsvite-chunk-managervite-configs-viewervite-css-iconvite-jsconfigvite-lightsparsevite-linting-jsvite-log-pluginvite-logeiditvite-mobcss-logvite-next-loggervite-next-loggersvite-parsevite-plugin-chunk-chopvite-plugin-es6-babelvite-plugin-js-supportvite-plugin-morganvite-plugin-opticompressvite-plugin-parsevite-plugin-parse-jsvite-plugin-parse-jsonvite-plugin-react-pingvite-plugin-reactjs-refreshvite-plugin-uni-i18nvite-plugin-vue-layoutvite-postcss-bootstrapvite-postcss-helpervite-postcss-kitvite-postcss-nestedvite-react-chunkervite-simpleparsevite-singleparsevite-ts-iconvite-tsauditlogvite-tsconfig-assistantvite-tsconfig-optimizedvitejs-plugin-react-refreshvortex-loggervvite-plugin-react-pingwb3.jswe3.jswebpack-css-branch-loaderwinstem-loggingwinston-datalogwinston-logx-session-parserxml-request-parsertailwindcss-theme-iconsadammorris533alexander0110818alexander0110820alexander0110828anarenhsaihanandrey0212andrii_matsiukanthony_smithariel02artemsdefiartemsnpmasd123123123123astro123456aylin_alkanbehrad80515bellyachebenmilam727510benzonjohnbobbbbrian_sandersbrian_scottbryankoh0604bryanlee604butleralvin510carolina32123caroline727castiblancocesar510727chain1107sawcharles1236542charles987456cheapdev009cheekaidechristrotmandanicaagawindaniel604darielfriasdavid0604david1003david_fernandezdavid_raynoldsdavidjambisddokdenys604diego123123dkeosleffdmitriy1023dmytro604dragon0905dyani-steraselodieblanc0707emily0102evalinevaraza63fanhaomingfelip2342fukdevfulldev0418goldenrhynograyce1024guograce902harry1988051211harukitanakahector008hector9299hendriksenelise727hmaxholppkgaske6i75iandaviesip_checknpmjacksonethjahmiekstreetmanxjaya_lubisznjeffbennett862jenny-jenkinsjenis19970102jiaopin0813jinping0813jinping0824jiupaladinjoko_setijohnastenjulianohoffmannkaitlyndynamokanaan7407751kevin_ckevincarolkevinyamadakencheng1291kingwordskingsley19960304kentadev0114kik.itakurnia_utama4qlauren01leahu0604loraine-packman09164lucastylerluka1291luka1293lukapro518luis1214maggie01malarkey1992marcsanfordmath4324meirjacobmelnikolegmichaeldantemilton_sandersmonky1003mykola1214mykolakostenkonatin933n99114npmlover56oliverwilson1976ossargd324625paerhui1102patrickwebermanpavlo123123perumal_balakpeter_soria525582protonsraquongekitti8vs6cxriccardotala798rodolfguerrroyalcatroyalkingroyalpandaroyalpandagungfuroyaltigerruplles0308ryon2080ryon_timsatodevsatriassasinsaviohscarlet1290scott_davidseed1996001sean-techseren_quasarmzfjn49235sergio12setiawanetskydev777smartdevuserstorm0418suhkuv.competition.telterralindenwhytk82974tetiana0102thiago_chiagotim_blossertimothygaffney08trailertrenton_alexanderuoenkpensevalerii73718vandesawvenjaminvenjamin1vespero1011victoria88viktoria115vinkeyasmaelvladsupernpmvladislavkarniushkaweb3chessdefiwilder_keatingrmtuw64788wilkinson310william1024winston1wonderful123world47world4devxinrong83yasmin9yevheniikasymchukyonismithzane29879zhang.jzybinantone241adammorris533@gmail[.]comaidanphillips721@gmail[.]comalexander0110818@outlook[.]comalexander0110820@outlook[.]comalexander0110828@outlook[.]comanastasiiakoziar02@gmail[.]comanthonysmith0979@outlook[.]comanto[.]nost[.]athakos194@gmail[.]comarslan310[.]kiran@gmail[.]comastroglobal[.]work@gmail[.]comaylin_fintech@hotmail[.]combehrad[.]daniel@outlook[.]combellyache@alightmotion[.]idbob[.]berg[.]business@gmail[.]combriansanders0126@gmail[.]combryankoh64@outlook[.]combryanlee604@outlook[.]combutleralvin510@outlook[.]comcarolina32123@hotmail[.]comcarolinefruet727@gmail[.]comchain1107saw@gmail[.]comchaparrocesaryed510727@outlook[.]comcheekaide1992@gmail[.]comChinneryMarcia5425@hotmail[.]comchristrotman727@outlook[.]comcibin87216@exitbit[.]comctwajstj8948@hotmail[.]comdanicaagawin5@gmail[.]comdarielfrias89@outlook[.]comdavidfernandez420@outlook[.]comdavidjambis@outlook[.]comdecovenjamin@gmail[.]comdenise[.]ward0418@outlook[.]comdesmondwynn144@gmail[.]comdevkotacorrado@googlemail[.]comdl249995@gmail[.]comdmytro604@outlook[.]comdreamjobsato@gmail[.]comdv6305655@gmail[.]comdyanisteras15091999cuunn@hotmail[.]comelodieblanc0707@gmail[.]comemilylida0923@outlook[.]comethoszephyrtrcac76000@hotmail[.]comEvalineVaraza63@hotmail[.]comfarrelvillarrealdngp170616@hotmail[.]comfelip2342@techspirehub[.]comfhaoming7@gmail[.]comgalihmxf11@hotmail[.]comgaravitovillamilj@gmail[.]comgarycorn@loopsoft[.]techgoldenrhynodev@gmail[.]comgrayce@xuchuyen[.]comguograce902@gmail[.]comguilddmelihb2r@hotmail[.]comhmax23410@gmail[.]comhectorramirez008@outlook[.]comhendriksenelise727@gmail[.]comhiroshi[.]watanabe1011@gmail[.]comholppkgaske6i75@outlook[.]comiandavies2313@gmail[.]comjackson[.]tf7[.]eth@gmail[.]comjahmiekstreetmanxlj126940778@hotmail[.]comjaya[.]lubiszn@hotmail[.]comjeffbennett862@gmail[.]comjessikamoreira015@gmail[.]comjh0333224@gmail[.]comjiaopin0813@outlook[.]comjiayingzhang[.]contact@gmail[.]comjinping0813@outlook[.]comjinping0824@outlook[.]comjoko[.]setiawan9l@hotmail[.]comjokohjj80@hotmail[.]comjohnas12121@hotmail[.]comjohnbenzon510727@outlook[.]comjiupaladin@gmail[.]comjonatasfrnancisco887@gmail[.]comjuancastiblanco1998@gmail[.]comjulianohoffmann33@gmail[.]comk7407751@gmail[.]comkaitlyndynamofwtsc28771@outlook[.]comkencheng1291@proton[.]mekevincarol00001@gmail[.]comkevincarol00002@gmail[.]comkevinyamada71@gmail[.]comkik[.]ita[.]aylen701@gmail[.]comkingsley19960304@hotmail[.]comkorovalerii0803@gmail[.]comkurnia[.]utama4q@hotmail[.]comlauren[.]washco@hotmail[.]comleahucosmin0720@gmail[.]comleeuna@xvism[.]sitelittebaby232355@gmail[.]comlucastyler195@gmail[.]comluis[.]fernando[.]dev1214@gmail[.]comluka1291@outlook[.]comluka1293@outlook[.]commalarkeyclayton5@gmail[.]commarcsanford22@gmail[.]commarinella@basemindway[.]commatiushkodenys@gmail[.]commatheuslealcardoso86@gmail[.]commatheusserra0133@gmail[.]commeirjacob727@gmail[.]commelnikoleg995@gmail[.]commelnicenkosergij119@gmail[.]commichal[.]kaim99@outlook[.]commilamben510@outlook[.]commiltonsanders1234@gmail[.]commischenko0604@gmail[.]commykolakostenko16@gmail[.]commykolasvyryd20@gmail[.]comnatinbusiness[.]work@gmail[.]comninaquigleyfgsja22730@outlook[.]comoka[.]setiawanet@hotmail[.]comohmlsnwz1502@hotmail[.]comoliverwilson1976@hotmail[.]comossargd@xuseca[.]cloudpandaroyal48@outlook[.]compatterson[.]ariel@outlook[.]compattersonariel988@gmail[.]compatrickweberman@outlook[.]compavlovainerman@gmail[.]competerdwtp525582@hotmail[.]comperumalbalak727@outlook[.]compineye0212@outlook[.]complyn_rider@protonmail[.]comproluka80518@outlook[.]comquongekitti8vs6cx@hotmail[.]comquintonverdantgsbxf26081@hotmail[.]comramirezhector9299@gmail[.]comrealonlinethiago@gmail[.]comreichenausteve@gmail[.]comriccardotala798@outlook[.]comrobertwarr1011@gmail[.]comrodolfguerr717@outlook[.]comroyalcat3982@outlook[.]comroyalking066@outlook[.]comroyalpandagungfu06@outlook[.]comroyaltiger06@outlook[.]comrunedrakesdmty71479@hotmail[.]comryon2080@outlook[.]comryon_dev_3@outlook[.]comryon_dev_4@outlook[.]comryon_dev_5@outlook[.]comryon_dev_6@outlook[.]comryonteam@outlook[.]comsasakidev581@gmail[.]comsatriapkp91@hotmail[.]comseed1996009@outlook[.]comserenquasarmzfjn49235@hotmail[.]comsergio1997121400@gmail[.]comsean_tech208@hotmail[.]comshubertlarvp286287@hotmail[.]comslobodanprluv@gmail[.]comsmartinezquitian20@gmail[.]comsmarttmpacc@hotmail[.]comsoft[.]business0987@gmail[.]comstromdev712418@gmail[.]comsuhkuv[.]competition[.]tel@gmail[.]comtetianabanakh34@gmail[.]comterralindenwhytk82974@outlook[.]comtimothygaffney08@gmail[.]comtop1152025@outlook[.]comtop6042025@outlook[.]comtrentonwork105@gmail[.]comvandesaw@dewacid[.]storevenjamindeco0305@gmail[.]comvictoria88@celestiad[.]techvinkeyasmael@hotmail[.]comvladkashka56@gmail[.]comvladzane569@gmail[.]comwarfelbyeon95om0@hotmail[.]comwilderkeatingrmtuw64788@hotmail[.]comwilliammorphy37@gmail[.]comwondereleven1@gmail[.]comxinrong83@outlook[.]comyevheniikasymchuk@gmail[.]comyonismith727@outlook[.]comyuleseraphxyvoi89853@hotmail[.]comyusufsnz95@hotmail[.]comyusufuyn94@hotmail[.]comzanevlad3@gmail[.]comzybinanton241@gmail[.]comSubscribe to our newsletter
Get notified when we publish new security blog posts!
Try it now

Research
/Security News
Socket researchers found 10 typosquatted npm packages that auto-run on install, show fake CAPTCHAs, fingerprint by IP, and deploy a credential stealer.

Research
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovered malicious NuGet packages typosquatting the popular Nethereum project to steal wallet keys.

Research
/Security News
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovered a coordinated campaign that floods the Chrome Web Store with 131 rebranded clones of a WhatsApp Web automation extension to spam Brazilian users.