
Research
Malicious NuGet Packages Typosquat Nethereum to Exfiltrate Wallet Keys
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovered malicious NuGet packages typosquatting the popular Nethereum project to steal wallet keys.
com.commercetools.rmf:codegen-renderers
Advanced tools
RAML API client code generators based on the REST Modeling Framework. https://github.com/vrapio/rest-modeling-framework
RAML API client code generators based on the RMF (REST Modeling Framework). The code generators are written in kotlin.
JAVA_CLIENT:
TYPESCRIPT_CLIENT:
CSHARP_CLIENTPHP_CLIENTPOSTMAN: Collection file for the Postman API ClientRAML_DOC: Emits RAML files targeted at generating robust and stable API documentation. Fully flattens and resolves types and resources. The output RAML has a fixed canonical filesystem structure and every type or resource file contains all information to fully document it. It's used by the commercetools-docs-kitrmf-codegen CLITo install the rmf-codegen cli, run the following command
curl -o- -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/commercetools/rmf-codegen/main/scripts/install.sh | bash
You will find a new command available rmf-codegen, you can check that all is good by executing rmf-codegen -v
The commercetools-docs-kit provides an NPM package that automates the download of the JAR and provides the rmf-codegen command to JavaScript projects without global installation. (find at NPM)
Docker images for the code generator are available in the Github Container Registry
docker pull docker.pkg.github.com/commercetools/rmf-codegen/codegen:latest
General Usage:
Usage: rmf-codegen [-hv] [COMMAND]
Allows to validate RAML files and generate code from them
-h, --help display this help message
-v, --version print version information and exit
Commands:
generate Generate source code from a RAML specification.
verify Allows to verify if a raml spec is valid.
validate Validate the raml spec against defined rules and generate a validation report.
Generating Client SDKs or normalized RAML for documentation:
Usage: rmf-codegen generate [-hvw] [-b=<basePackageName>]
[-c=<clientPackageName>] [-m=<modelPackageName>]
-o=<outputFolder> [-s=<sharedPackage>] -t=<target>
<ramlFileLocation>
Generate source code from a RAML specification.
<ramlFileLocation> Api file location
-b, --base-package=<basePackageName>
The base package, this package in case the model or
client models aren't provided
-c, --client-package=<clientPackageName>
The client package, This will be used as the package
for the client stub.
-h, --help display this help message
-m, --model-package=<modelPackageName>
The models package, this will be used as the model
package in the generated code.
-o, --output-folder=<outputFolder>
Output folder for generated files.
-s, --shared-package=<sharedPackage>
The shared package to be used for the generated code.
-t, --target=<target> Specifies the code generation target
Valid values: JAVA_CLIENT, TYPESCRIPT_CLIENT,
CSHARP_CLIENT, PHP_CLIENT, PHP_BASE, PHP_TEST,
POSTMAN, RAML_DOC
-v, --verbose If set, this would move the verbosity level to debug.
-w, --watch Watches the files for changes
Verifying a RAML API:
Usage: rmf-codegen verify [-hw] <ramlFileLocation>
Allows to verify if a RAML spec is valid.
<ramlFileLocation> Api file location
-h, --help display this help message
-w, --watch Watches the files for changes
Validating a RAML API and generating a validity report:
Usage: <main class> validate [-hvw] [--list-rules] [-f=<outputFormat>]
[-l=<linkBase>] [-lf=<linkFormat>]
[-o=<outputTarget>] [-r=<rulesetFile>]
[-s=<checkSeverity>] [-t=<tempFile>]
<ramlFileLocation>
Allows to verify if a raml spec is valid according to CT guidelines and generates a validation report
<ramlFileLocation> Api file location
-f, --format=<outputFormat> Specifies the output format. Valid values: CLI, JSON, MARKDOWN
-h, --help display this help message
-l, --link-base=<linkBase>
-lf, --link-format=<linkFormat> Specifies the link format. Valid values: CLI, GITHUB
--list-rules Show all rules
-o, --outputTarget=<outputTarget>
-r, --ruleset=<rulesetFile> Ruleset configuration
-s, --severity=<checkSeverity> Diagnostic severity. Valid values: info, warn, error
-t, --temp=<tempFile> Temporary folder
-v, --verbose Verbose
-w, --watch Watches the files for changes
A single "fat jar" is built with the following commands:
cd tools/cli-application/
../../gradlew build
The JAR can then be found at ./rmf-codegen.jar
A native executable is built with the following commands:
cd tools/cli-application/
../../gradlew nativeImage
The native executable can then be found at ./tools/cli-application/build/graal/rmf-codegen.
It's currently only tested with Mac OS X. It emits error messages but the functionality works.
We choose kotlin because of the following features:
These features help in developing code generators for different programming languges/frameworks.
Our TestCodeGenerator test can be run against a user provided RAML file by setting
the TEST_RAML_FILE environment variable to the file path.
FAQs
RAML API client code generators based on the REST Modeling Framework. https://github.com/vrapio/rest-modeling-framework
We found that com.commercetools.rmf:codegen-renderers demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 0 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovered malicious NuGet packages typosquatting the popular Nethereum project to steal wallet keys.
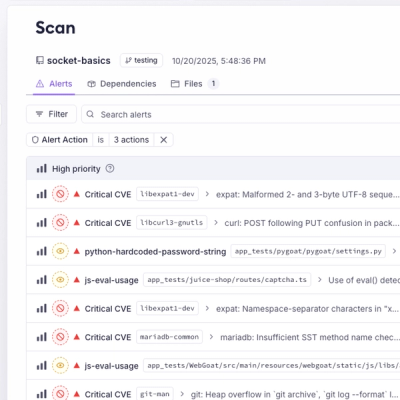
Product
A single platform for static analysis, secrets detection, container scanning, and CVE checks—built on trusted open source tools, ready to run out of the box.

Product
Socket is launching experimental protection for the Hugging Face ecosystem, scanning for malware and malicious payload injections inside model files to prevent silent AI supply chain attacks.