Mobius.kt




Kotlin Multiplatform framework for managing state evolution and side-effects, based on spotify/Mobius.
What is Mobius?
The core construct provided by Mobius is the Mobius Loop, best described by the official documentation. (Embedded below)
A Mobius loop is a part of an application, usually including a user interface.
In a Spotify context, there is usually one loop per feature such as “the album page”, “login flow”, etc., but a loop can also be UI-less and for instance be tied to the lifecycle of an application or a user session.
Mobius Loop
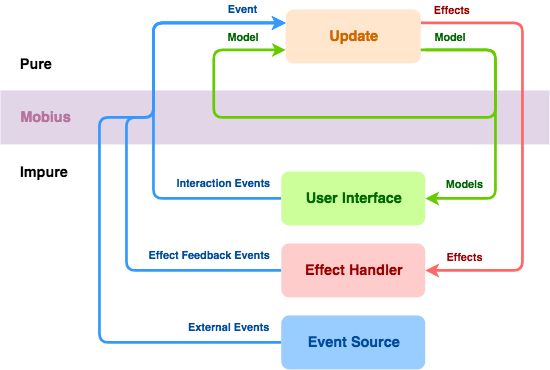
A Mobius loop receives Events, which are passed to an Update function together with the current Model.
As a result of running the Update function, the Model might change, and Effects might get dispatched.
The Model can be observed by the user interface, and the Effects are received and executed by an Effect Handler.
'Pure' in the diagram refers to pure functions, functions whose output only depends on their inputs, and whose execution has no observable side effects.
See Pure vs Impure Functions for more details.
(Source: Spotify/Mobius - Concepts > Mobius Loop)
By combining Mobius Loops with Kotlin's MPP features, mobius.kt allows you to write and test pure functions (application and/or business logic) in Kotlin and deploy them everywhere.
This leaves impure functions to be written in multiplatform Kotlin code or the target platform's primary language (Js, Java, Objective-c/Swift), depending on your use-case.
Example
typealias Model = Int
enum class Event { ADD, SUB, RESET }
typealias Effect = Unit
val update = Update<Model, Event, Effect> { model, event ->
when (event) {
Event.ADD -> next(model + 1)
Event.SUB -> next(model - 1)
Event.RESET -> next(0)
}
}
val effectHandler = Connectable<Effect, Event> { output ->
object : Connection<Effect> {
override fun accept(value: Effect) = Unit
override fun dispose() = Unit
}
}
val loopFactory = Mobius.loop(update, effectHandler)
To create a simple loop use loopFactory.startFrom(model) which returns a MobiusLoop with two states: running and disposed.
Simple Loop Example (Click to expand)
val loop = loopFactory.startFrom(0)
val observerRef: Disposable = loop.observer { model ->
println("Model: $model")
}
loop.dispatchEvent(Event.ADD)
loop.dispatchEvent(Event.ADD)
loop.dispatchEvent(Event.RESET)
loop.dispatchEvent(Event.SUB)
loop.dispose()
Alternatively a loop can be managed with a MobiusLoop.Controller, giving the loop a more flexible lifecycle.
Loop Controller Example (Click to expand)
val loopController = Mobius.controller(loopFactory, 0)
loopController.connect { output ->
buttonAdd.onClick { output.accept(Event.ADD) }
buttonSub.onClick { output.accept(Event.SUB) }
buttonReset.onClick { output.accept(Event.RESET) }
object : Consumer<Model> {
override fun accept(value: Model) {
println(value.toString())
}
override fun dispose() {
buttonAdd.removeOnClick()
buttonSub.removeOnClick()
buttonReset.removeOnClick()
}
}
}
loopController.start()
loopController.dispatchEvent(Event.ADD)
loopController.dispatchEvent(Event.ADD)
loopController.dispatchEvent(Event.RESET)
loopController.dispatchEvent(Event.SUB)
loopController.stop()
loopController.disconnect()
Modules
Testing
The mobiuskt-test module provides a DSL for behavior driven tests and a light re-implementation of Hamcrest style APIs to test mobius loops (See Download).
Behavior testing DSL Example (Click to expand)
UpdateSpec(update)
.given(0)
.whenEvent(Event.ADD)
.then(assertThatNext(hasModel()))
UpdateSpec(update)
.given(0)
.whenEvent(Event.ADD)
.then(assertThatNext(hasModel(-1)))
For more details on the available matchers, see the API documentation.
Coroutines
Coroutines and Flows are supported with the mobiuskt-coroutines module (See Download).
Coroutine Module Example (Click to expand)
val effectHandler = subtypeEffectHandler<Effect, Event> {
addAction<Effect.SubType1> { }
addConsumer<Effect.SubType2> { effect -> }
addFunction<Effect.SubType3> { effect -> Event.Result() }
addValueCollector<Effect.SubType4> { effect ->
emit(Event.Result())
emitAll(createEventFlow())
}
addLatestValueCollector<Effect.SubType5> {
}
addTransformer<Effect.SubType6> { effects ->
effects.map { effect -> Event.Result() }
}
}
val loopFactory = FlowMobius.loop(update, effectHandler)
Notes
External dependencies
Mobius.kt depends on kotlinx.atomicfu for object synchronization, this results in a runtime dependency for Kotlin/Native targets only.
Language Support
MobiusLoops can be created and managed in Javascript, Swift, and Java code without major interoperability concerns.
Using Mobius.kt for shared logic does not require consuming projects to be written in or know about Kotlin.
Kotlin/Native
Kotlin/Native's new memory manager is generally supported but as of Kotlin 1.6.10 may result in higher memory usage and in rare cases, delayed runtime errors.
The following notes are relevant only to the original memory manager where state shared across threads cannot be mutated.
A MobiusLoop is single-threaded on native targets and cannot be frozen.
Generally this is acceptable behavior, even when the loop exists on the main thread.
If required, Effect Handlers are responsible for passing Effects into and Events out of a background thread.
Coroutines and Flows are ideal for handing Effects in the background with the mobiuskt-coroutines module or manual example below.
Coroutine Example (Click to expand)
Connectable<Effect, Event> { output: Consumer<Event> ->
object : Connection<Effect> {
private val scope = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main + SupervisorJob())
private val effectFlow = MutableSharedFlow<Effect.Subtype2>(
onBufferOverflow = BufferOverflow.SUSPEND
)
init {
effectFlow
.debounce(200)
.mapLatest { effect -> handleSubtype2(effect) }
.onEach { event -> output.accept(event) }
.launchIn(scope)
}
override fun accept(value: Effect) {
scope.launch {
when (value) {
is Effect.Subtype1 -> output.accept(handleSubtype1(value))
is Effect.Subtype2 -> effectFlow.emit(value)
}
}
}
override fun dispose() {
scope.cancel()
}
private suspend fun handleSubtype1(effect: Effect.Subtype1): Event {
return withContext(Dispatcher.Default) {
try {
val result = longRunningSuspendFun(effect.data)
Event.Success(result)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
Event.Error(e)
}
}
}
private suspend fun handleSubtype2(effect: Effect.Subtype2): Event {
return withDispatcher(Dispatcher.Default) {
try {
val result = throttledSuspendFun(effect.data)
Event.Success(result)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
Event.Error(e)
}
}
}
}
}
Download











repositories {
mavenCentral()
maven("https://s01.oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/")
}
dependencies {
implementation("org.drewcarlson:mobiuskt-core:$MOBIUS_VERSION")
implementation("org.drewcarlson:mobiuskt-test:$MOBIUS_VERSION")
implementation("org.drewcarlson:mobiuskt-extras:$MOBIUS_VERSION")
implementation("org.drewcarlson:mobiuskt-android:$MOBIUS_VERSION")
implementation("org.drewcarlson:mobiuskt-coroutines:$MOBIUS_VERSION")
}















