
Security News
PyPI’s New Archival Feature Closes a Major Security Gap
PyPI now allows maintainers to archive projects, improving security and helping users make informed decisions about their dependencies.
@datadog/mobile-react-native
Advanced tools
A client-side React Native module to interact with Datadog
Datadog Real User Monitoring (RUM) enables you to visualize and analyze the real-time performance and user journeys of your application’s individual users.
To install with NPM, run:
npm install @datadog/mobile-react-native
To install with Yarn, run:
yarn add @datadog/mobile-react-native
Minimum React Native version: SDK supports React Native version 0.63.4 or higher. Compatibility with older versions is not guaranteed out of the box.
Versions 1.0.0-rc5 and higher require you to have compileSdkVersion = 31 in the Android application setup, which implies that you should use Build Tools version 31, Android Gradle Plugin version 7, and Gradle version 7 or higher. To modify the versions, change the values in the buildscript.ext block of your application's top-level build.gradle file. Datadog recommends using React Native version 0.67 or higher.
react-native as your Application Type.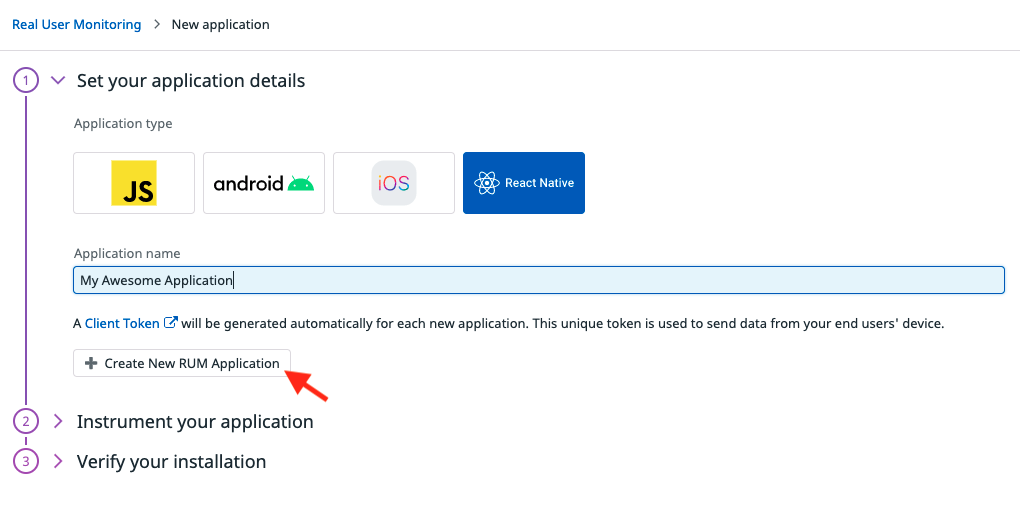
To ensure the safety of your data, you must use a client token. You cannot use only Datadog API keys to configure the @datadog/mobile-react-native library, because they would be exposed client-side. For more information about setting up a client token, see the Client Token documentation.
import {
DatadogProvider,
DatadogProviderConfiguration
} from '@datadog/mobile-react-native';
const datadogConfiguration = new DatadogProviderConfiguration(
'<CLIENT_TOKEN>',
'<ENVIRONMENT_NAME>',
'<RUM_APPLICATION_ID>',
true, // track User interactions (e.g.: Tap on buttons. You can use 'accessibilityLabel' element property to give tap action the name, otherwise element type will be reported)
true, // track XHR Resources
true // track Errors
);
// Optional: Select your Datadog website (one of "US1", "US3", "US5", EU1", or "US1_FED"). Default is "US1".
datadogConfiguration.site = 'US1';
// Optional: enable or disable native crash reports
datadogConfiguration.nativeCrashReportEnabled = true;
// Optional: sample RUM sessions (here, 80% of session will be sent to Datadog. Default = 100%)
datadogConfiguration.sessionSamplingRate = 80;
// Optional: sample tracing integrations for network calls between your app and your backend (here, 80% of calls to your instrumented backend will be linked from the RUM view to the APM view. Default = 20%)
// You need to specify the hosts of your backends to enable tracing with these backends
datadogConfiguration.resourceTracingSamplingRate = 80;
datadogConfiguration.firstPartyHosts = ['example.com']; // matches 'example.com' and subdomains like 'api.example.com'
// Optional: set the reported service name (by default, it'll use the package name / bundleIdentifier of your Android / iOS app respectively)
datadogConfiguration.serviceName = 'com.example.reactnative';
// Optional: let the SDK print internal logs (above or equal to the provided level. Default = undefined (meaning no logs))
datadogConfiguration.verbosity = SdkVerbosity.WARN;
export default function App() {
return (
<DatadogProvider configuration={datadogConfiguration}>
<Navigation />
</DatadogProvider>
);
}
Because React Native offers a wide range of libraries to create screen navigation, by default only manual View tracking is supported. You can manually start and stop a View using the following startView() and stopView methods.
import {
DdSdkReactNative,
DdSdkReactNativeConfiguration,
DdLogs,
DdRum
} from '@datadog/mobile-react-native';
// Start a view with a unique view identifier, a custom view url, and an object to attach additional attributes to the view
DdRum.startView('ViewKey', 'ViewName', Date.now(), {
'custom.foo': 'something'
});
// Stops a previously started view with the same unique view identifier, and an object to attach additional attributes to the view
DdRum.stopView('ViewKey', Date.now(), { 'custom.bar': 42 });
Before data is uploaded to Datadog, it is stored in cleartext in your application's cache directory. This cache folder is protected by Android's Application Sandbox, meaning that on most devices this data can't be read by other applications. However, if the mobile device is rooted, or someone tempers with the linux kernel, the stored data might become readable.
Before data is uploaded to Datadog, it is stored in cleartext in the cache directory (Library/Caches)
of your application sandbox, which can't be read by any other app installed on the device.
FAQs
A client-side React Native module to interact with Datadog
The npm package @datadog/mobile-react-native receives a total of 85,256 weekly downloads. As such, @datadog/mobile-react-native popularity was classified as popular.
We found that @datadog/mobile-react-native demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
PyPI now allows maintainers to archive projects, improving security and helping users make informed decisions about their dependencies.

Research
Security News
Malicious npm package postcss-optimizer delivers BeaverTail malware, targeting developer systems; similarities to past campaigns suggest a North Korean connection.

Security News
CISA's KEV data is now on GitHub, offering easier access, API integration, commit history tracking, and automated updates for security teams and researchers.