Product
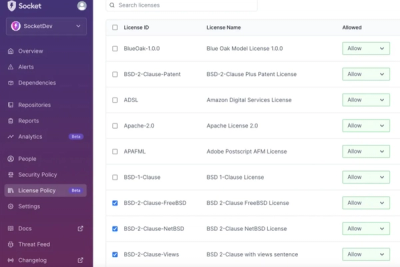
Introducing License Enforcement in Socket
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
This is a loader script for web components that were written down in HTML, as they should be! The Custom Element LOader, aka Celo, listens for changes in DOM and when it detects a custom element, it fetches its markup and inserts it in the document.
Celo will autoload web components for you if your follow the rules:
Celo uses a MutationObserver to listen for any element inserted in the DOM that carries a hyphen (ie. a custom element). Upon detection, if it hasn't done it already it fetches the markup and add its code to a hidden <div> with an id of "_celo". Any custom element already parsed when Celo is called in is then reinserted into the DOM to be reparsed.
Celo has no dependencies, but the non-minified version assumes ES6.
Celo is an ES6 module (4.3kB) that could be called with the code below.
<script type="module">
import celo from '/celo.mjs'
</script>
The minified version is not a module, and is transpiled to ES5. You could just link to it as an external script, or add a nomodule attribute to make it a fallback:
<script nomodule src="/celo.js"></script>
Either way, celo is just an iife -- it won't pollute the global namespace, but it won't return you anything. You're just meant to unleash it.
In this latest version Celo is an ES6 module. Under the hood, because modules are asynchronous, Celo will now retroactively address all components already parsed by the time it is loaded. This is done by detaching then appending the elements in the same position in the DOM, as not to brake any references.
From a developer's perspective this change only affects how Celo is imported into your app. It doesn't require being in the <head> anymore, and you should preferably used as an ES6 module with a nomodule fallback. If you update Celo on an app with the previous version without addressing this, it will brake.
You can have multiple components in a single html file, but you should only do it if you have one main component and then subcomponents for it. Think of a subcomponent as:
Subcomponents are separated from their masters only for clarity. If you add the subcomponent tag directly to your html, Celo will try to load it from a file matching its tagName, resulting in a non-fatal error.
Any <script> tag you include in the root of yout html file will be executed right away. That's typically not the case if your <script> tags are inside <template> tags. That's because web components typically use the cloneNode() function which flags the scripts as being already executed. Please note that:
If you must for some reason have the <script> execute from within the shadowRoot, you can check out Celo's recreateScripts() function for a reference on how to do it. But, again, you would be much better off handling your scripts in the component's class definition.
Below you will find how a "simple-example.html" file could look like (I'm not advocating this is the right way to do it, just stating that it works). It has two root elements: a <template> and a <script>. All the markup goes into the <template>, including any <style>.
Note that <script> is outside <template> so it will run as soon as the component is fetched. It also means the code won't be inside the shadowRoot -- I would recommend placing all needed code inside the class definition and leave the <template> clear of it.
<template id="tpl-simple-example">
<div>
<p>This is a demo web component.</p>
</div>
<style>
p{
padding: 5px 10px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
}
</style>
</template>
<script>
class SimpleExample extends HTMLElement{
constructor(){
super()
const el = document.querySelector("#tpl-simple-example")
.content.cloneNode(true)
this.attachShadow({mode:'open'}).appendChild( el )
}
}
customElements.define( 'simple-example',SimpleExample )
</script>
FAQs
A loader for HTML-based web components.
The npm package celo receives a total of 5 weekly downloads. As such, celo popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that celo demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
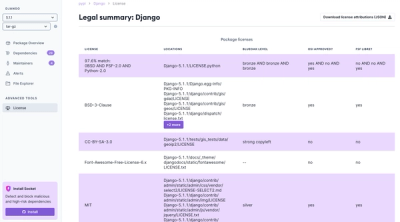
Product
We're launching a new set of license analysis and compliance features for analyzing, managing, and complying with licenses across a range of supported languages and ecosystems.
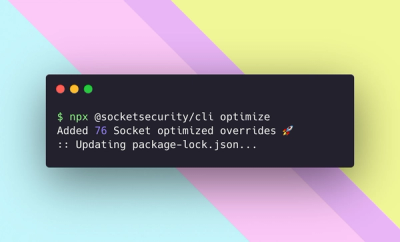
Product
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.