clerx 💁
A Timely Suite of RxJS Operators and Observables
Install
npm install clerx
Try out the example
Operators
As defined in the RxJS docs:
Operators are the essential pieces that
allow complex asynchronous code to be easily composed in a declarative manner.
Operators are functions.
rateLimiter(count, slidingWindowTime)
Defer sending events if count events occur within slidingWindowTime (milliseconds). Optionally, stop deferring if the wait time goes past timeoutDue. Returns an Observable.
Examples
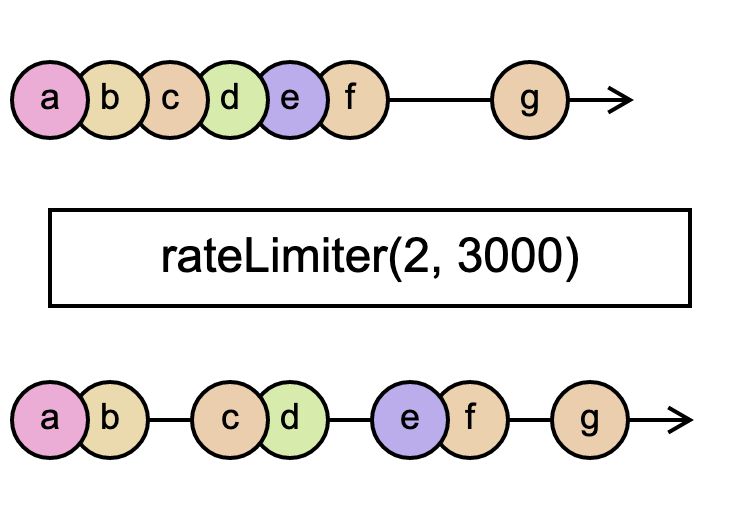
Only send two events within three seconds
In this example, only 2 (count) events are sent during a 3 second
(3000 ms slidingWindowTime) sliding window. As displayed in the marble
diagram, additional events beyond 2 events in the sliding window will be
deferred.
abcdef--g---
> rateLimiter(2, 3000)
ab-cd-ef-g--
Only one event within five seconds
Similarly, this example limits events to one (count) event in a five second
(5000 ms slidingWindowTime) window. The marble diagram shows how the events are distributed over time.
-(abc)def
> rateLimiter(1, 5000)
-a----b----c----d----e----f----

Observables
As defined in the RxJS docs:
Observables are lazy Push collections of multiple values.
postDelay(event: T, dueTime): Observable<T>
Creates an observable that emits the event then waits dueTime (milliseconds) before
closing the observable, like so:
event--{ dueTime }--|
Example: Delay 5 seconds after emitting an event
> postDelay("a", 5000)
a----|

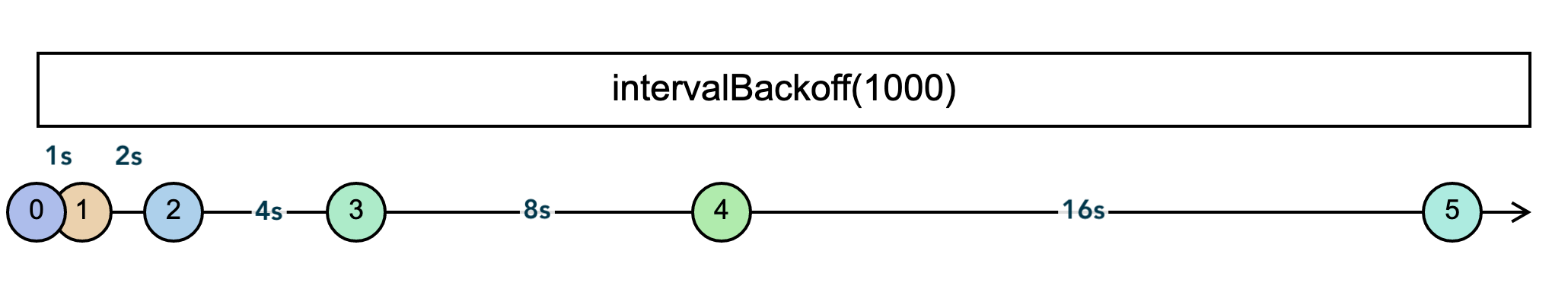
intervalBackoff(backoff: number): Observable<number>
Creates an Observable that emits sequential numbers in an exponentially increasing interval of time. backoff is the starting time interval, in milliseconds, and will exponentially increase with each event.
Example: Exponentially increase delay starting at a one second interval
The marble diagram illustrates the exponentially growing duration between events.
> intervalBackoff(1000)
01-2---3-------4---------------5