Product
Introducing Socket Optimize
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.
compromise
Advanced tools


npm install compromise



 compromise tries its best to parse text.
compromise tries its best to parse text.


let doc = nlp(entireNovel)
doc.match('the #Adjective of times').text()
// "the blurst of times?"
if (!doc.has('simon says #Verb')) {
return 'do nothing'
}
let doc = nlp('she sells seashells by the seashore.')
doc.verbs().toPastTense()
doc.text()
// 'she sold seashells by the seashore.'
let doc = nlp('the purple dinosaur')
doc.nouns().toPlural()
doc.text()
// 'the purple dinosaurs'

let doc = nlp('ninety five thousand and fifty two')
doc.numbers().add(2)
doc.text()
// 'ninety five thousand and fifty four'
let doc = nlp("we're not gonna take it, no we ain't gonna take it.")
// match an implicit term
doc.has('going') // true
// transform
doc.contractions().expand()
dox.text()
// 'we are not going to take it, no we are not going to take it.'


Use it on the client-side:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/compromise"></script>
<script>
var doc = nlp('two bottles of beer')
doc.numbers().minus(1)
document.body.innerHTML = doc.text()
// 'one bottle of beer'
</script>
or the back:
import nlp from 'compromise'
var doc = nlp('London is calling')
doc.verbs().toNegative()
// 'London is not calling'

full api:
compromise/one
A tokenizer of words, sentences, and punctuation.

import nlp from 'compromise/one'
let doc = nlp("Wayne's World, party time")
let data = doc.json()
// [{ terms:[{ text:"Wayne's", normal:"wayne"}, ...] }]
(all match methods use the match-syntax.)
.sort('method') - re-arrange the order of the matches (in place)
.reverse() - reverse the order of the matches, but not the words
.normalize({}) - clean-up the text in various ways
.unique() - remove any duplicate matches
.split('') - return a Document with three parts for every match ('splitOn')
.splitBefore('') - partition a phrase before each matching segment
.splitAfter('') - partition a phrase after each matching segment
.segment({}) - split a document into labeled sections
.join('') - make all phrases into one phrase

compromise/two
A part-of-speech tagger, and grammar-interpreter.

import nlp from 'compromise/two'
let doc = nlp("Wayne's World, party time")
let str = doc.match('#Possessive #Noun').text()
// "Wayne's World"
.contractions() - things like "didn't"
.contractions().expand() - things like "didn't"

compromise/three
Phrase and sentence tooling.

import nlp from 'compromise/three'
let doc = nlp("Wayne's World, party time")
let str = doc.people().normalize().text()
// "wayne"
'wash-out''(939) 555-0113''#nlp''hi@compromise.cool':)💋'@nlp_compromise''compromise.cool''quickly''he''but''of''Mrs.'people() + places() + organizations()"Spencer's"'FBI''eats, shoots, and leaves'
'football captain' → 'football captains''turnovers' → 'turnover''s to the end, in a safe manner.'will go' → 'went''walked' → 'walks''walked' → 'will walk''walks' → 'walk''walks' → 'walking''drive' → 'driven' - otherwise simple-past ('walked')'went' → 'did not go'"didn't study" → 'studied'25 kilos'1/3rdfive or fifth5 or 5thfifth or 5thfive or 5'$2.50'
he walks -> he walkedhe walked -> he walkshe walks -> he will walkhe walks -> he didn't walkhe doesn't walk -> he walks?!? or !!?.

compromise is 180kb (minified):
it's pretty fast. It can run on keypress:
it works mainly by conjugating all forms of a basic word list.
The final lexicon is ~14,000 words:
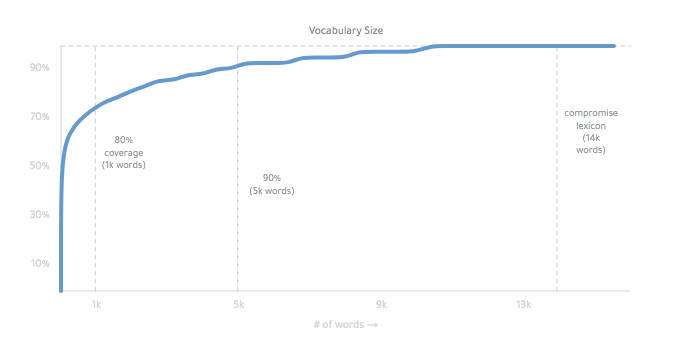
you can read more about how it works, here. it's weird.
decide how words get interpreted:
let myWords = {
kermit: 'FirstName',
fozzie: 'FirstName',
}
let doc = nlp(muppetText, myWords)
or make heavier changes with a compromise-plugin.
const nlp = require('compromise')
nlp.extend((Doc, world) => {
// add new tags
world.addTags({
Character: {
isA: 'Person',
notA: 'Adjective',
},
})
// add or change words in the lexicon
world.addWords({
kermit: 'Character',
gonzo: 'Character',
})
// add methods to run after the tagger
world.postProcess(doc => {
doc.match('light the lights').tag('#Verb . #Plural')
})
// add a whole new method
Doc.prototype.kermitVoice = function () {
this.sentences().prepend('well,')
this.match('i [(am|was)]').prepend('um,')
return this
}
})



| Concepts | API | Plugins | | ------------------ | :---------------------------------: | ---------------------------: | --- | | Accuracy | Accessors | Adjectives | | Caching | Constructor-methods | Dates | | Case | Contractions | Export | | Filesize | Insert | Hash | | Internals | Json | Html | | Justification | Lists | Keypress | | Lexicon | Loops | Ngrams | | Match-syntax | Match | Numbers | | Performance | Nouns | Paragraphs | | Plugins | Output | Scan | | Projects | Selections | Sentences | | Tagger | Sorting | Syllables | | Tags | Split | Pronounce | | | Tokenization | Text | Strict | | Named-Entities | Utils | Penn-tags | | Whitespace | Verbs | Typeahead | | World data | Normalization | | | Fuzzy-matching | Typescript | |


(these methods are on the nlp object)
.json() result
These are some helpful extensions:
npm install compromise-adjectives
quick
quick to quickestquick to quickerquick to quicklyquick to quickenquick to quicknessnpm install compromise-dates
June 8th or 03/03/18
2 weeks or 5mins
4:30pm or half past five
npm install compromise-export
npm install compromise-html
npm install compromise-hash
npm install compromise-keypress
npm install compromise-plugin-stats
npm install compromise-paragraphs
this plugin creates a wrapper around the default sentence objects.
npm install compromise-strict
npm install compromise-syllables
npm install compromise-penn-tags

we're committed to typescript/deno support, both in main and in the official-plugins:
import nlp from 'compromise'
import ngrams from 'compromise-ngrams'
import numbers from 'compromise-numbers'
const nlpEx = nlp.extend(ngrams).extend(numbers)
nlpEx('This is type safe!').ngrams({ min: 1 })
nlpEx('This is type safe!').numbers()

slash-support:
We currently split slashes up as different words, like we do for hyphens. so things like this don't work:
nlp('the koala eats/shoots/leaves').has('koala leaves') //false
inter-sentence match:
By default, sentences are the top-level abstraction.
Inter-sentence, or multi-sentence matches aren't supported without a plugin:
nlp("that's it. Back to Winnipeg!").has('it back')//false
nested match syntax:
the danger beauty of regex is that you can recurse indefinitely.
Our match syntax is much weaker. Things like this are not (yet) possible:
doc.match('(modern (major|minor))? general')
complex matches must be achieved with successive .match() statements.
dependency parsing: Proper sentence transformation requires understanding the syntax tree of a sentence, which we don't currently do. We should! Help wanted with this.

en-pos - very clever javascript pos-tagger by Alex Corvi
naturalNode - fancier statistical nlp in javascript
compendium-js - POS and sentiment analysis in javascript
nodeBox linguistics - conjugation, inflection in javascript
reText - very impressive text utilities in javascript
superScript - conversation engine in js
jsPos - javascript build of the time-tested Brill-tagger
spaCy - speedy, multilingual tagger in C/python
Prose - quick tagger in Go by Joseph Kato

MIT
FAQs
modest natural language processing
The npm package compromise receives a total of 41,136 weekly downloads. As such, compromise popularity was classified as popular.
We found that compromise demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 3 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.

Product
We're excited to announce that Socket now supports the Java programming language.

Security News
Socket detected a malicious Python package impersonating a popular browser cookie library to steal passwords, screenshots, webcam images, and Discord tokens.