
Security News
PyPI Introduces Digital Attestations to Strengthen Python Package Security
PyPI now supports digital attestations, enhancing security and trust by allowing package maintainers to verify the authenticity of Python packages.
CST means Concrete Syntax Tree. Unlike an AST (Abstract Syntax Tree), a CST contains all the information
from the JavaScript source file: whitespace, punctuators, comments. This information is extremely useful for
code style checkers and other code linters. CST is also useful for cases when you need to apply modifications
to existing JavaScript files while preserving the initial file formatting.
This CST implementation is designed to be 100% compatible with JS AST (https://github.com/estree/estree).
Main principles:
Let's see an example:
x = 0;
if (x) x++;
The CST for this example:
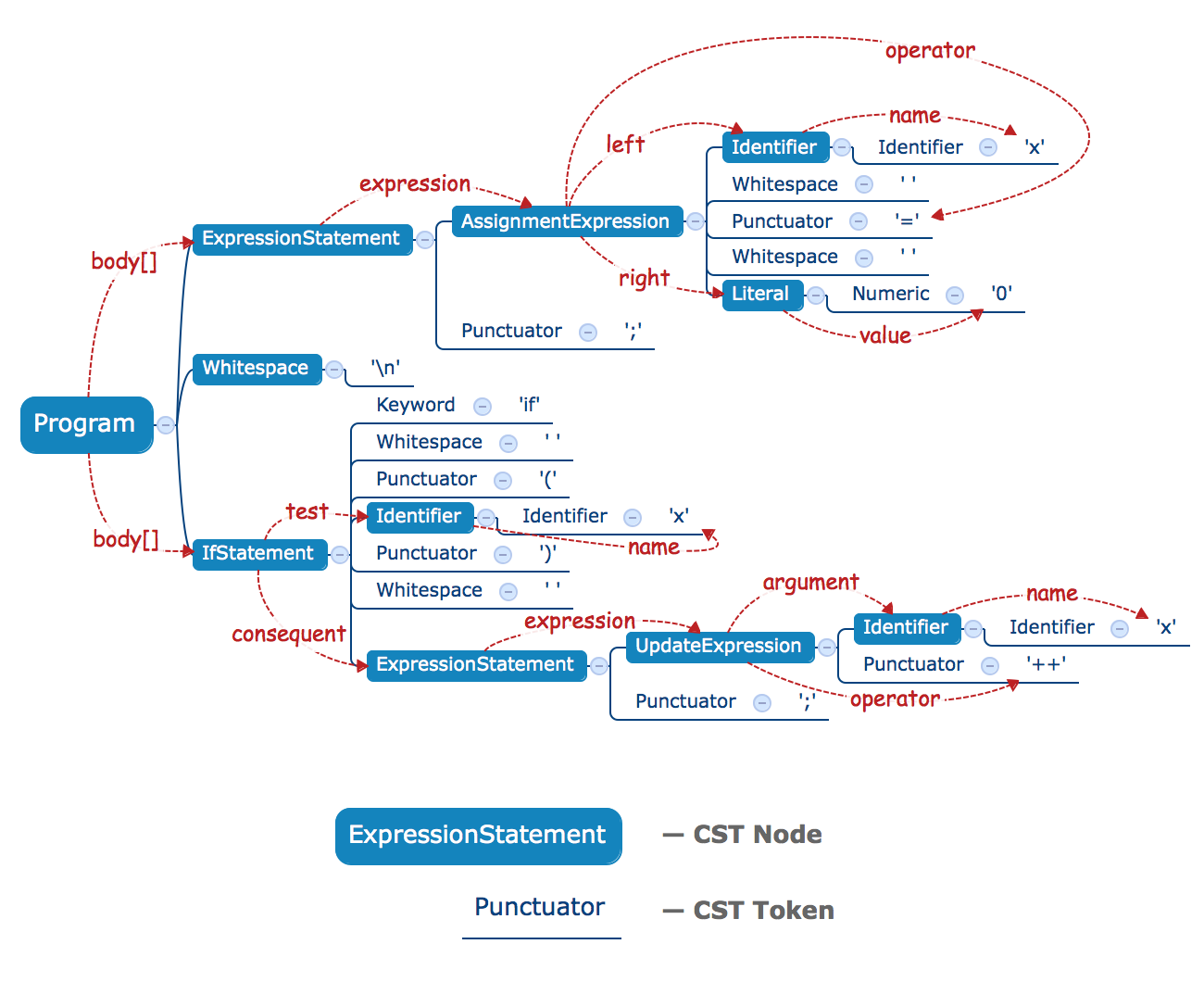
Element is the base class for Node and Token.
Provides traversing properties:
childElements: Element[], parentElement: Element|null: child/parent traversing.nextSibling: Element|null, previousSibling: Element|null: traversing between siblings.nextToken: Token|null, previousToken: Token|null: traversing to next/previous token.firstToken: Token|null, lastToken: Token|null: traversing to first/last tokens (not only direct tokens).firstChild: Token|null, lastChild: Token|null: traversing to first/last direct child.Code-related properties:
sourceCode: generates and returns JavaScript code of the specified ElementsourceCodeLength: returns JavaScript code lengthisToken, isNode, isExpression, isStatement, isWhitespace, isComment, isPattern, isAssignable,
isFragment, isModuleDeclaration, isModuleSpecifier : code entity flags.Provides mutation methods:
appendChild(element): appends child to the end of the ElementprependChild(element): prepends child to the end of the ElementinsertChildBefore(element, referenceChild): inserts child before referenceChildreplaceChildren(element, firstChildRef, lastChildRef): replaces specified child interval (from firstChildRef to
lastChildRef) with specified child.Location properties:
range: [Number, Number]: calculates and returns Element range.loc: {start: {line: Number, column: Number}, end: {line: Number, column: Number}}: calculates and returns
Element location.Node extends Element. The Nodes are the "AST part of a CST". If you drop everything but Nodes from a CST, you will
get a pure AST from the Node structure. So it is fair to say that Nodes provide the AST logic for a CST. Currently
only Nodes can contain children.
The Node property isNode always returns true.
Token extends Element. The purpose of a CST is to have tokens in the tree. By only manipulating tokens,
we can change code formatting without any effect on the behaviour.
The Token property isToken always returns true.
FAQs
JavaScript CST Implementation
The npm package cst receives a total of 0 weekly downloads. As such, cst popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that cst demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 3 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
PyPI now supports digital attestations, enhancing security and trust by allowing package maintainers to verify the authenticity of Python packages.

Security News
GitHub removed 27 malicious pull requests attempting to inject harmful code across multiple open source repositories, in another round of low-effort attacks.

Security News
RubyGems.org has added a new "maintainer" role that allows for publishing new versions of gems. This new permission type is aimed at improving security for gem owners and the service overall.