Product
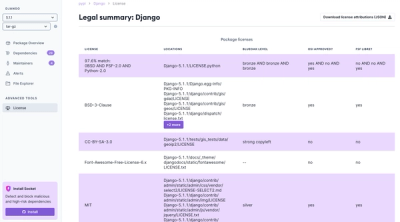
Introducing License Enforcement in Socket
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
data-structure-typed
Advanced tools
Data Structures of Javascript & TypeScript. Heap, Binary Tree, RedBlack Tree, Linked List, Deque, Trie, HashMap, Directed Graph, Undirected Graph, Binary Search Tree(BST), AVL Tree, Priority Queue, Graph, Queue, Tree Multiset, Singly Linked List, Doubly L




Data Structures of Javascript & TypeScript.
Do you envy C++ with STL (std::), Python with collections, and Java with java.util ? Well, no need to envy anymore! JavaScript and TypeScript now have data-structure-typed.
Now you can use this in Node.js and browser environments
CommonJS:require export.modules =
ESModule: import export
Typescript: import export
UMD: var Deque = dataStructureTyped.Deque
npm i data-structure-typed --save
yarn add data-structure-typed
import {
BinaryTree, Graph, Queue, Stack, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, TreeMultimap,
DirectedVertex, AVLTreeNode
} from 'data-structure-typed';
Copy the line below into the head tag in an HTML document.
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/data-structure-typed/dist/umd/data-structure-typed.js'></script>
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/data-structure-typed/dist/umd/data-structure-typed.min.js'></script>
Copy the code below into the script tag of your HTML, and you're good to go with your development.
const {Heap} = dataStructureTyped;
const {
BinaryTree, Graph, Queue, Stack, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, TreeMultimap,
DirectedVertex, AVLTreeNode
} = dataStructureTyped;
Try it out, or you can run your own code using our visual tool
import {BST, BSTNode} from 'data-structure-typed';
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.getNode(6); // BSTNode
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
bst.getLeftMost()?.key === 1; // true
bst.delete(6);
bst.get(6); // undefined
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true
bst.bfs()[0] === 11; // true
bst.print()
// ______________11_____
// / \
// ___3_______ _13_____
// / \ / \
// 1_ _____8____ 12 _15__
// \ / \ / \
// 2 4_ _10 14 16
// \ /
// 5_ 9
// \
// 7
const objBST = new BST<{height: number, age: number}>();
objBST.add(11, { "name": "Pablo", "age": 15 });
objBST.add(3, { "name": "Kirk", "age": 1 });
objBST.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5], [
{ "name": "Alice", "age": 15 },
{ "name": "Bob", "age": 1 },
{ "name": "Charlie", "age": 8 },
{ "name": "David", "age": 13 },
{ "name": "Emma", "age": 16 },
{ "name": "Frank", "age": 2 },
{ "name": "Grace", "age": 6 },
{ "name": "Hannah", "age": 9 },
{ "name": "Isaac", "age": 12 },
{ "name": "Jack", "age": 14 },
{ "name": "Katie", "age": 4 },
{ "name": "Liam", "age": 7 },
{ "name": "Mia", "age": 10 },
{ "name": "Noah", "age": 5 }
]
);
objBST.delete(11);
const {BST, BSTNode} = require('data-structure-typed');
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.getNode(6);
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
const leftMost = bst.getLeftMost();
leftMost?.key === 1; // true
bst.delete(6);
bst.get(6); // undefined
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true or false
const bfsIDs = bst.bfs();
bfsIDs[0] === 11; // true
import {AVLTree} from 'data-structure-typed';
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.delete(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
import {RedBlackTree} from 'data-structure-typed';
const rbTree = new RedBlackTree();
rbTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
rbTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
rbTree.delete(10);
rbTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
rbTree.print()
// ___6________
// / \
// ___4_ ___11________
// / \ / \
// _2_ 5 _8_ ____14__
// / \ / \ / \
// 1 3 7 9 12__ 15__
// \ \
// 13 16
import {DirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new DirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.hasVertex('A'); // true
graph.hasVertex('B'); // true
graph.hasVertex('C'); // false
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // true
graph.hasEdge('B', 'A'); // false
graph.deleteEdgeSrcToDest('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // false
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'C');
const topologicalOrderKeys = graph.topologicalSort(); // ['A', 'B', 'C']
import {UndirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new UndirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addVertex('D');
graph.deleteVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'D');
const dijkstraResult = graph.dijkstra('A');
Array.from(dijkstraResult?.seen ?? []).map(vertex => vertex.key) // ['A', 'B', 'D']
| Data Structure | Unit Test | Performance Test | API Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binary Tree |  |  | Binary Tree |
| Binary Search Tree (BST) |  |  | BST |
| AVL Tree |  |  | AVLTree |
| Red Black Tree |  |  | RedBlackTree |
| Tree Multiset |  |  | TreeMultimap |
| Segment Tree |  | SegmentTree | |
| Binary Indexed Tree |  | BinaryIndexedTree | |
| Heap |  |  | Heap |
| Priority Queue |  |  | PriorityQueue |
| Max Priority Queue |  |  | MaxPriorityQueue |
| Min Priority Queue |  |  | MinPriorityQueue |
| Trie |  |  | Trie |
| Graph |  |  | AbstractGraph |
| Directed Graph |  |  | DirectedGraph |
| Undirected Graph |  |  | UndirectedGraph |
| Queue |  |  | Queue |
| Deque |  |  | Deque |
| Linked List |  |  | SinglyLinkedList |
| Singly Linked List |  |  | SinglyLinkedList |
| Doubly Linked List |  |  | DoublyLinkedList |
| Stack |  |  | Stack |
| Data Structure Typed | C++ STL | java.util | Python collections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heap<E> | priority_queue<T> | PriorityQueue<E> | heapq |
| Deque<E> | deque<T> | ArrayDeque<E> | deque |
| Queue<E> | queue<T> | Queue<E> | - |
| HashMap<K, V> | unordered_map<K, V> | HashMap<K, V> | defaultdict |
| DoublyLinkedList<E> | list<T> | LinkedList<E> | - |
| SinglyLinkedList<E> | - | - | - |
| BinaryTree<K, V> | - | - | - |
| BST<K, V> | - | - | - |
| RedBlackTree<E> | set<T> | TreeSet<E> | - |
| RedBlackTree<K, V> | map<K, V> | TreeMap<K, V> | - |
| TreeMultimap<K, V> | multimap<K, V> | - | - |
| - | multiset<T> | - | - |
| Trie | - | - | - |
| DirectedGraph<V, E> | - | - | - |
| UndirectedGraph<V, E> | - | - | - |
| PriorityQueue<E> | priority_queue<T> | PriorityQueue<E> | - |
| Array<E> | vector<T> | ArrayList<E> | list |
| Stack<E> | stack<T> | Stack<E> | - |
| Set<E> | - | HashSet<E> | set |
| Map<K, V> | - | HashMap<K, V> | dict |
| - | unordered_set<T> | HashSet<E> | - |
| Map<K, V> | - | - | OrderedDict |
| - | unordered_multiset | - | Counter |
| - | - | LinkedHashSet<E> | - |
| HashMap<K, V> | - | LinkedHashMap<K, V> | - |
| - | unordered_multimap<K, V> | - | - |
| - | bitset<N> | - | - |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 add randomly | 31.32 | 31.93 | 3.67e-4 |
| 10,000 add & delete randomly | 70.90 | 14.10 | 0.00 |
| 10,000 addMany | 40.58 | 24.64 | 4.87e-4 |
| 10,000 get | 27.31 | 36.62 | 2.00e-4 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 add randomly | 12.35 | 80.99 | 7.17e-5 |
| 1,000 add & delete randomly | 15.98 | 62.58 | 7.98e-4 |
| 1,000 addMany | 10.96 | 91.27 | 0.00 |
| 1,000 get | 18.61 | 53.73 | 0.00 |
| 1,000 dfs | 164.20 | 6.09 | 0.04 |
| 1,000 bfs | 58.84 | 17.00 | 0.01 |
| 1,000 morris | 256.66 | 3.90 | 7.70e-4 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 add randomly | 31.59 | 31.66 | 2.74e-4 |
| 10,000 add & delete randomly | 74.56 | 13.41 | 8.32e-4 |
| 10,000 addMany | 29.16 | 34.30 | 0.00 |
| 10,000 get | 29.24 | 34.21 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 add | 85.85 | 11.65 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 add & delete randomly | 211.54 | 4.73 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 getNode | 37.92 | 26.37 | 1.65e-4 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRC PQ 10,000 add | 0.57 | 1748.73 | 4.96e-6 |
| CJS PQ 10,000 add | 0.57 | 1746.69 | 4.91e-6 |
| MJS PQ 10,000 add | 0.57 | 1749.68 | 4.43e-6 |
| SRC PQ 10,000 add & pop | 3.47 | 288.14 | 6.38e-4 |
| CJS PQ 10,000 add & pop | 3.39 | 295.36 | 3.90e-5 |
| MJS PQ 10,000 add & pop | 3.37 | 297.17 | 3.03e-5 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 addVertex | 0.10 | 9534.93 | 8.72e-7 |
| 1,000 addEdge | 6.30 | 158.67 | 0.00 |
| 1,000 getVertex | 0.05 | 2.16e+4 | 3.03e-7 |
| 1,000 getEdge | 22.31 | 44.82 | 0.00 |
| tarjan | 210.90 | 4.74 | 0.01 |
| tarjan all | 214.72 | 4.66 | 0.01 |
| topologicalSort | 172.52 | 5.80 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 set | 275.88 | 3.62 | 0.12 |
| 1,000,000 Map set | 211.66 | 4.72 | 0.01 |
| 1,000,000 Set add | 177.72 | 5.63 | 0.02 |
| 1,000,000 set & get | 317.60 | 3.15 | 0.02 |
| 1,000,000 Map set & get | 274.99 | 3.64 | 0.03 |
| 1,000,000 Set add & has | 172.23 | 5.81 | 0.02 |
| 1,000,000 ObjKey set & get | 929.40 | 1.08 | 0.07 |
| 1,000,000 Map ObjKey set & get | 310.02 | 3.23 | 0.05 |
| 1,000,000 Set ObjKey add & has | 283.28 | 3.53 | 0.04 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 add & pop | 5.80 | 172.35 | 8.78e-5 |
| 10,000 fib add & pop | 357.92 | 2.79 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 221.57 | 4.51 | 0.03 |
| 1,000,000 unshift | 229.02 | 4.37 | 0.07 |
| 1,000,000 unshift & shift | 169.21 | 5.91 | 0.02 |
| 1,000,000 insertBefore | 314.48 | 3.18 | 0.07 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 push & pop | 212.98 | 4.70 | 0.01 |
| 10,000 insertBefore | 250.68 | 3.99 | 0.01 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 refill & poll | 8.91 | 112.29 | 2.26e-4 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 add & pop | 103.59 | 9.65 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 14.55 | 68.72 | 6.91e-4 |
| 1,000,000 push & pop | 23.40 | 42.73 | 5.94e-4 |
| 1,000,000 push & shift | 24.41 | 40.97 | 1.45e-4 |
| 1,000,000 unshift & shift | 22.56 | 44.32 | 1.30e-4 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 39.90 | 25.07 | 0.01 |
| 1,000,000 push & shift | 81.79 | 12.23 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 37.60 | 26.60 | 0.00 |
| 1,000,000 push & pop | 47.01 | 21.27 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 push | 45.97 | 21.76 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 getWords | 66.20 | 15.11 | 0.00 |
| Algorithm | Function Description | Iteration Type |
|---|---|---|
| Binary Tree DFS | Traverse a binary tree in a depth-first manner, starting from the root node, first visiting the left subtree, and then the right subtree, using recursion. | Recursion + Iteration |
| Binary Tree BFS | Traverse a binary tree in a breadth-first manner, starting from the root node, visiting nodes level by level from left to right. | Iteration |
| Graph DFS | Traverse a graph in a depth-first manner, starting from a given node, exploring along one path as deeply as possible, and backtracking to explore other paths. Used for finding connected components, paths, etc. | Recursion + Iteration |
| Binary Tree Morris | Morris traversal is an in-order traversal algorithm for binary trees with O(1) space complexity. It allows tree traversal without additional stack or recursion. | Iteration |
| Graph BFS | Traverse a graph in a breadth-first manner, starting from a given node, first visiting nodes directly connected to the starting node, and then expanding level by level. Used for finding shortest paths, etc. | Recursion + Iteration |
| Graph Tarjan's Algorithm | Find strongly connected components in a graph, typically implemented using depth-first search. | Recursion |
| Graph Bellman-Ford Algorithm | Finding the shortest paths from a single source, can handle negative weight edges | Iteration |
| Graph Dijkstra's Algorithm | Finding the shortest paths from a single source, cannot handle negative weight edges | Iteration |
| Graph Floyd-Warshall Algorithm | Finding the shortest paths between all pairs of nodes | Iteration |
| Graph getCycles | Find all cycles in a graph or detect the presence of cycles. | Recursion |
| Graph getCutVertexes | Find cut vertices in a graph, which are nodes that, when removed, increase the number of connected components in the graph. | Recursion |
| Graph getSCCs | Find strongly connected components in a graph, which are subgraphs where any two nodes can reach each other. | Recursion |
| Graph getBridges | Find bridges in a graph, which are edges that, when removed, increase the number of connected components in the graph. | Recursion |
| Graph topologicalSort | Perform topological sorting on a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to find a linear order of nodes such that all directed edges go from earlier nodes to later nodes. | Recursion |
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Practicality | Follows ES6 and ESNext standards, offering unified and considerate optional parameters, and simplifies method names. |
| Extensibility | Adheres to OOP (Object-Oriented Programming) principles, allowing inheritance for all data structures. |
| Modularization | Includes data structure modularization and independent NPM packages. |
| Efficiency | All methods provide time and space complexity, comparable to native JS performance. |
| Maintainability | Follows open-source community development standards, complete documentation, continuous integration, and adheres to TDD (Test-Driven Development) patterns. |
| Testability | Automated and customized unit testing, performance testing, and integration testing. |
| Portability | Plans for porting to Java, Python, and C++, currently achieved to 80%. |
| Reusability | Fully decoupled, minimized side effects, and adheres to OOP. |
| Security | Carefully designed security for member variables and methods. Read-write separation. Data structure software does not need to consider other security aspects. |
| Scalability | Data structure software does not involve load issues. |
FAQs
Javascript Data Structure. Heap, Binary Tree, Red Black Tree, Linked List, Deque, Trie, HashMap, Directed Graph, Undirected Graph, Binary Search Tree(BST), AVL Tree, Priority Queue, Graph, Queue, Tree Multiset, Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Max
The npm package data-structure-typed receives a total of 6,808 weekly downloads. As such, data-structure-typed popularity was classified as popular.
We found that data-structure-typed demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
Product
We're launching a new set of license analysis and compliance features for analyzing, managing, and complying with licenses across a range of supported languages and ecosystems.
Product
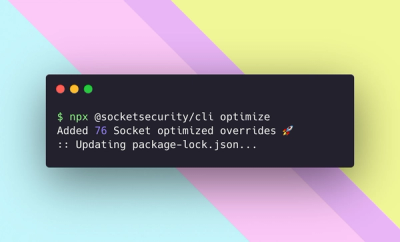
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.