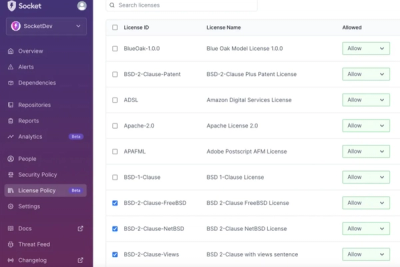
Product
Introducing License Enforcement in Socket
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
express-json-validator-middleware
Advanced tools
An Express middleware to validate requests against JSON Schemas
express.js middleware for JSON schema validation.
This package is a work in progress - feedback is heavily appreciated
Based heavily on https://github.com/trainiac/express-jsonschema. A big thank you to @trainiac for the original package!
express-json-validator-middleware is being actively maintained by @JouzaLoL$ npm install express-json-validator-middleware --save-dev
var { Validator, ValidationError } = require('express-json-validator-middleware');
var validator = new Validator({allErrors: true});
var validate = validator.validate;
validate({
request_property: schema_to_use
})
Example: Validate req.body against BodySchema
app.post('/street/', validate({body: BodySchema}), function(req, res) {
// route code
});
On encountering erroneous data, the validator will call next with a ValidationError object. It is recommended to setup a general error handler for your express app where you will catch errors of type ValidationError
Error example (pseudocode):
ValidationError {
name: 'JsonSchemaValidationError',
validationErrors: {
body: [AjvError]
}
}
Information on Ajv errors can be found here: ajv#errors
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
var bodyParser = require('body-parser');
var { Validator, ValidationError } = require('express-json-validator-middleware');
// Initialize a Validator instance first
var validator = new Validator({allErrors: true}); // pass in options to the Ajv instance
// Define a shortcut. It is perfectly okay ot use validator.validate()
var validate = validator.validate;
// Define a JSON Schema
var StreetSchema = {
type: 'object',
required: ['number, name, type'],
properties: {
number: {
type: 'number'
},
name: {
type: 'string'
},
type: {
type: 'string',
enum: ['Street', 'Avenue', 'Boulevard']
}
}
}
// This route validates req.body against the StreetSchema
app.post('/street/', validate({body: StreetSchema}), function(req, res) {
// At this point req.body has been validated and you can
// begin to execute your application code
});
Sometimes your route may depend on the body and query both having a specific format. In this example I use body and query but you can choose to validate any request properties you'd like.
var TokenSchema = {
type: 'object', // req.query is of type object
required: ['token'] // req.query.token is required
properties: {
token: { // validate token
type: 'string',
format: 'alphanumeric',
minLength: 10,
maxLength: 10
}
}
}
app.post('/street/', validate({body: StreetSchema, query: TokenSchema}), function(req, res) {
// application code
});
A valid request must now include a token URL query. Example valid URL: /street/?token=F42G5N5BGC
Ajv supports custom keywords out of the box. They must be defined only after you initialize a Validator, but before you any validate() middleware. Example:
var { Validator, ValidationError } = require('express-json-validator-middleware');
var validator = new Validator({allErrors: true});
validator.ajv.addKeyword('constant', { validate: function (schema, data) {
return typeof schema == 'object' && schema !== null
? deepEqual(schema, data)
: schema === data;
}, errors: false });
More info on custom keywords: ajv#customs-keywords
The Ajv instance can be accessed via validator.ajv.
var { Validator, ValidationError } = require('express-json-validator-middleware');
var validator = new Validator({allErrors: true});
validator.ajv // ajv instance
npm install
npm test
Tests include an independent validation test and a simulated Express middleware test.
In express-jsonschema, you could define a required property in two ways. Ajv only supports the latter.
// WRONG
{
type: 'object',
properties: {
foo: {
type: 'string',
required: true
}
}
}
// CORRECT
{
type: 'object',
properties: {
foo: {
type: 'string'
},
required: ['foo']
}
}
FAQs
An Express middleware to validate requests against JSON Schemas
The npm package express-json-validator-middleware receives a total of 15,995 weekly downloads. As such, express-json-validator-middleware popularity was classified as popular.
We found that express-json-validator-middleware demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
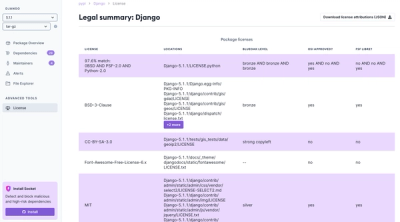
Product
We're launching a new set of license analysis and compliance features for analyzing, managing, and complying with licenses across a range of supported languages and ecosystems.
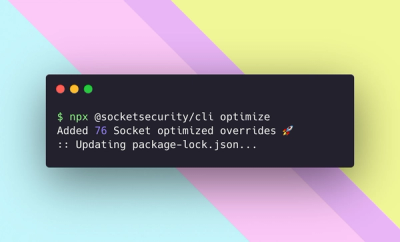
Product
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.