
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Package Typosquats react-login-page to Deploy Keylogger
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
mem-fs-editor
Advanced tools
Package description
The mem-fs-editor package is a utility for working with the file system in memory. It provides a way to perform file operations such as reading, writing, and modifying files without directly interacting with the disk until you decide to commit the changes. This is particularly useful for scaffolding tools and generators.
Reading Files
This feature allows you to read the content of a file from the file system into memory. The code sample demonstrates how to read a file using mem-fs-editor.
const memFs = require('mem-fs');
const editor = require('mem-fs-editor');
const store = memFs.create();
const fs = editor.create(store);
const content = fs.read('path/to/file.txt');
console.log(content);Writing Files
This feature allows you to write content to a file in memory and then commit the changes to the disk. The code sample demonstrates how to write to a file and commit the changes.
const memFs = require('mem-fs');
const editor = require('mem-fs-editor');
const store = memFs.create();
const fs = editor.create(store);
fs.write('path/to/file.txt', 'Hello, World!');
fs.commit(() => {
console.log('File written to disk');
});Modifying Files
This feature allows you to modify files in memory, such as copying or moving files. The code sample demonstrates how to copy a file from one location to another and commit the changes.
const memFs = require('mem-fs');
const editor = require('mem-fs-editor');
const store = memFs.create();
const fs = editor.create(store);
fs.copy('path/to/source.txt', 'path/to/destination.txt');
fs.commit(() => {
console.log('File copied');
});fs-extra is a package that extends the native Node.js fs module with additional methods for working with the file system. It provides similar functionalities such as reading, writing, and copying files, but it operates directly on the disk rather than in memory. This makes it less suitable for scenarios where you want to batch file operations before committing them.
vinyl-fs is a file system utility for working with streams in Gulp. It allows you to read, write, and modify files using a stream-based approach. While it provides similar functionalities to mem-fs-editor, it is more focused on stream processing and is commonly used in build systems.
graceful-fs is a drop-in replacement for the native fs module that improves handling of file system operations, especially in environments with high concurrency. It provides similar file operation methods but focuses on enhancing the reliability and performance of file system interactions.
Readme
File edition helpers working on top of mem-fs
import memFs from 'mem-fs';
import editor from 'mem-fs-editor';
const store = memFs.create();
const fs = editor.create(store);
fs.write('somefile.js', 'var a = 1;');
#read(filepath, [options])Read a file and return its contents as a string.
You can alternatively get the raw contents buffer if you pass options.raw = true.
By default, calling read() on a file path that does not exist throws error. You can, however, pass options.defaults = 'your default content' to get a default content you pass in, if you prefer to not deal with try/catch.
#readJSON(filepath, [defaults])Read a file and parse its contents as JSON.
readJSON() internally calls read() but will not throw an error if the file path you pass in does not exist. If you pass in an optional defaults, the defaults content will be returned in case of the target file is missing, instead of undefined. (Error would still be thrown if JSON.parse failed to parse your target file.)
#write(filepath, contents)Replace the content of a file (existing or new) with a string or a buffer.
#writeJSON(filepath, contents[, replacer [, space]])Replace the content of a file (existing or new) with an object that is to be converted by calling JSON.stringify().
contents should usually be a JSON object, but it can technically be anything that is acceptable by JSON.stringify.
Optionally pass replacer and space as the last two arguments, as defined by JSON.stringify. spacer is used to format the output string (prettify).
Default value for space is 2, when not specified.
#append(filepath, contents, [options])Append the new contents to the current file contents.
options.trimEnd (default true). Trim trailing whitespace of the current file contents.options.separator (default os.EOL). Separator to insert between current and new contents.options.create (default false). Create the file if doesn't exists.#appendTpl(filepath, contents, context[, templateOptions[, [options]])Append the new contents to the exsting filepath content and parse the new contents as an ejs template where context is the template context (the variable names available inside the template).
options.trimEnd (default true). Trim trailing whitespace of the current file contents.options.separator (default os.EOL). Separator to insert between current and new contents.#extendJSON(filepath, contents[, replacer [, space]])Extend the content of an existing JSON file with the partial objects provided as argument.
Optionally take the same JSON formatting arguments than #writeJSON().
#delete(filepath, [options])Delete a file or a directory.
filePath can also be a glob. If filePath is glob, you can optionally pass in an options.globOptions object to change its pattern matching behavior. The full list of options are being described here. The sync flag is forced to be true in globOptions.
#copy(from, to, [options], context[, templateOptions ])Copy file(s) from the from path to the to path.
When passing array, you should pass options.fromBasePath to be used to calculate the to relative path. The common directory will be detected and used as fromBasePath otherwise.
Optionally, pass an options.process function (process(contents)) returning a string or a buffer who'll become the new file content. The process function will take a single contents argument who is the copied file contents as a Buffer.
options.ignoreNoMatch can be used to silence the error thrown if no files match the from pattern.
options.append can be used to append from contents to to instead of copying, when the file is already loaded in mem-fs (safe for regeneration).
from can be a glob pattern that'll be match against the file system. If that's the case, then to must be an output directory. For a globified from, you can optionally pass in an options.globOptions object to change its pattern matching behavior. The full list of options are being described here. The nodir flag is forced to be true in globOptions to ensure a vinyl object representing each matching directory is marked as deleted in the mem-fs store.
Optionally, when from is a glob pattern, pass an options.processDestinationPath function (processDestinationPath(destinationFile)) returning a string who'll become the new file name.
options.noGlob can be used to by bypass glob matching entirely. In that case, from will directly match file paths against the file system.
#copyAsync(from, to, [options], context[, templateOptions ])Async version of copy.
copy loads from to memory and copy its contents to to.
copyAsync copies directly from the disk to to, falling back to copy behavior if the file doesn't exists on disk.
Same parameters of copy (see copy() documentation for more details).
#copyTpl(from, to, context[, templateOptions [, copyOptions]])Copy the from file and, if it is not a binary file, parse its content as an ejs template where context is the template context (the variable names available inside the template).
You can optionally pass a templateOptions object. mem-fs-editor automatically setup the filename option so you can easily use partials.
You can also optionally pass a copyOptions object (see copy() documentation for more details).
Templates syntax looks like this:
<%= value %>
<%- include('partial.ejs', { name: 'Simon' }) %>
Dir syntax looks like this:
/some/path/dir<%= value %>/...
Refer to the ejs documentation for more details.
#copyTplAsync(from, to, [options], context[, templateOptions ])Async version of copyTpl that uses copyAsync instead of copy.
Can be used for best performance. Reduces overheads.
Same parameters of copyTpl (see copyTpl() documentation for more details).
#move(from, to, [options])Move/rename a file from the from path to the to path.
#move internally uses #copy and #delete, so from can be a glob pattern, and you can provide options.globOptions with it.
#exists(filepath)Returns true if a file exists. Returns false if the file is not found or deleted.
#commit([filters,] [stream,] callback)Persist every changes made to files in the mem-fs store to disk.
If provided, filters is an array of TransformStream to be applied on a stream of vinyl files (like gulp plugins).
If provided, stream is a stream of vinyl files.
callback is called once the files are updated on disk.
#dump([cwd,] [filter])Dump files to compare expected result.
Provide a cwd for relative path. Allows to omit temporary path.
Provide a filter function or a pattern to focus on specific files.
dump returns only modified (committed or not) files when no filter or a pattern is provided.
FAQs
Unknown package
The npm package mem-fs-editor receives a total of 854,488 weekly downloads. As such, mem-fs-editor popularity was classified as popular.
We found that mem-fs-editor demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
Security News
The JavaScript community has launched the e18e initiative to improve ecosystem performance by cleaning up dependency trees, speeding up critical parts of the ecosystem, and documenting lighter alternatives to established tools.
Product
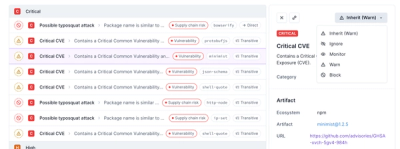
Socket now supports four distinct alert actions instead of the previous two, and alert triaging allows users to override the actions taken for all individual alerts.