
Security News
GitHub Removes Malicious Pull Requests Targeting Open Source Repositories
GitHub removed 27 malicious pull requests attempting to inject harmful code across multiple open source repositories, in another round of low-effort attacks.
merkletreejs
Advanced tools
The merkletreejs package is a JavaScript library for constructing and verifying Merkle Trees. Merkle Trees are a fundamental component in blockchain technology and cryptographic applications, providing a way to efficiently and securely verify the integrity of data. This package allows you to create Merkle Trees, generate proofs, and verify proofs.
Creating a Merkle Tree
This feature allows you to create a Merkle Tree from an array of data. The example uses the keccak256 hashing algorithm to hash the data and then constructs the tree. The root of the tree is then printed.
const { MerkleTree } = require('merkletreejs');
const keccak256 = require('keccak256');
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'c'].map(x => keccak256(x));
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, keccak256, { sortPairs: true });
const root = tree.getRoot().toString('hex');
console.log(root);Generating a Proof
This feature allows you to generate a proof for a specific leaf in the Merkle Tree. The proof can be used to verify that the leaf is part of the tree.
const leaf = keccak256('a');
const proof = tree.getProof(leaf);
console.log(proof);Verifying a Proof
This feature allows you to verify a proof against the root of the Merkle Tree. It checks if the provided leaf and proof match the root, ensuring the integrity of the data.
const isValid = tree.verify(proof, leaf, root);
console.log(isValid);The merkletree package is another library for creating and verifying Merkle Trees. It offers similar functionalities to merkletreejs but may have different API conventions and additional features.
The merkle-tools package provides tools for creating and managing Merkle Trees. It includes functionalities for creating trees, generating proofs, and verifying proofs, similar to merkletreejs. It also offers additional utilities for working with Merkle Trees.
The merkle-lib package is a lightweight library for creating and verifying Merkle Trees. It focuses on simplicity and ease of use, providing core functionalities similar to merkletreejs.

Construct Merkle Trees and verify proofs in JavaScript.
Diagram of Merkle Tree

Diagram of Merkle Tree Proof

Diagram of Invalid Merkle Tree Proofs
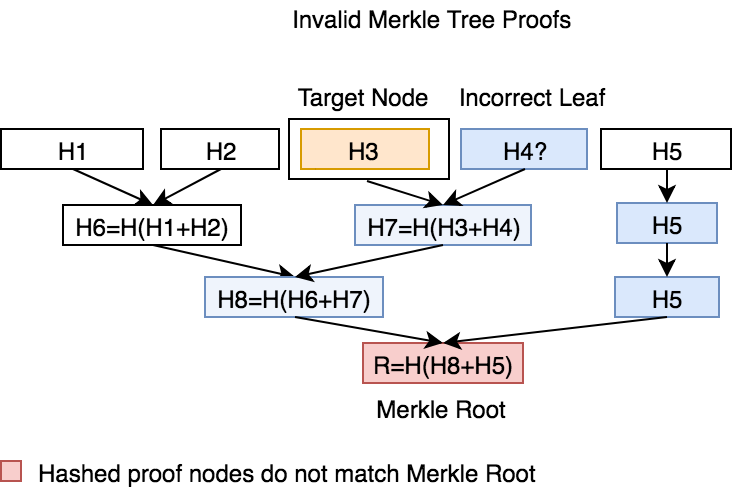
Diagram of Bitcoin Merkle Tree

npm install merkletreejs
Construct tree, generate proof, and verify proof:
const { MerkleTree } = require('merkletreejs')
const SHA256 = require('crypto-js/sha256')
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'c'].map(x => SHA256(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, SHA256)
const root = tree.getRoot().toString('hex')
const leaf = SHA256('a')
const proof = tree.getProof(leaf)
console.log(tree.verify(proof, leaf, root)) // true
const badLeaves = ['a', 'x', 'c'].map(x => SHA256(x))
const badTree = new MerkleTree(badLeaves, SHA256)
const badLeaf = SHA256('x')
const badProof = tree.getProof(badLeaf)
console.log(tree.verify(badProof, leaf, root)) // false
Print tree to console:
MerkleTree.print(tree)
Output
└─ 311d2e46f49b15fff8b746b74ad57f2cc9e0d9939fda94387141a2d3fdf187ae
├─ 176f0f307632fdd5831875eb709e2f68d770b102262998b214ddeb3f04164ae1
│ ├─ 3ac225168df54212a25c1c01fd35bebfea408fdac2e31ddd6f80a4bbf9a5f1cb
│ └─ b5553de315e0edf504d9150af82dafa5c4667fa618ed0a6f19c69b41166c5510
└─ 0b42b6393c1f53060fe3ddbfcd7aadcca894465a5a438f69c87d790b2299b9b2
└─ 0b42b6393c1f53060fe3ddbfcd7aadcca894465a5a438f69c87d790b2299b9b2
Class reprensenting a Merkle Tree
namespace: MerkleTree
MerkleTree
⊕ new MerkleTree(leaves: any, hashAlgorithm: any, options?: *Options
desc: Constructs a Merkle Tree. All nodes and leaves are stored as Buffers. Lonely leaf nodes are promoted to the next level up without being hashed again.
example:
const MerkleTree = require('merkletreejs')
const crypto = require('crypto')
function sha256(data) {
// returns Buffer
return crypto.createHash('sha256').update(data).digest()
}
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'c'].map(x => sha3(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, sha256)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| leaves | any | - | Array of hashed leaves. Each leaf must be a Buffer. |
| hashAlgorithm | any | - | Algorithm used for hashing leaves and nodes |
Default value options | Options | {} as any | Additional options |
Returns: MerkleTree
● duplicateOdd: boolean
● hashAlgo: function
▸(value: any): any
Parameters:
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| value | any |
Returns: any
● hashLeaves: boolean
● isBitcoinTree: boolean
● layers: any[]
● leaves: any[]
● sortLeaves: boolean
● sortPairs: boolean
▸ createHashes(nodes: any): void
Parameters:
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| nodes | any |
Returns: void
▸ getLayers(): any[]
getLayers
desc: Returns array of all layers of Merkle Tree, including leaves and root.
example:
const layers = tree.getLayers()
Returns: any[]
▸ getLayersAsObject(): any
Returns: any
▸ getLeaves(): any[]
getLeaves
desc: Returns array of leaves of Merkle Tree.
example:
const leaves = tree.getLeaves()
Returns: any[]
▸ getProof(leaf: any, index?: any): any[]
getProof
desc: Returns the proof for a target leaf.
example:
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2])
example:
const leaves = ['a', 'b', 'a'].map(x => sha3(x))
const tree = new MerkleTree(leaves, sha3)
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2], 2)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| leaf | any | Target leaf |
Optional index | any |
Returns: any[]
▸ getRoot(): any
getRoot
desc: Returns the Merkle root hash as a Buffer.
example:
const root = tree.getRoot()
Returns: any
▸ print(): void
Returns: void
▸ toString(): any
Returns: any
▸ toTreeString(): any
Returns: any
▸ verify(proof: any, targetNode: any, root: any): boolean
verify
desc: Returns true if the proof path (array of hashes) can connect the target node to the Merkle root.
example:
const root = tree.getRoot()
const proof = tree.getProof(leaves[2])
const verified = tree.verify(proof, leaves[2], root)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| proof | any | Array of proof objects that should connect target node to Merkle root. |
| targetNode | any | Target node Buffer |
| root | any | Merkle root Buffer |
Returns: boolean
<Static> bufferify▸ bufferify(x: any): any
Parameters:
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| x | any |
Returns: any
<Static> print▸ print(tree: any): void
Parameters:
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| tree | any |
Returns: void
● duplicateOdd: boolean
If set to true, an odd node will be duplicated and combined to make a pair to generate the layer hash.
● hashLeaves: boolean
If set to true, the leaves will hashed using the set hashing algorithms.
● isBitcoinTree: boolean
If set to true, constructs the Merkle Tree using the Bitcoin Merkle Tree implementation. Enable it when you need to replicate Bitcoin constructed Merkle Trees. In Bitcoin Merkle Trees, single nodes are combined with themselves, and each output hash is hashed again.
● sortLeaves: boolean
If set to true, the leaves will be sorted.
● sortPairs: boolean
If set to true, the hashing pairs will be sorted.
npm test
As is, this implemenation is vulnerable to a second pre-image attack. Use a difference hashing algorithm function for leaves and nodes, so that H(x) != H'(x).
Also, as is, this implementation is vulnerable to a forgery attack for an unbalanced tree, where the last leaf node can be duplicated to create an artificial balanced tree, resulting in the same Merkle root hash. Do not accept unbalanced tree to prevent this.
More info here.
Bitcoin mining the hard way: the algorithms, protocols, and bytes
Why aren't Solidity sha3 hashes not matching what other sha3 libraries produce?
What is the purpose of using different hash functions for the leaves and internals of a hash tree?
FAQs
Construct Merkle Trees and verify proofs
The npm package merkletreejs receives a total of 54,090 weekly downloads. As such, merkletreejs popularity was classified as popular.
We found that merkletreejs demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
GitHub removed 27 malicious pull requests attempting to inject harmful code across multiple open source repositories, in another round of low-effort attacks.

Security News
RubyGems.org has added a new "maintainer" role that allows for publishing new versions of gems. This new permission type is aimed at improving security for gem owners and the service overall.

Security News
Node.js will be enforcing stricter semver-major PR policies a month before major releases to enhance stability and ensure reliable release candidates.