
Security News
PyPI Introduces Digital Attestations to Strengthen Python Package Security
PyPI now supports digital attestations, enhancing security and trust by allowing package maintainers to verify the authenticity of Python packages.
pixl-logger
Advanced tools
This module provides a simple logging class, which appends to a text log file with bracket-delimited columns. You can define any number of columns you want, or use some of the built-in auto-populated columns. You can populate columns by name, or by using one of the shortcut methods described below.
Use npm to install the module:
npm install pixl-logger
Then use require() to load it in your code:
var Logger = require('pixl-logger');
To use the module, instantiate an object, and start logging:
var columns = ['hires_epoch', 'date', 'hostname', 'component', 'category', 'code', 'msg', 'data'];
var logger = new Logger( 'logs/debug.log', columns );
logger.set('hostname', 'myserver.com');
logger.print({
category: 'debug',
component: 'main',
code: 1,
msg: "Hello log!"
});
This would append the following like to logs/debug.log:
[1423462332.437][2015-02-08 22:12:12][myserver.com][main][debug][1][Hello log!][]
Some column names are special, and automatically populated (see below), but the rest are free-form. You can include any number of columns you like, and name them however you want.
All the log "columns" are basically just key/value pairs stored in an args property in the class, which don't have to be specified on every call to print(). Meaning, you can set some of them once, and only have to set them again when they change. Example:
logger.set('component', 'main');
logger.set('category', 'debug');
logger.print({
code: 1,
msg: "Hello log!"
});
Note that when you pass arguments to print() they are not saved for subsequent calls. They are only used for that one log row. You need to call set() to make them stick.
You can also fetch arg values using get(). Pass in a key to fetch one arg, or omit to get the entire args object back.
In order to protect the log format and syntax, all column values are "cleansed" before being written. Specifically, any newlines are converted to single spaces, and the character sequence ][ is stripped (as it would corrupt the log column layout). All other characters are allowed. Example:
logger.debug( 1, "This won't go well\n[Hi][There]\r\nGoodbye.\n" );
This would be logged as:
[1423466726.159][2015-02-08 23:25:26][myserver.com][main][debug][1][This won't go well [HiThere] Goodbye. ]
The logger library provides the following three shortcut methods, which accept a list of common arguments instead of a hash:
The debug() method is designed to assist with writing to a debug log. It automatically sets the category column to debug. It requires two arguments, which are values for the code (debug level) and msg columns, with the 3rd argument being an optional data object, if you want. Examples:
logger.debug( 1, "Logged at debug level 1" );
logger.debug( 2, "Logged at debug level 2", {some:"data"} );
An extra feature with the debug() call is that you can set a debugLevel arg on your class instance, and it'll only log entries if they have an equal or lower level (a.k.a. code). So imagine this setup:
logger.set( 'debugLevel', 2 );
logger.debug( 1, "Logged at debug level 1" );
logger.debug( 2, "Logged at debug level 2" );
logger.debug( 3, "This won't be logged at all!" );
In this case we set the debugLevel arg to 2, so only the first two calls will be logged. The third call, which is logged at a higher (more verbose) level than the debugLevel value, will be silently skipped.
If you need to see if a particular debug level would be logged, you can call the shouldLog() method and pass in a level to query. If the current debugLevel is equal to or higher than the level number passed in, it returns true, otherwise it returns false. Example:
if (logger.shouldLog(9)) {
// do something here like serializing complex data into a string
logger.debug(9, "Complex data here: " + complex_data);
}
The idea is that entire code block wouldn't even be executed if the debugLevel was less than 9, saving you the CPU time of serializing the complex data to be logged.
Keep in mind that you can simply pass an Object to debug() as an optional 3rd argument, and it'll automatically be serialized to JSON and logged if the debug level is acceptable.
The error() method is designed to assist with logging errors. It automatically sets the category column to error. It requires two arguments, which are values for the code and msg columns, with the 3rd argument being an optional data object, if you want. Example:
logger.error( 1005, "An error of type 1005 occurred!" );
This would be equivalent to calling print() with the following:
logger.print({
category: 'error',
code: 1005,
msg: "An error of type 1005 occurred!"
});
The transaction() method is designed to assist with logging transactions. A "transaction" is whatever action you define in your app as something you want logged, for audit or replay purposes. It automatically sets the category column to transaction. It requires two arguments, which are values for the code and msg columns, with the 3rd argument being an optional data object, if you want. Example:
logger.transaction( "user_update", "User jhuckaby was updated", {username:"jhuckaby"} );
This would be equivalent to calling print() with the following:
logger.print({
category: 'transaction',
code: "user_update",
msg: "User jhuckaby was updated",
data: {username:"jhuckaby"}
});
If you set the echo arg to any true value, the logger will echo all log entries to process.stdout, in addition to the log file. This is useful for running CLI scripts or your app in debug mode. Example:
logger.set( 'echo', true );
logger.debug( 1, "This will be logged and echoed to the console!" );
If you set the color arg to any true value, the logger will echo all log entries in color (assuming you have a terminal that supports color), using the chalk module. The color sequence is gray, red, green, yellow, blue, magenta and cyan. If your log has more than 7 columns, the colors repeat. The bracket dividers are printed in dim. Here is a screenshot:
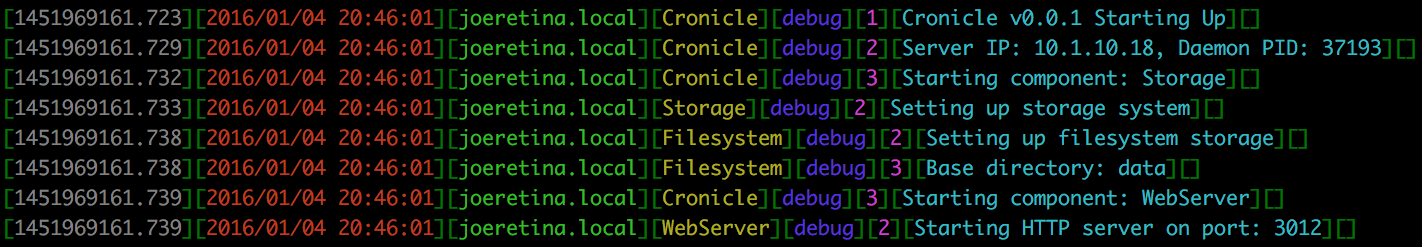
Example:
logger.set( 'echo', true );
logger.set( 'color', true );
logger.debug( 1, "This will be colored in the console!" );
Note that the color only affects the local echo in your terminal. The log file itself is still written in plain text.
To grab the last line logged by the logger, pull the lastRow property off the class instance. It is the fully formatted line, including an EOL. Example:
var line = logger.lastRow;
Several column names are special, in that they are automatically populated, or have special behavior. Here they are:
Any column named epoch will automatically be populated with the current local server time, represented in integer Epoch seconds. Example:
[1423433821]
Any column named hires_epoch will automatically be populated with the current local server time, represented in high precision floating point Epoch seconds, with up to 3 digits after the decimal. Example:
[1423433807.277]
Any column named date will automatically be populated with a human-friendly version of the current local server time, in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS format. Example:
[2015-02-08 14:16:58]
Any column named hostname will automatically be populated with the server's hostname, obtained by calling os.hostname() once at construction. Example:
[host01.mydomain.com]
Any column named pid will automatically be populated with the current Process ID (PID), obtained by calling process.pid once at construction. Example:
[13702]
The data column is special, in that if it contains an object, it will be serialized to JSON. Example:
[{"code":0,"description":"Success"}]
The category column is only special in that the shortcut methods debug(), error() and transaction() automatically populate it to match their names.
There are a number of optional hooks available for you to customize your logs even further. These can be specified in the args object passed to the constructor, by calling set(), or simply by setting them on an instance object.
The pather hook allows you to intercept and alter the log path on disk per each log row, and generate your own path based on the current args passed to the logger. Using this you can change the log file per each log row. Your hook function is passed the current path, and the current args object containing all the column keys/values. Example:
logger.pather = function(path, args) {
return '/var/log/MyApp-' + args.category + '.log';
};
In this example the category column is used to dynamically construct the log filename. So if the category column was set to debug, the log path would be /var/log/MyApp-debug.log. This is a great way to generate multiple logs based on any criteria you want.
The filter hook allows you to intercept each log column value as it is being added to the columns array for serialization. This is typically where column values are stripped of any illegal characters, and whitespace compressed. If you specify this hook, the default cleansing operation does not take place, and your function is expected to do all the filtering necessary. Your hook function is called for each column in each row, so keep that in mind for performance purposes, and passed the current column value, and its array index. Example:
logger.filter = function(value, idx) {
if (typeof(value) == 'object') value = JSON.stringify(value);
return value.toString().replace(/[\r\n]/g, ' ').replace(/\]\[/g, '');
};
Note that it is up to your filter function to convert objects into strings here, if you are trying to log any raw objects.
The serializer hook allows you to intercept the log columns just as they are being serialized into a string for appending to your log file. Using this you can completely change how your log file is formatted. The default format is [bracket][delimited][rows] but you can serialize columns into any format of string you want. Your function is passed the current columns array (filtered) and the args object. For example, here is how to produce a CSV (comma-separated) log:
logger.serializer = function(cols, args) {
return cols.join(',') + "\n";
};
Your serializer function is expected to return a full formatted log row (line) ending in a EOL character.
The echoer hook allows you to control exactly how your log is echoed to the console, if Echo to Console mode is enabled. The default behavior is to simply reprint the formatted log line to STDOUT, in addition to appending it to your log file. However, if you specify the echoer hook, this no longer happens, and instead your function is expected to do the echoing. The function is passed the formatted log line string (already appended to the log file), the array of columns that were serialized (these are filtered), and the current args object. Example:
logger.echoer = function(line, cols, args) {
console.log( args.category + ": " + args.msg );
if (args.data) console.dir(args.data);
};
In this example we are only echoing certain columns to the console (just category and msg) using the args object, and allowing Node.js to serialize the data column via console.dir(). This way if you are using a debugger, it may be navigable.
If you specify a filesystem path as the echoer instead of a function, it will be appended to. Using this technique you can have the logger append to two different log files at once (the primary log and the echoer log). This file append honors the sync flag as well.
Note that your echoer hook is only ever called if Echo to Console mode is enabled.
To rotate a log file, call the rotate() method, passing in a destination filesystem path and a callback. This will atomically move the file to the destination directory/filename, attempting a rename, and falling back to a "copy to temp file + rename" strategy. Example:
logger.rotate( '/logs/pickup/myapp.log', function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
} );
If you omit a filename on the destination path and leave a trailing slash, the source log filename will be appended to it.
You can actually rotate any log file you want by specifying three arguments, with the custom source log file path as the first argument. Example:
logger.rotate( '/path/to/logfile.log', '/logs/pickup/otherapp.log', function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
} );
You can also "archive" logs using the archive() method. Archiving differs from rotation in that the log file is atomically copied to a custom location which may contain date/time directories (all auto-created as needed), and then the file is compressed using gzip. You can archive any number of logs at once by using filesystem glob syntax. Example:
var src_spec = '/logs/myapp/*.log';
var dest_path = '/archives/myapp/[yyyy]/[mm]/[dd]/[filename]-[hh].log.gz';
var epoch = ((new Date()).getTime() / 1000) - 1800; // 30 minutes ago
logger.archive( src_spec, dest_path, epoch, function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
} );
This example would find all the log files found in the /logs/myapp/ directory that end in .log, and archive them to destination directory /archives/myapp/[yyyy]/[mm]/[dd]/, with a destination filename pattern of [filename]-[hh].log.gz. All the bracket-delimited placeholders are expanded using the timestamp provided in the epoch variable. The special [filename] placeholder expands to the source log filename, sans extension. All directories are created as needed.
By default, the logger will append to your log files asynchronously. This has the benefit of not blocking your main thread, and can help if your log drive is suffering lag or high I/O wait. But it may cause issues with log entries appearing out of order for extremely high traffic apps, and also some final log entries may be lost if process.exit() is called immediately after.
To get around these potential issues, you can write log entries synchronously. Just set the sync arg to true:
logger.set( 'sync', true );
logger.debug( 1, "This will be logged synchronously, even if we exit right NOW!" );
process.exit(0);
The MIT License
Copyright (c) 2015 - 2018 Joseph Huckaby
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
FAQs
A simple logging class which generates [bracket][delimited] log columns.
The npm package pixl-logger receives a total of 688 weekly downloads. As such, pixl-logger popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that pixl-logger demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
PyPI now supports digital attestations, enhancing security and trust by allowing package maintainers to verify the authenticity of Python packages.

Security News
GitHub removed 27 malicious pull requests attempting to inject harmful code across multiple open source repositories, in another round of low-effort attacks.

Security News
RubyGems.org has added a new "maintainer" role that allows for publishing new versions of gems. This new permission type is aimed at improving security for gem owners and the service overall.