Product
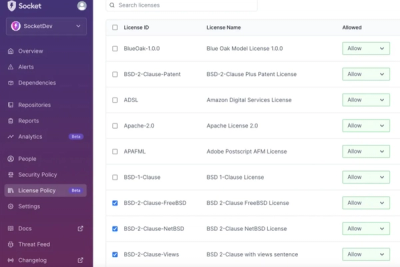
Introducing License Enforcement in Socket
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
postcss-styled-syntax
Advanced tools
PostCSS syntax for template literals CSS-in-JS (e. g. styled-components).
PostCSS syntax for template literals CSS-in-JS (e. g. styled-components, Emotion). Built to be used as Stylelint custom syntax or with PostCSS plugins.
Syntax supports:
styled.foostyled(Component)styled.foo.attrs({})styled(Component).attrs({})csscreateGlobalStylelet Component = styled.p`
color: #bada55;
`;
npm install --save-dev postcss-styled-syntax
Install syntax and add to a Stylelint config:
{
"customSyntax": "postcss-styled-syntax"
}
Stylelint custom syntax documentation.
Install syntax and add to a PostCSS config:
module.exports = {
syntax: 'postcss-styled-syntax',
plugins: [ /* ... */ ],
};
Example assumes using PostCSS CLI or other PostCSS runner with config support.
Syntax parser JavaScript/TypeScript code and find all supported components and functions (e. g. css``). Then it go over them and builds a PostCSS AST, where all found components become Root nodes inside Document node.
All interpolations within found component CSS are end up in the AST. E. g. for a declaration color: ${brand} Decl node will look like:
Decl {
prop: 'color',
value: '${brand}',
}
When interpolation is not part of any node it goes to the next node's raws.before. For example for the following code:
let Component = styled.p`
${textStyles}
color: red;
`;
AST will look like:
Decl {
prop: 'color',
value: 'red',
raws: {
before: '\n\t${textStyles}\n\n\t',
// ...
}
}
If there is not next node after interpolation, it will go to parents raws.after. For example for the following code:
let Component = styled.p`
color: red;
${textStyles}
`;
AST will look like:
Root {
nodes: [
Decl {
prop: 'color',
value: 'red',
},
],
raws: {
after: '\n\n\t${textStyles}\n'
// ...
},
}
Mostly it works just as default PostCSS stringifyer. The main difference is css helper in interpolations within a styled component code. E. g. situatians like this:
let Component = styled.p`
${(props) =>
props.isPrimary
? css`
background: green;
`
: css`
border: 1px solid blue;
`}
color: red;
`;
css helper inside an interpolation within Component code.
During parsing whole interpolation (${(props) ... }) is added as raws.before to color: red node. And it should not be modified. Each css helpers remember their original content (as a string).
When stringifyer reaches raws.before of a node it checks if it has interpolations with css helpers. If yes, then it searchs for css helper original content and replace it with stringified css helper. This way changes made to the AST of css helper will be stringified.
Double slash comments (//) will result in parsing error. Use standard CSS comments instead (/* */). It is definitelly possible to add support for double slash comment, but let's use standard CSS as much as possible
Source maps won't work or could not be trusted. I did not disable them on purpose. But did not test them at all. Because of the way we need handle css helpers within styled component, source.end positions on a node might change if css AST changes. See “How it works” section on stringifying for more info.
PostCSS for tokenizer, parser, stringifier and tests for them.
Prettier for styled-components detection function in an ESTree AST.
0.3.1
FAQs
PostCSS syntax for template literals CSS-in-JS (e. g. styled-components).
The npm package postcss-styled-syntax receives a total of 249,489 weekly downloads. As such, postcss-styled-syntax popularity was classified as popular.
We found that postcss-styled-syntax demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
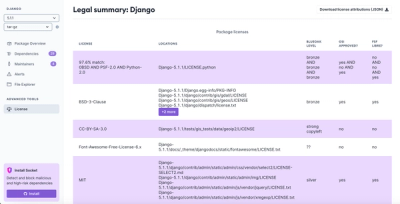
Product
We're launching a new license scanner with an improved suite of features for analyzing, managing, and complying with licenses across a range of supported languages and ecosystems.
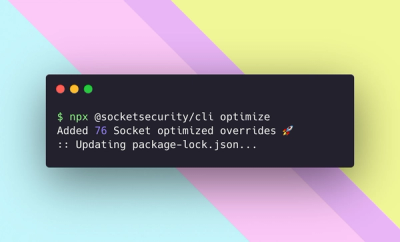
Product
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.