State Machine cat
write beautiful state charts






What?
Makes this
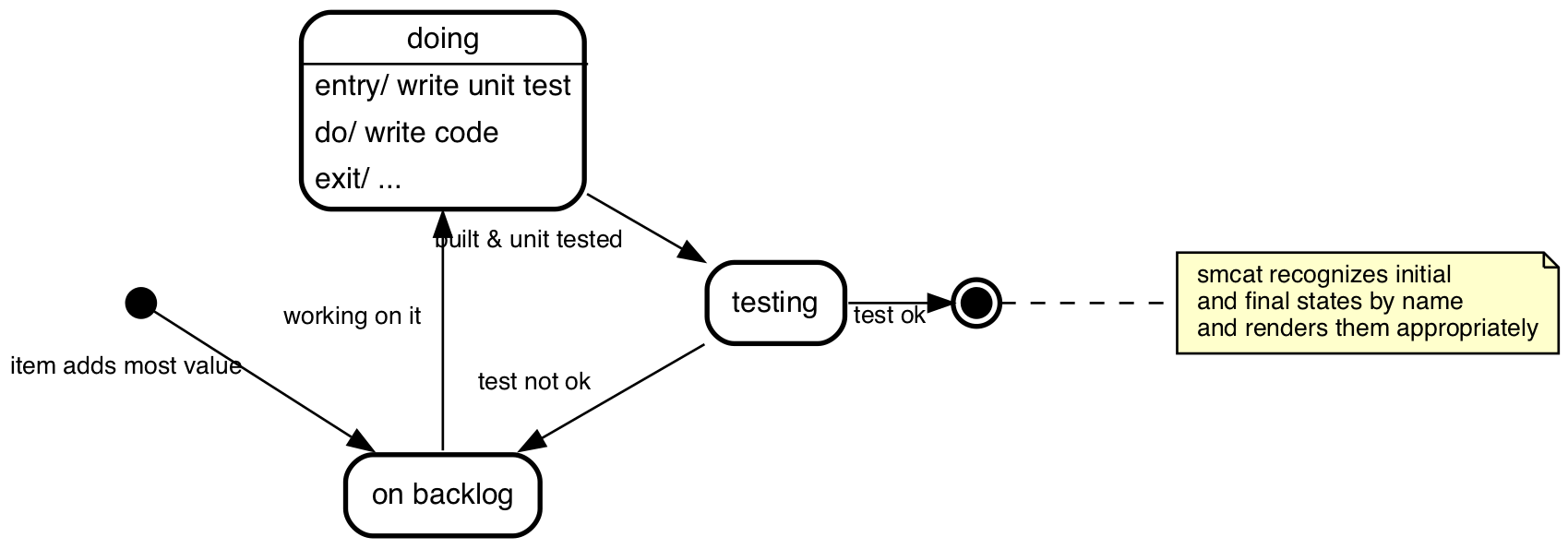
from this
initial,
doing: entry/ write unit test
do/ write code
exit/ ...,
# smcat recognizes initial
# and final states by name
# and renders them appropriately
final;
initial => "on backlog" : item adds most value;
"on backlog" => doing : working on it;
doing => testing : built & unit tested;
testing => "on backlog" : test not ok;
testing => final : test ok;
Why
To enable me to make state charts ...
- ... that look good
- ... with the least effort possible
- ... whithout having to interact with drag and drop tools. Entering text
is fine, doing my own layout is not.
- ... without having to dive into GraphViz
dot each time. GraphViz is cool,
but is was not designed to write & maintain conceptual documents in
(You'll know what I'm talking about if you ever tried to get it to draw nested nodes. Or edges between those. )
Usage
On line
A no-frills interpreter on line: state-machine-cat.js.org.
Command line interface
Just npm install --global state-machine-cat and run smcat
This is what smcat --help would get you:
Usage: smcat [options] [infile]
Write beautiful state charts - https://github.com/sverweij/state-machine-cat
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
-T --output-type <type> svg|eps|ps|ps2|dot|smcat|json|ast|scxml|oldsvg|scjson|pdf|png (default: "svg")
-I --input-type <type> smcat|json|scxml (default: "smcat")
-E --engine <type> dot|circo|fdp|neato|osage|twopi (default: "dot")
-d --direction <dir> top-down|bottom-top|left-right|right-left (default: "top-down")
-o --output-to <file> File to write to. use - for stdout.
--desugar transform pseudo states into transitions (!experimental!)
-l --license Display license and exit
-h, --help display help for command
... so to convert the above chart to sample.svg
smcat docs/sample.smcat
Or, if you'd rather pull dot output through GraphViz dot yourself:
smcat -T dot docs/sample.smcat -o - | dot -T svg -odoc/sample.svg
Leaving the options at the default settings usually deliver the best
results already, so if they bewilder you: don't worry.
When you pass the --desugar (⨻ experimental) switch, state-machine-cat will,
before rendering, transform some pseudo states into transitions - see
de-sugaring state machines for details.
In addition to what's documented in the --help you can use the following 'advanced'
options:
--dot-graph-attrs <string> graph attributes to pass to the dot render engine
--dot-node-attrs <string> node attributes to pass to the dot render engine
--dot-edge-attrs <string> edge attributes to pass to the dot render engine
With these you can override default attributes in the generated picture; e.g. to
get a transparent background and draw edges as line segments instead of
splines, use this:
smcat --dot-graph-attrs "bgcolor=transparent splines=line" docs/sample.smcat
Syntax highlighting
State chart XML (SCXML)
state machine cat can write and read valid core constructs
scxml documents. If you're into that sort
of thing you can read all about it in State Machine Cat and SCXML.
Programmatically
After you npm i 'd state-machine-cat:
import smcat from "state-machine-cat";
try {
const lSVGInAString = smcat.render(
`
initial => backlog;
backlog => doing;
doing => test;
`,
{
outputType: "svg",
},
);
console.log(lSVGInAString);
} catch (pError) {
console.error(pError);
}
Read more in docs/api.md
There's also a script available to embed state machines into html with script
tags like <script type="text/x-smcat"></script>. Documentation for that
'in page' feature resides over at state-machine-cat.js.org/inpage.html
The language
Short tutorial
simplest
on => off;
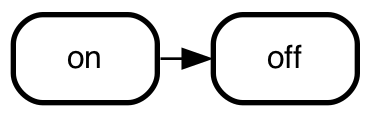
- smcat automatically declares the states. You can explicitly declare
them if you want them to have more than a name only - see state
declarations below.
labels
on => off: switch;
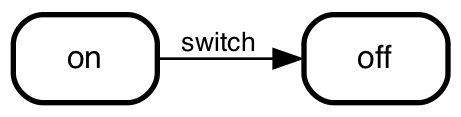
UML prescribes to place conditions after events, to place
conditions within squares and to place actions
after a /: from => to: event [conditions]/ actions, e.g. on => off: switch flicked [not an emergency]/ light off;.
You're free to do so, but smcat doesn't check for it. It internally takes
the notation into account, though and if you choose to export to json, scxml
or scjson you'll see them nicely split out.
on => off: switch flicked/
light off;
off => on: switch flicked/
light on;
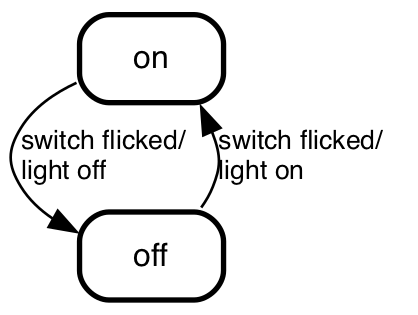
You note that smcat rendered the states in this chart top down instead of
left to right. It did that because we told it so. You can do that too
with --direction on the command line
notes
# this is a note
on => off;
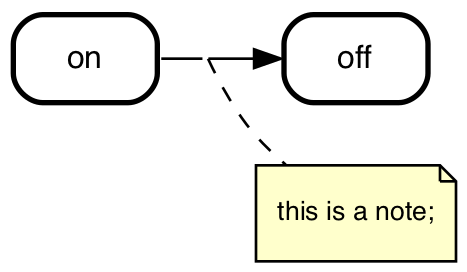
state declarations
If you need to define activities (e.g. entry or exit triggers) on
a state, you can explicitly declare the state and put the activites
after a colon:
# yep, notes get rendered here as well
# multiple notes translate into multiple
# lines in notes in the diagram
doing:
entry/ make a feature branch
exit/ deploy code on production
...;
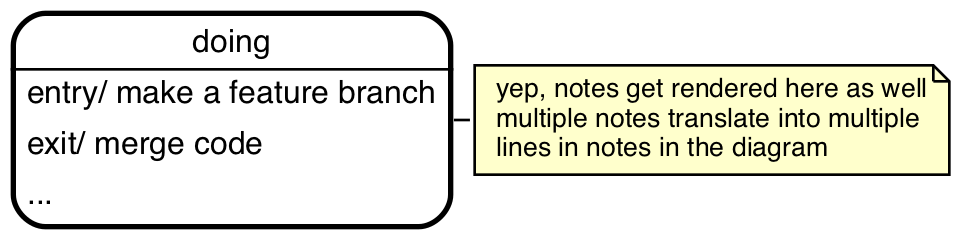
smcat recognizes the entry/ and exit/ keywords and treats
everything after it on the same line to be the 'body' of the
trigger.
Here too: you're free to use them, but you don't have to.
smcat takes them into account in its internal representation
and uses them in exports to json, scxml and scjson.
state display names
If you want to use a display names that differ from how you
name the states (e.g. if the display names are long),
you can do so by adding a label to them:
on [label="Lamp aan"],
off [label="Lamp uit"];
off => on: on pushed;
on => off: off pushed;

initial and final
When initial or final, is part of a state's name smcat treats
it as the UML 'pseudo states' initial and final respectively:
initial => todo;
todo => doing;
doing => done;
done => final;

history
smcat recognizes states with history in their name as history states:
initial,
"power off",
running {
running.history;
washing -> rinsing: 20 min;
rinsing -> spinning: 20 min;
spinning -> final: 20 min;
},
final;
initial => washing;
running => "power off": power out;
"power off" => running.history: restore power;
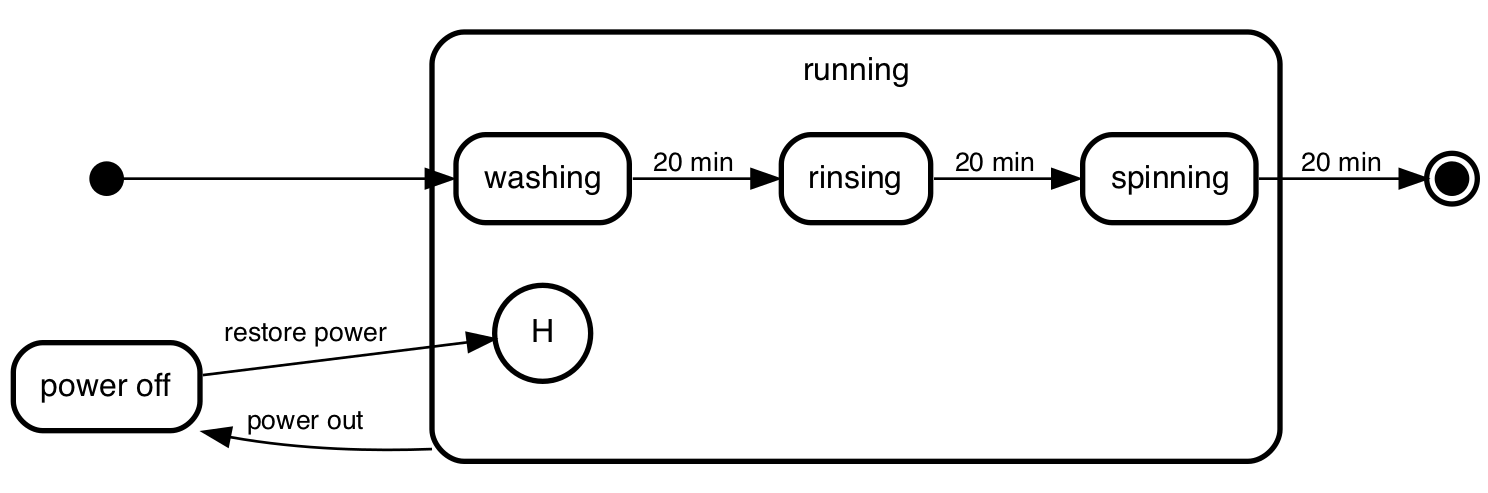
History states are shallow by default. If you want a history state to
be deep just put that somewhere in the name (e.g. "running deep history"
or running.history.deep) - and smcat will render them as such.
Choice - ^
smcat treats states starting with ^ as UML pseudo state choice. Strictly
speaking 'choice' is a superfluous element of the UML state machine
specification, but it is there and sometimes it makes diagrams easier to read.
^fraud?: transaction fraudulent?;
initial -> reserved;
reserved -> quoted:
quote
requested;
quoted -> ^fraud?: payment;
^fraud? -> ticketed: [no];
^fraud? -> removed: [yes];
ticketed -> final;
removed -> final;
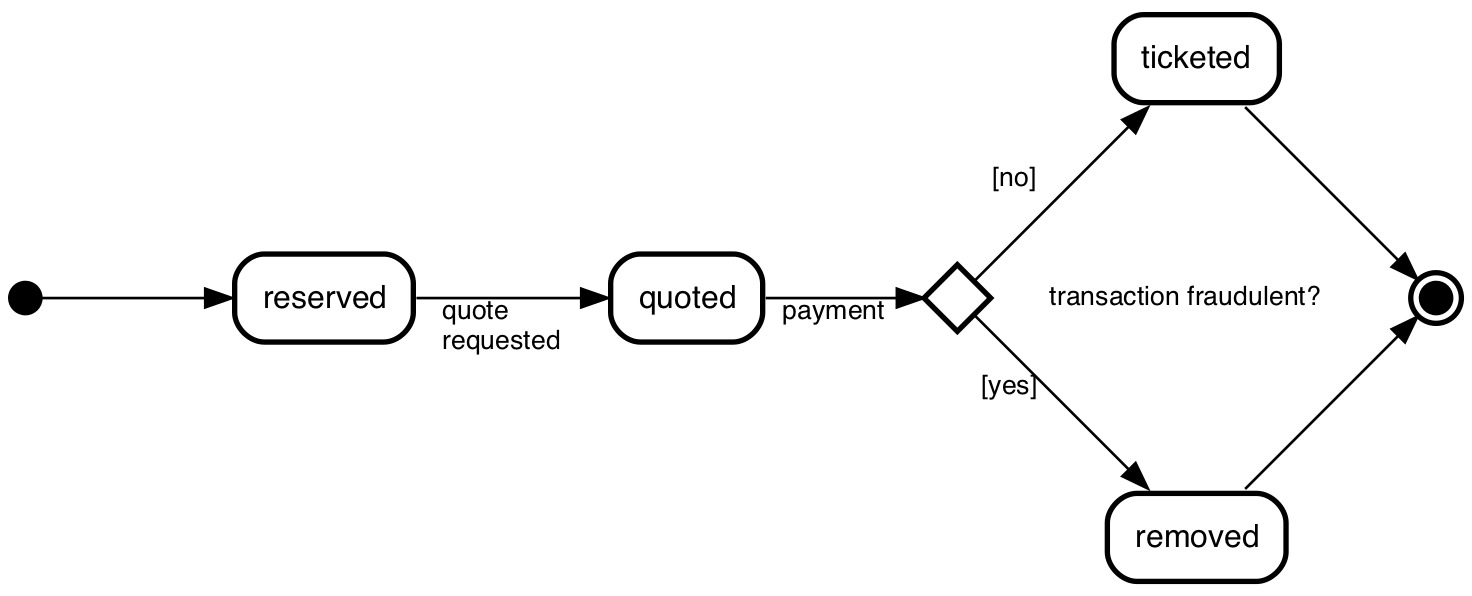
Forks, joins and junctions - ]
In UML you can fork state transitions into multiple or join them into one
with the fork (one to many) join (many to one) and junction (many to many)
pseudo states. Fork and join are represented by a black bar, junction
by a filled circle.
To make a join, fork or junction pseudo state, start its
name with a ].
Here's an example of a join:
a => ]join;
b => ]join;
]join => c;
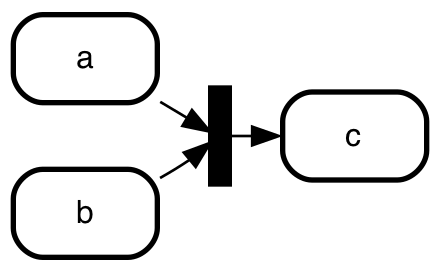
State machine cat automatically derives which of the three types
you meant by counting the number of incoming and the number of
outgoing connections:
- one incoming and multiple outgoing: it's a fork
- multiple incoming and one outgoing: it's a join
- all other cases: it's a junction
If you want to defy UML semantics you can do that with
explicit type overrides .
a => ]junction;
b => ]junction;
]junction => c;
]junction => d;
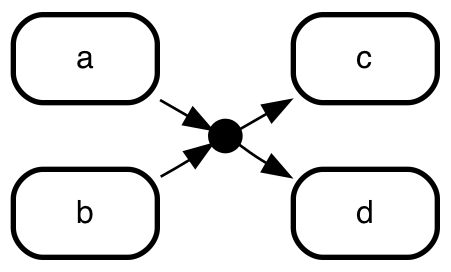
Terminate
UML has a special pseudo state to indicate your state machine didn't
exit properly: terminate. If you want to use it, declare it
explicitly:
Aahnohd [type=terminate label="Terminated"];
a => Aahnohd: [hit by meteorite];
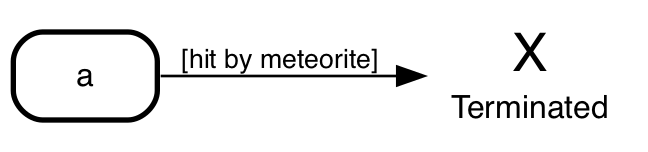
For proper exits you'd typically use the final state.
Gotchas
- when you need
;, ,, {, [ or spaces as part of a state - place em in quotes
"a state" - Activities have the same restriction, except they allow spaces.
- Labels have the same restriction as activities, except they allow for
, too. - State declaration precedence is: deep wins from shallow; explicit wins from
implicit
- It's possible to declare the same state multiple times on the same level, buts
smcat will take the last declaration into account only. For example:
This
# first declaration of "cool state"
"cool state",
"other state",
# second declaration of "cool state"
"cool state": cool down;
results in (/ is equivalent to):
# second declaration of "cool state"
"cool state": cool down,
"other state";
nested state machines
It's possible to have state machines within states.
the states stopped, playing and pause can only occur when
the tape player is on:
initial,
"tape player off",
"tape player on":
entry/ LED on
exit/ LED off
{
stopped, playing, paused;
stopped => playing : play;
playing => stopped : stop;
playing => paused : pause;
paused => playing : pause;
paused => stopped : stop;
};
initial => "tape player off";
"tape player off" => stopped : power;
"tape player on" => "tape player off" : power;
As you can see in this sample you can use activities (like entry and exit
triggers) in the composite state declaration, just as you'd do for state that
does not contain a state machine.
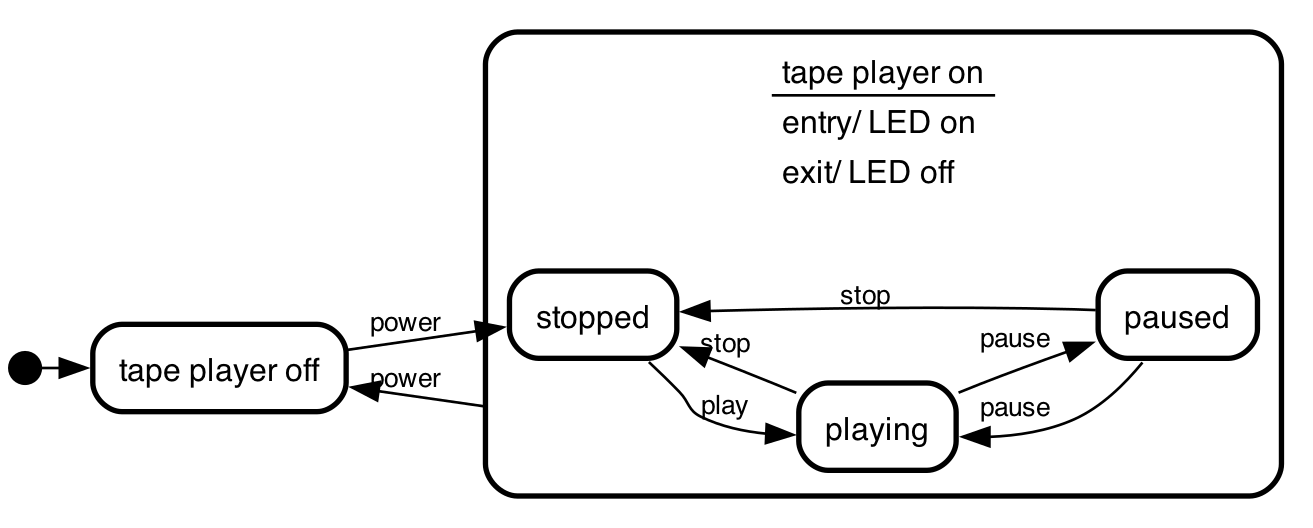
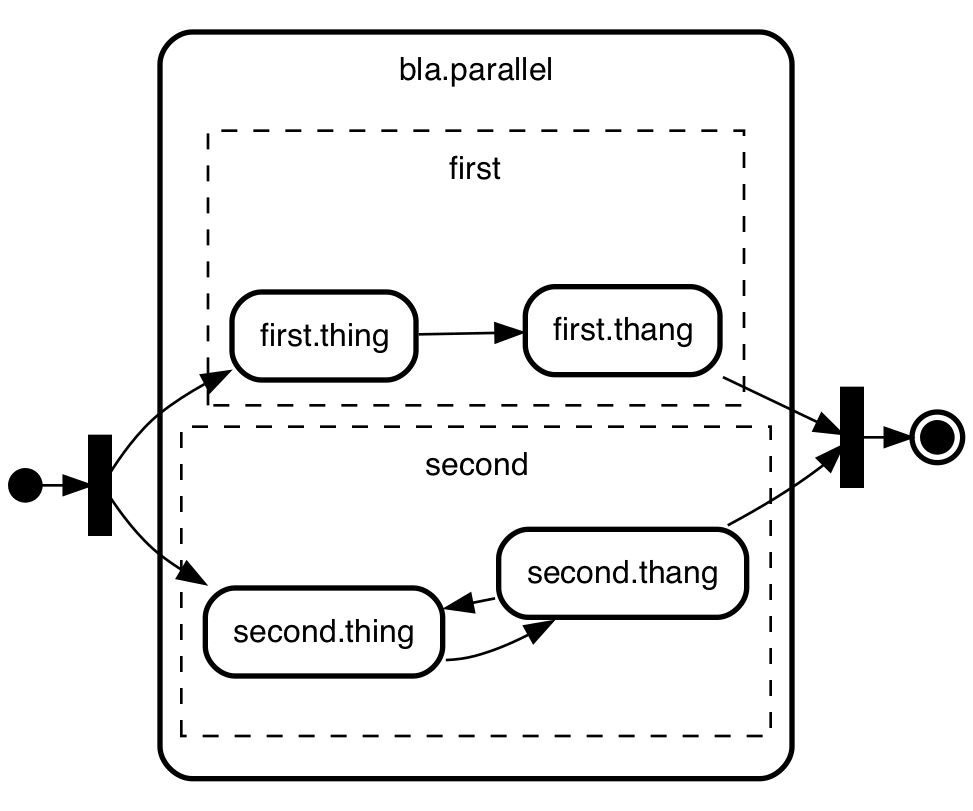
parallel states
If stuff is happening in parallel within a state you can express
that too. Just make sure the state has the word "parallel" in there:
initial,
bla.parallel {
first{
first.thing -> first.thang;
},
second{
second.thing -> second.thang;
second.thang -> second.thing;
};
},
final;
initial -> ]split;
]split -> first.thing;
]split -> second.thing;
first.thang -> ]merge;
second.thang -> ]merge;
]merge -> final;
internal and external transitions
If you need to mark a transition in a nested state machine as either internal
or external - use the type attribute. The default type for a transition
is external - just like it is in SCXML.
playing {
resting => walking;
walking => resting;
};
playing => playing: ingest food;
playing => playing [type=internal]: ingest drink;

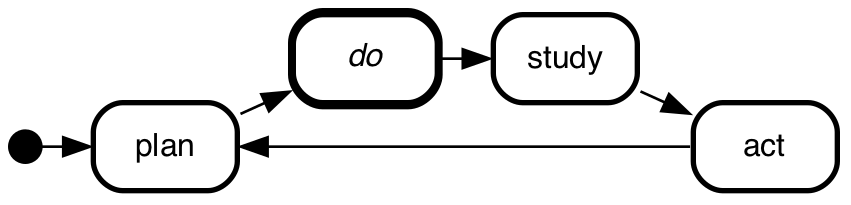
marking states active
You can mark one or more states as active by adding active as an
attribute for that state. E.g. to make the do state an active one
in the demming circle, do this:
do [active];
initial -> plan;
plan -> do;
do -> study;
study -> act;
act -> plan;
which will result in
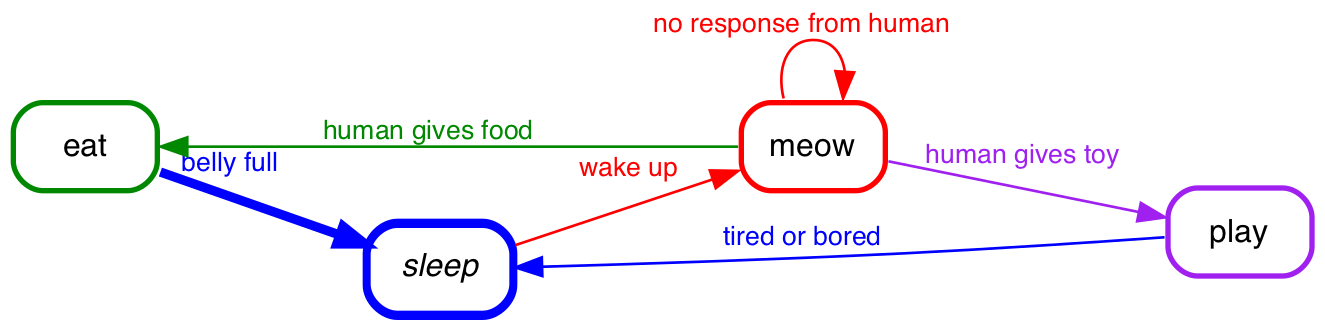
colors and line width
As of version 4.2.0 state-machine-cat has (experimental) support for colors on both
states and transitions and from version 8.1.0 for width on transitions.
For example, this ...
eat [color="#008800"],
sleep [color="blue" active],
meow [color="red"],
play [color="purple"];
sleep -> meow [color="red"] : wake up;
meow -> meow [color="red"] : no response from human;
meow -> eat [color="#008800"] : human gives food;
meow -> play [color="purple"] : human gives toy;
play -> sleep [color="blue"] : tired or bored;
eat -> sleep [color="blue" width=3.5] : belly full;
... would yield this diagram:
What does 'experimental' mean?
The color attribute is probably here to stay, as will the width
However, I haven't found the balance between ease of use
and expressiveness yet. Should the text in a state be rendered in the same color?
should the background color automatically be rendered as well? In the same color,
or in a shade smartly derived? Or should I include a bunch of color attributes
(e.g. fillcolor, textcolor, textbgcolor) for ultimate control?
classes
As of version 7.4.0 you can use the keyword class as an extended keyword on
both states and transitions. When you render svg or dot you'll see what you
entered there in the output in the class attributes of their respective
elements, along with the type of element (either 'state' or 'transition') and
optionally the type of state or transtion (e.g. for state: 'initial', 'regular',
'final' etc.).
For example, this ...
a [class="dismissed"],
b [class="y"];
a => b [class="a bunch of classes"];
... will yield this 'dot' program ...
digraph "state transitions" {
fontname="Helvetica" fontsize=12 penwidth=2.0 splines=true ordering=out compound=true overlap=scale nodesep=0.3 ranksep=0.1
node [shape=plaintext style=filled fillcolor="#FFFFFF01" fontname=Helvetica fontsize=12 penwidth=2.0]
edge [fontname=Helvetica fontsize=10]
"a" [margin=0 class="state regular dismissed" label= <
<table align="center" cellborder="0" border="2" style="rounded" width="48">
<tr><td width="48" cellpadding="7">a</td></tr>
</table>
>]
"b" [margin=0 class="state regular y" label= <
<table align="center" cellborder="0" border="2" style="rounded" width="48">
<tr><td width="48" cellpadding="7">b</td></tr>
</table>
>]
"a" -> "b" [label=" " class="transition a bunch of classes"]
}
Which will pass the class attributes on to the svg like so. E.g. the svg snippet
for the a state will look like this:
<g id="node1" class="node state regular dismissed">
<title>a</title>
<polygon fill="#ffffff" fill-opacity="0.003922" stroke="transparent" stroke-width="2" points="56,-100 0,-100 0,-64 56,-64 56,-100"></polygon>
<text text-anchor="start" x="24.6646" y="-78.2" font-family="Helvetica,sans-Serif" font-size="12.00" fill="#000000">a</text>
<path fill="none" stroke="#000000" stroke-width="2" d="M12.3333,-65C12.3333,-65 43.6667,-65 43.6667,-65 49.3333,-65 55,-70.6667 55,-76.3333 55,-76.3333 55,-87.6667 55,-87.6667 55,-93.3333 49.3333,-99 43.6667,-99 43.6667,-99 12.3333,-99 12.3333,-99 6.6667,-99 1,-93.3333 1,-87.6667 1,-87.6667 1,-76.3333 1,-76.3333 1,-70.6667 6.6667,-65 12.3333,-65"></path>
</g>
Gotchas
- You will have to provide the style sheet defining the classes yourself in the
context where you render the svg in order for them to actually show up
- The characters you can use for class names is limited to alpha-numerics, dashes,
underscores - and spaces to separate them. This to make it harder to use
state-machine-cat to construct svg's that are either invalid or malicious. The
limited character set is in contrast to what css allows, which is
everything under the sun and then some -
but it seems like a reasonable compromise.
overriding the type of a state
As you read above, state machine cat derives the type of a state from its name.
In some cases that might not be what you want. In those cases, you can
override the type with the type attribute, like in this example for the
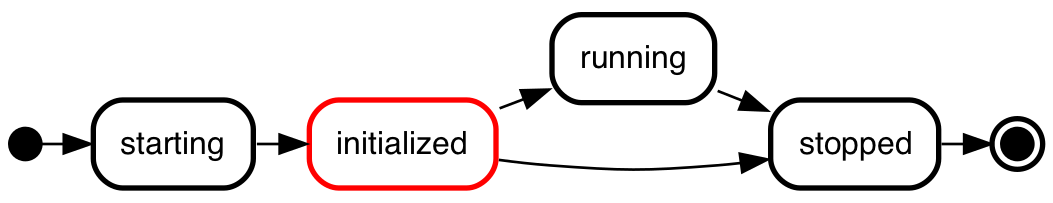
initialized state.
initial,
starting,
initialized [color="red" type=regular],
running,
final;
initial => starting;
starting => initialized;
initialized => running;
initialized => stopped;
running => stopped;
stopped => final;
The values you can use for the type of a state:
| type | example |
|---|
regular |  |
initial |  |
final |  |
history |  |
deephistory |  |
choice |  |
fork |  |
join |  |
forkjoin |  |
junction |  |
parallel |  |
terminate |  |
grammar
I made the parser with peggy - you can find it at
src/parse/peg/smcat-parser.peggy, and
railroad diagrams generated from these on state-machine-cat.js.org/grammar.html
Status
- Thoroughly tested and good enough for public use.
- Despite this you might bump into the occasional issue - don't hesitate to
report it on GitHub.
- Runs on latest versions of firefox, safari and chrome and node versions >= 18.17.0
Although it might run on other environments, it's not tested there. I will
reject issues on these other environments, unless they're accompanied with
sufficient enticement to make it worth my while.