 Theo
Theo


Theo is an abstraction for transforming and formatting Design Tokens.
Looking for the gulp plugin?
As of Theo v6, the gulp plugin is distributed as a separate package: gulp-theo.
Example
props:
button_background:
value: "{!primary_color}"
imports:
- ./aliases.yml
global:
type: color
category: buttons
aliases:
primary_color:
value: "#0070d2"
const theo = require('theo');
theo
.convert({
transform: {
type: 'web',
file: 'buttons.yml'
},
format: {
type: 'scss'
}
})
.then(scss => {
})
.catch(error => console.log(`Something went wrong: ${error}`));
Transforms
Theo is divided into two primary features: transforms and formats.
Transforms are a named group of value transforms. Theo ships with several predefined transforms.
| Name | Value Transforms |
|---|
raw | [] |
web | ['color/rgb'] |
ios | ['color/rgb', 'relative/pixelValue', 'percentage/float'] |
android | ['color/hex8argb', 'relative/pixelValue', 'percentage/float'] |
Value Transforms
Value transforms are used to conditionaly transform the value of a property. Below are the value transforms that ship with Theo along with the predicate that triggers them.
| Name | Predicate | Description |
|---|
color/rgb | prop.type === 'color' | Convert to rgb |
color/hex | prop.type === 'color' | Convert to hex |
color/hex8rgba | prop.type === 'color' | Convert to hex8rgba |
color/hex8argb | prop.type === 'color' | Convert to hex8argb |
percentage/float | /%/.test(prop.value) | Convert a percentage to a decimal percentage |
relative/pixel | isRelativeSpacing | Convert a r/em value to a pixel value |
relative/pixelValue | isRelativeSpacing | Convert a r/em value to a pixel value (excluding the px suffix) |
Custom Transforms / Value Transforms
theo.registerValueTransform(
"easing/web",
prop => prop.get("type") === "easing",
prop => {
const [x1, y1, x2, y2] = prop.get("value").toArray();
return `cubic-bezier(${x1}, ${y1}, ${x2}, ${y2})`;
}
);
theo.registerTransform("web", ["color/rgb", "easing/web"]);
Formats
Theo ships with the following predefined formats.
custom-properties.css
:root {
--prop-name: PROP_VALUE;
}
cssmodules.css
@value prop-name: PROP_VALUE;
scss
// If prop has 'comment' key, that value will go here.
$prop-name: PROP_VALUE;
sass
// If prop has 'comment' key, that value will go here.
$prop-name: PROP_VALUE
less
@prop-name: PROP_VALUE;
styl
// If prop has 'comment' key, that value will go here.
$prop-name = PROP_VALUE
map.scss
$file-name-map: (
// If prop has 'comment' key, that value will go here.
"prop-name": (PROP_VALUE),
);
map.variables.scss
$file-name-map: (
// If prop has 'comment' key, that value will go here.
"prop-name": ($prop-name)
);
list.scss
$file-name-list: (
// If prop has 'comment' key, that value will go here.
"prop-name"
);
module.js
export const propName = 'PROP_VALUE';
common.js
module.exports = {
propName: 'PROP_VALUE'
};
html
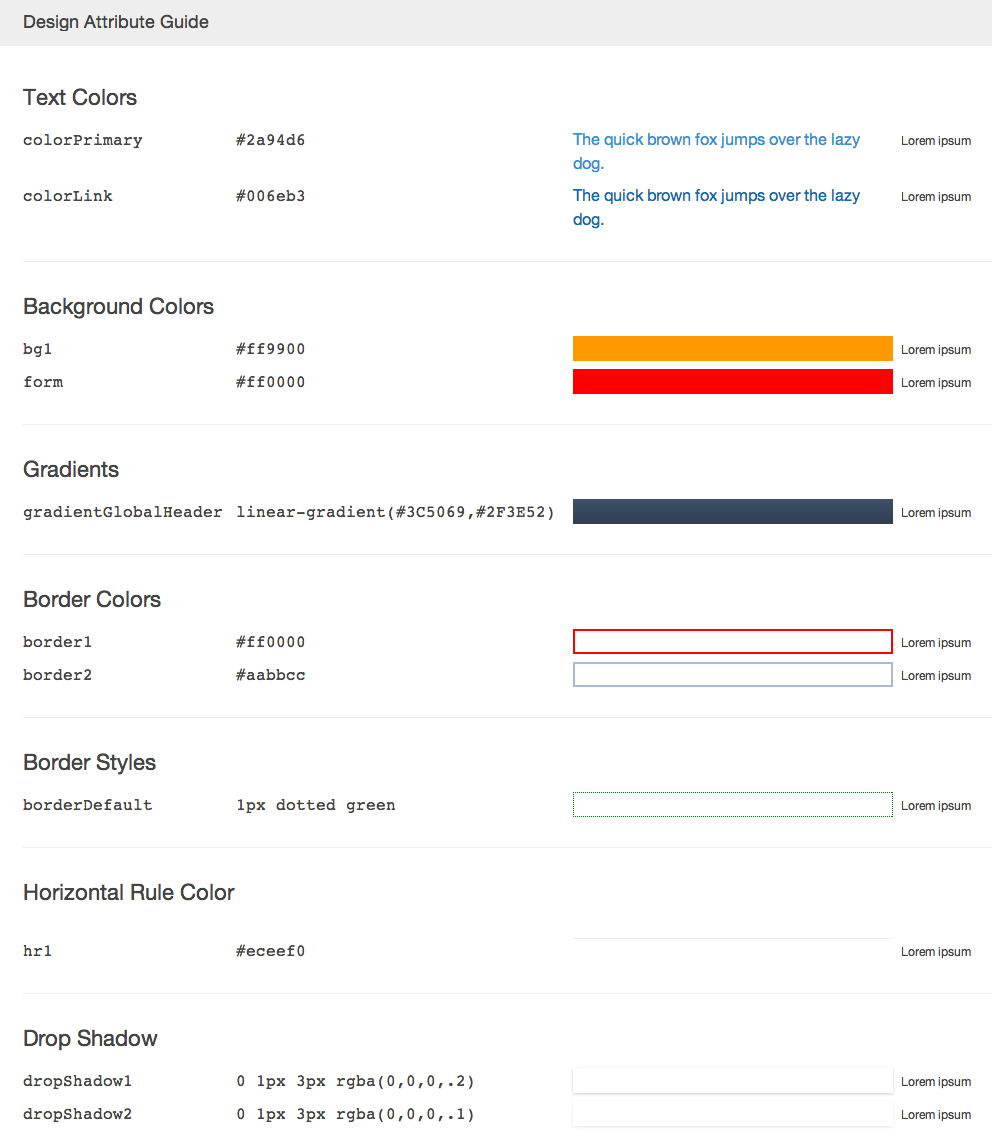
let formatOptions = {
type: 'html',
options: {
transformPropName: name => name.toUpperCase()
}
};
json
{
"PROP_NAME": "PROP_VALUE"
}
raw.json
{
"props": {
"PROP_NAME": {
"value": "PROP_VALUE",
"type": "PROP_TYPE",
"category": "PROP_CATEGORY"
}
}
}
ios.json
{
"properties": [
{
"name": "propName",
"value": "PROP_VALUE",
"type": "PROP_TYPE",
"category": "PROP_CATEGORY"
}
]
}
android.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<color name="PROP_NAME" category="PROP_CATEGORY">PROP_VALUE</color>
<dimen name="PROP_NAME" category="PROP_CATEGORY">PROP_VALUE</dimen>
<string name="PROP_NAME" category="PROP_CATEGORY">PROP_VALUE</string>
<integer name="PROP_NAME" category="PROP_CATEGORY">PROP_VALUE</integer>
<property name="PROP_NAME" category="PROP_CATEGORY">PROP_VALUE</property>
</resources>
aura.tokens
<aura:tokens>
<aura:token name="propName" value="PROP_VALUE" />
</aura:tokens>
Custom Format (Handlebars)
const theo = require('theo');
theo.registerFormat(
'array.js',
`
// Source: {{stem meta.file}}
module.exports = [
{{#each props as |prop|}}
{{#if prop.comment}}{{{commoncomment prop.comment}}}{{/if}}
['{{camelcase prop.name}}', '{{prop.value}}'],
{{/each}}
]
`
);
A plethora of handlebars helpers,
such as camelcase and stem, are available and will assist in formatting strings in templates.
Custom Format (function)
You may also register a format using a function:
const camelCase = require('lodash/camelCase');
const path = require('path');
const theo = require('theo');
theo.registerFormat('array.js', result => {
return `
module.exports = [
// Source: ${path.basename(result.getIn(['meta', 'file']))}
${result
.get('props')
.map(
prop => `
['${camelCase(prop.get('name'))}', '${prop.get('value')}'],
`
)
.toJS()}
]
`;
});
API
type ConvertOptions = {
transform: TransformOptions,
format: FormatOptions
}
type TransformOptions = {
type?: string,
file: string,
data?: string
}
type FormatOptions = {
type: string,
options?: object
}
type Prop = Immutable.Map
type Result = Immutable.Map
theo.convert(options: ConvertOptions): Promise<string>
theo.convertSync(options: ConvertOptions): string
theo.registerFormat(
name: string,
format: string | (result: Result) => string
): void
theo.registerValueTransform(
name: string,
predicate: (prop: Prop) => boolean,
transform: (prop: Prop) => any
): void
theo.registerTransform(
name: string,
valueTransforms: Array<string>
): void
CLI
Please refer to the documentation of the CLI
Design Tokens
Theo consumes Design Token files which are a central location to store
design related information such as colors, fonts, widths, animations, etc. These raw
values can then be transformed and formatted to meet the needs of any platform.
Let's say you have a web, native iOS, and native Android application that
would like to share information such as background colors.
The web might like to consume the colors as hsla values
formatted as Sass variables in an .scss file.
iOS might like rgba values formatted as .json.
Finally, Android might like 8 Digit Hex (AARRGGBB) values formatted as .xml.
Instead of hard coding this information in each platform/format, Theo
can consume the centralized Design Tokens and output files for
each platform.
Spec
A Design Token file is written in either
JSON (JSON5 supported)
or YAML and should conform to the following spec:
{
// Required
// A map of property names and value objects
"props": {
"color_brand": {
// Required
// Can be any valid JSON value
"value": "#ff0000",
// Required
// Describe the type of value
// [color|number|...]
"type": "color",
// Required
// Describe the category of this property
// Often used for style guide generation
"category": "background",
// Optional
// This value will be included during transform
// but excluded during formatting
"meta": {
// This value might be needed for some special transform
"foo": "bar"
}
}
},
// Optional
// Alternatively, you can define props as an array
// Useful for maintaining source order in output tokens
"props": [
{
// Required
"name": "color_brand",
// All other properties same as above
}
],
// Optional
// This object will be merged into each property
// Values defined on a property level will take precedence
"global": {
"category": "some-category",
"meta": {
"foo": "baz"
}
},
// Optional
// Share values across multiple props
// Aliases are resolved like: {!sky}
"aliases": {
"sky": "blue",
"grass": {
"value": "green",
"yourMetadata": "How grass looks"
}
},
// Optional
// Array of design token files to be imported
// "aliases" will be imported as well
// "aliases" will already be resolved
// "global" will already be merged into each prop
// Imports resolve according to the Node.js module resolution algorithm:
// https://nodejs.org/api/modules.html#modules_all_together
"imports": [
// Absolute file path
"/home/me/file.json",
// Relative file path: resolves from the directory of the file where the import occurs
"./some/dir/file.json",
// Module path
"some-node-module"
]
}

 Theo
Theo




