English | 简体中文

VueRequest
Status
Currently in RC version. For details, please see the changelog.
Why VueRequest
In the past projects, they were often confused by repeated implementations such as the management of the loading state, the requested throttling and debounce, the caching of request data, and pagination. Whenever we start a new project, we have to manually deal with the above problems, which will be a repetitive work, but also to ensure that the team is consistent.
VueRequest aims to provide developers with a convenient and fast way to manage the state of the request API. In the development, save repetitive work, and it can be used only with a simple configuration, focusing on the core of the development project.
Features
- 🌈 Support Vue 2 & 3
- 🚀 All data is reactive
- 🔄 Interval polling
- 🤖 Automatic error retry
- 🗄 Built-in cache
- 💧 Throttle and Debounce
- ⚙️ Powerful pagination extension and load more extensions
- 📠 Written in TypeScript
- ⚡️ Compatible with Vite
- 🍃 Lightweight
- 📦 Out of the box
Documentation
Install
You can install VueRequest with NPM, YARN, or a <script> via unpkg.com
NPM
npm install vue-request@next
yarn add vue-request@next
pnpm install vue-request@next
CDN
For production, we recommend linking to a specific version number and build to avoid unexpected breakage from newer versions.
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-request@next/dist/vue-request.min.js"></script>
Once you've added this you will have access to the window.VueRequest object and its exports.
Usage
<template>
<div>
<div v-if="loading">loading...</div>
<div v-if="error">failed to fetch</div>
<div v-if="data">Hey! {{ data }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const { data, loading, error } = useRequest(service);
return {
data,
loading,
error,
};
},
});
</script>
In this example, useRequest accepts a service function. service is a asynchronous function. In other words, you can use axios to fetch data and return a Promise. More specific instructions can be viewed in document.
useRequest also return 3 values: data, loading and error. When the request is not yet finished, data will be undefined and loading will be true. And when we get a response, it sets data and error based on the result of service and rerenders the component. This is because data and error are Reactivity(Refs), and their values will be set by the service response.
Some of the coolest features:
VueRequest has many features, such as error retry, cache, pagination, throttle, debounce..., here are two cool features
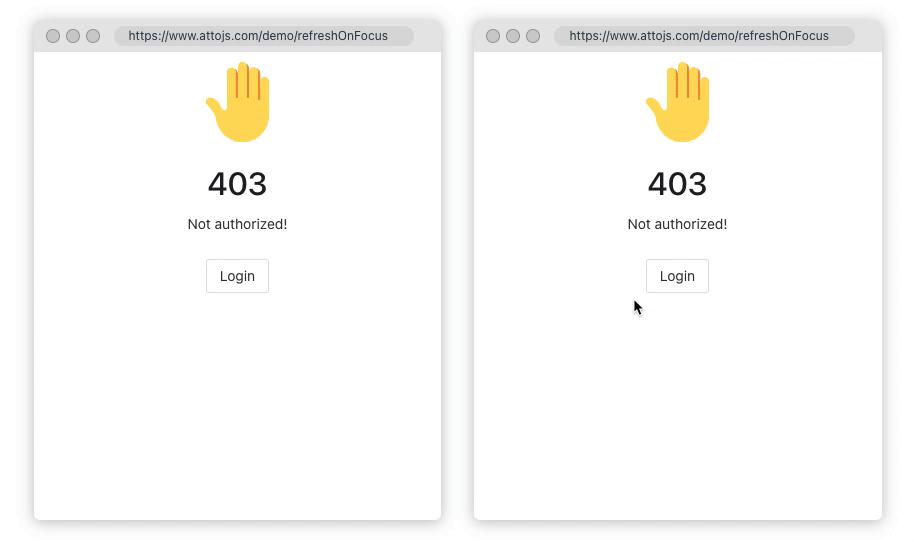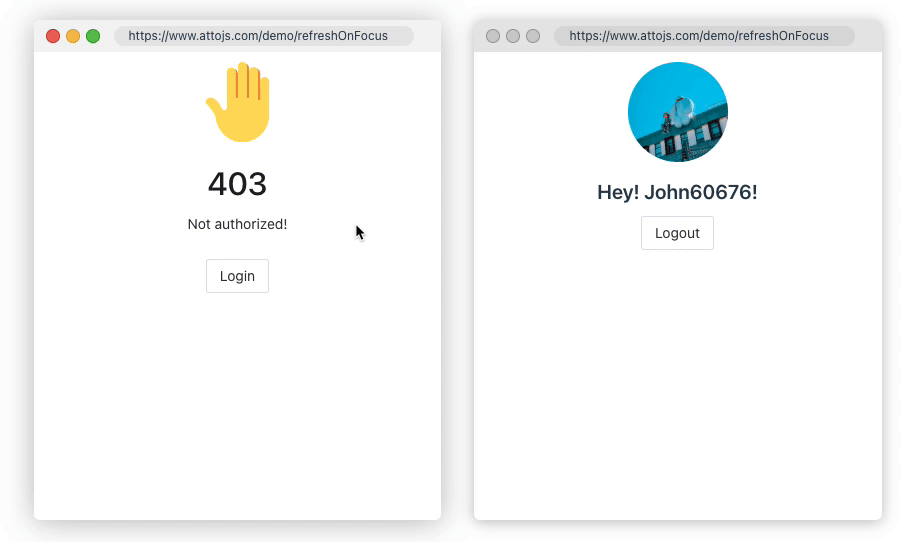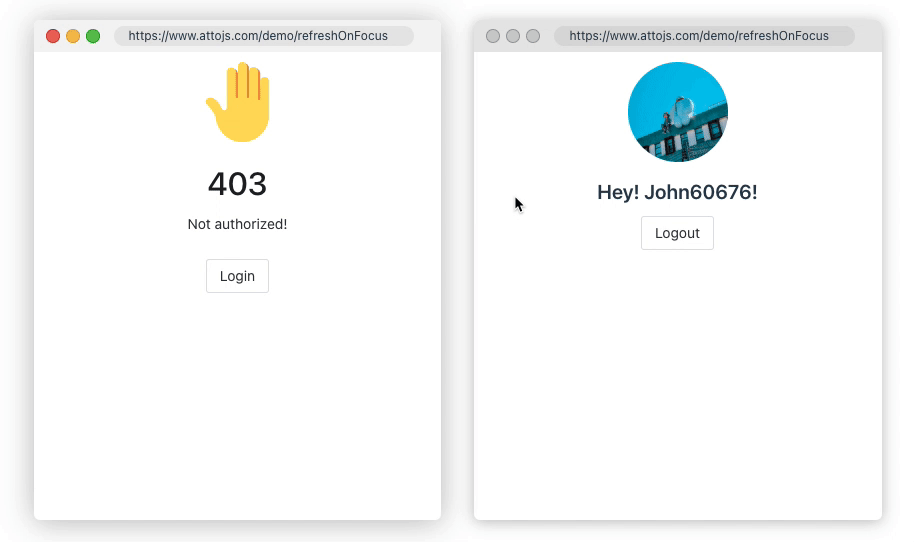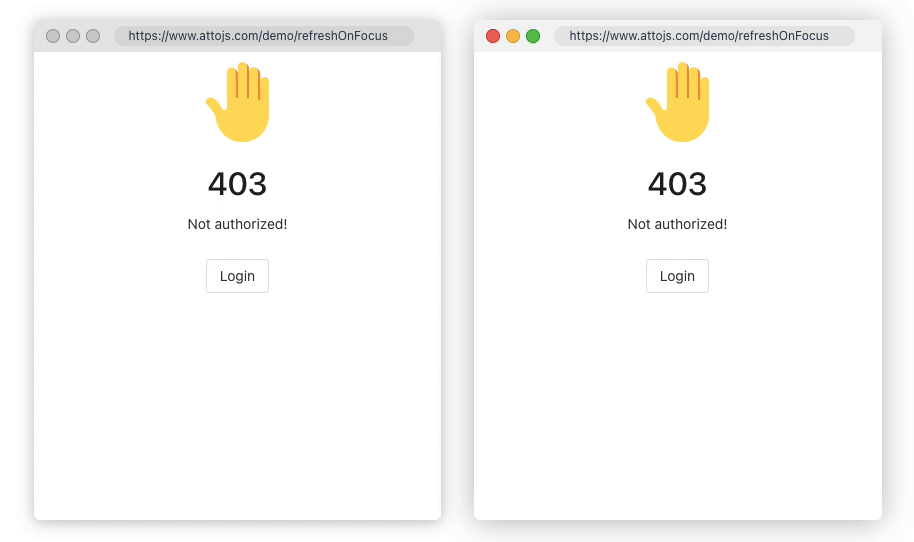
1.Refresh On Focus
Sometimes, you need to ensure data consistency between multiple browser windows; or when the user's computer is reactivated in the dormant state, the page data needs to be synchronized to the latest state. refreshOnWindowFocus may save you a lot of code. Click here to go to the document
const { data, error, run } = useRequest(getUserInfo, {
refreshOnWindowFocus: true,
refocusTimespan: 1000,
});
2.Polling Data
Sometimes, you want to ensure that data is synchronized and updated between multiple devices. At this time, we can use the pollingInterval provided by us to periodically re-request the request API, so that the data consistency between multiple devices can be guaranteed. When the user modifies the data, the two windows will be updated simultaneously in real time. Click here to go to the document
const { data, error, run } = useRequest(getUserInfo, {
pollingInterval: 1000,
});
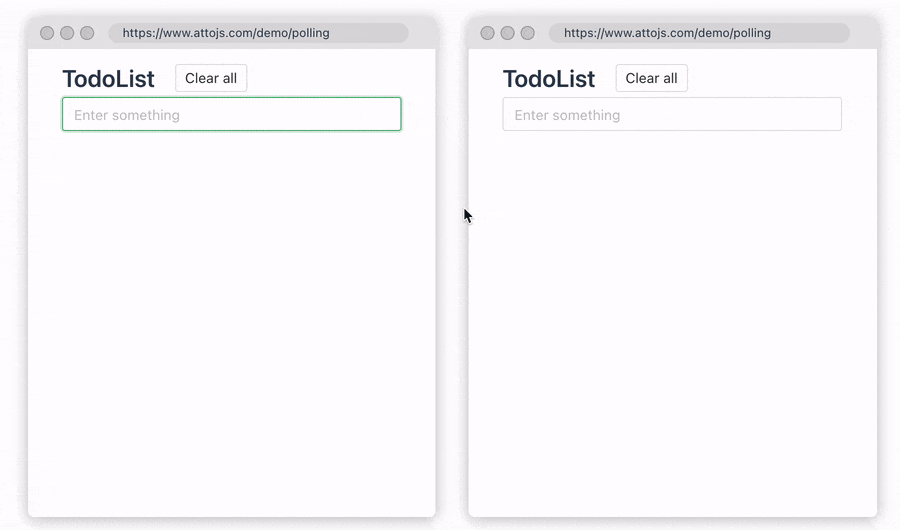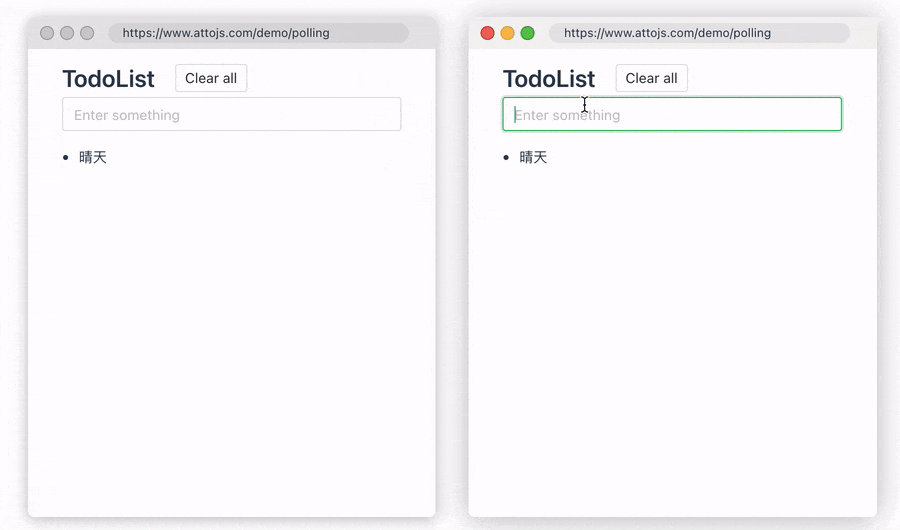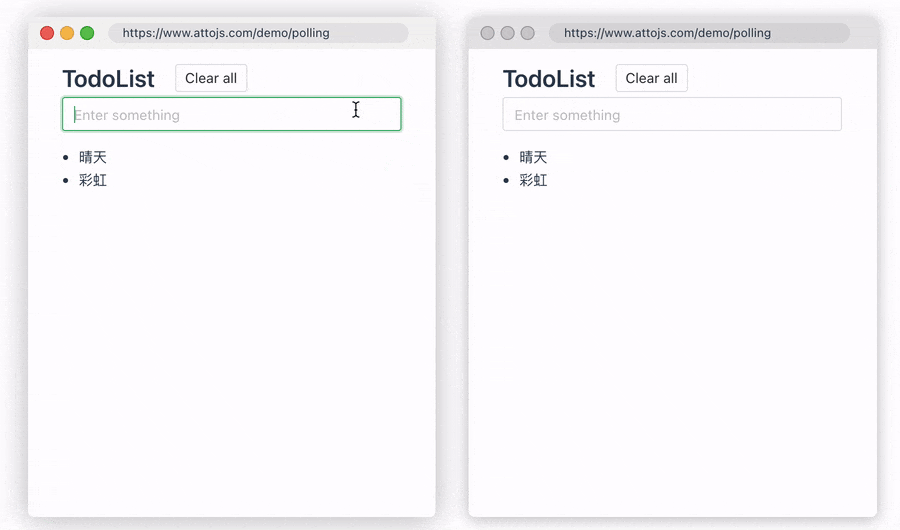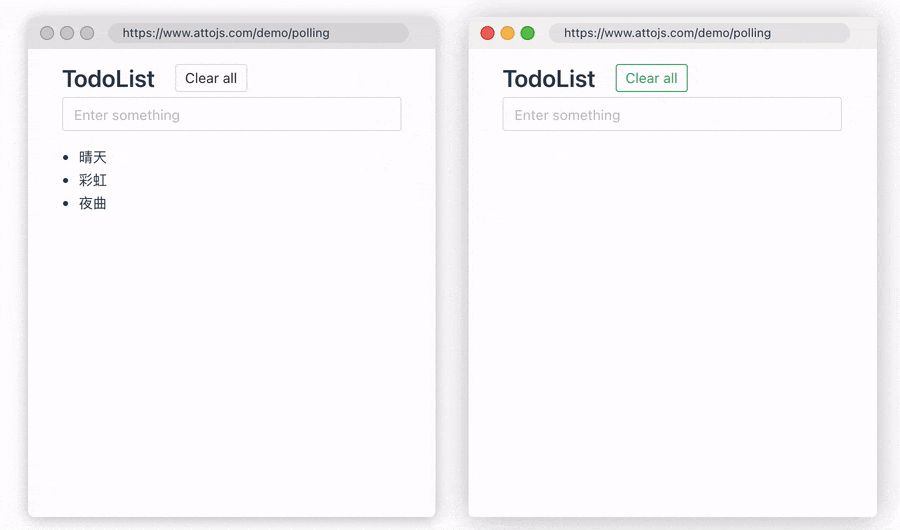
Thanks
Thank them for inspiring us.
License
MIT License © 2020-present AttoJS













