Product
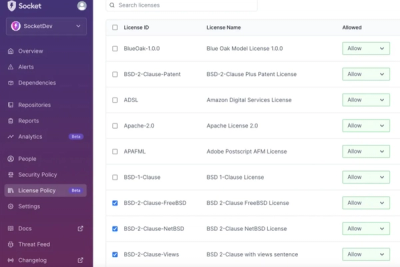
Introducing License Enforcement in Socket
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
Lightweight HTTP server mock used as a replacement for a production HTTP server in testing environments.
Mockallan is a lightweight HTTP server mock for CI and testing environments.
Command-line interface for CI and testing environments.
Configurable default and per-endpoint responses.
Assert expected requests performed by the system under test based on the endpoint and the request body.
Match the request body in assertions based on
Request history enables robust assertion capabilities.
Concise codebase focusing on simplicity.
API naming inspired by the Mock class from the Python unittest.mock standard library.
Mockallan is available on PyPI. Install it using pip.
pip install mockallan
mockallan.pypython mockallan.py
Listening on 0.0.0.0:8080
You can use curl to simulate a request performed by the system under test. For example, if we expect our system under test to perform a POST /orders/order_e2b9/products, run the following curl command.
curl -s -X POST http://localhost:8080/orders/order_e2b9/products --data '{
"product_id": "foo",
"description": "bar",
"amount": 1
}'
Mockallan will reply with the factory default response.
{
"status": "200",
"message": "This is mockallan factory default response."
}
curl -X GET "http://localhost:8080/assert-called?method=POST&path=/orders/order_e2b9/products"
If the assertion request returns 200 then everything went fine.
{
"status": 200,
"type": "assertion-success",
"title": "Assertion request GET /assert-called succeeded",
"detail": "POST /orders/order_e2b9/products called 1 times."
}
If it returns 409 then the assertion failed and the system under test did not behave as expected.
{
"status": 409,
"type": "assertion-error",
"title": "Assertion request GET /assert-called failed",
"detail": "Expected POST /orders/order_e2b9/products to be called 1 times. Called 0 times."
}
stub_config.json provided in this repository.E.g.
{
"endpoints": [
{
"request": {
"method": "POST",
"path": "/orders/order_e2b9/products"
},
"response": {
"status_code": 200,
"headers": {
"Content-type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"status": "200",
"message": "This is the configured response for POST /orders/order_e2b9/products"
}
}
}
]
}
mockallan.py and provide the JSON file.python mockallan.py -c stub_config.json
Run the system under test or simulate the request performed by it. The mock will reply with the configured response for POST /orders/order_e2b9/products.
Make assertions on the expected request.
curl -X GET "http://localhost:8080/assert-called?method=POST&path=/orders/order_e2b9/products"
If the assertion request returns 200 then everything went fine. If it returns 409 then the assertion failed and the system under test did not behave as expected.
/assert-called-with And /assert-called-once-withLet's explore additional validation options with the POST /assert-called-with and POST /assert-called-once-with endpoints. The body message provided in these requests corresponds to a
text/plain messageto match as shown in the following sections.
Add Content-Type: application/schema+json to the POST /assert-called-with or POST /assert-called-once-with request and place the JSON schema message in the body.
E.g.
curl -X POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json+schema' \
"http://localhost:8080/assert-called-with?method=POST&path=/orders/order_e2b9/products" \
--data '{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"orderNumber": {
"type": "string"
},
"products": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"productId": {
"type": "string"
},
"quantity": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1
}
},
"required": ["productId", "quantity"]
}
}
},
"required": ["orderNumber", "products"]
}'
Add Content-Type: application/xml to the POST /assert-called-with or POST /assert-called-once-with request and place the XML schema message in the body.
E.g.
curl -X POST --header 'Content-Type: application/xml' \
"http://localhost:8080/assert-called-with?method=POST&path=/orders/order_e2b9/products" \
--data '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="order">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="orderNumber" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="products" type="productListType"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="productListType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="product" type="productType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="productType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="productId" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="quantity" type="xs:integer"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>'
Add the custom header X-Mockallan-Validator: regex to the POST /assert-called-with or POST /assert-called-once-with request and place the regular expression in the body.
E.g.
curl -X POST --header 'X-Mockallan-Validator: regex' \
"http://localhost:8080/assert-called-with?method=POST&path=/orders/order_e2b9/products" \
--data '{"orderNumber":"\w+","products":\[\{"productId":"\w+","quantity":\d+}(,\{"productId":"\w+","quantity":\d+\})*\]}'
The Stub Configuration API allows the test client to configure the mock at runtime.
| Method | Path | Query Params | Request Body | Status | Response Body |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | /configure | - | JSON stub configuration | 204; 400 | - |
| GET | /configure | - | - | 200 | JSON stub configuration |
The Assertion API allows for the validation of expected requests.
| Method | Path | Query Params | Request Body | Status | Response Body |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /assert-called | method, path | - | 200 OK; 400; 409 | Assertion success or error message |
| GET | /assert-called-once | method, path | - | 200 OK; 400; 409 | Assertion success or error message |
| POST | /assert-called-with | method, path | JSON object, JSON schema, XML schema or regex | 200 OK; 400; 409 | Assertion success or error message |
| POST | /assert-called-once-with | method, path | JSON object, JSON schema, XML schema, regex or message body | 200 OK; 400; 409 | Assertion success or error message |
| GET | /request-body | - | - | 200 OK; 409 | The request body that the mock was last called with |
| GET | /request-body-list | - | - | 200 OK | List of all the requests made to the mock in sequence |
| GET | /request-count | - | - | 200 OK | Request count |
Stub Configuration API and Assertion API naming are inspired by class Mock from the standard python package unittest.mock.
Found a bug, facing some unexpected quirks, or got ideas for making this project better? Don't hesitate to raise an issue. Your help is appreciated.
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.
FAQs
Lightweight HTTP server mock used as a replacement for a production HTTP server in testing environments.
We found that mockallan demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
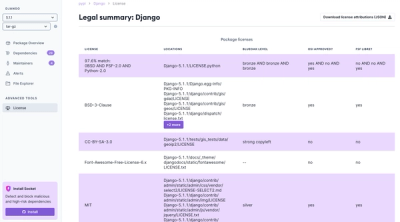
Product
We're launching a new set of license analysis and compliance features for analyzing, managing, and complying with licenses across a range of supported languages and ecosystems.
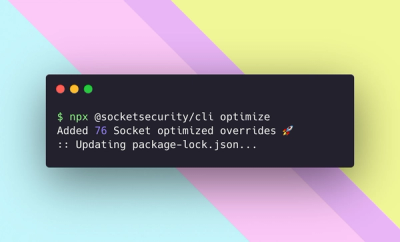
Product
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.