@appnest/lit-translate





🤔 What is this?
This is a lightweight blazing-fast internationalization (i18n) library for your next web-based project. Go here to see a demo https://appnest-demo.firebaseapp.com/lit-translate/.
Features
- Simple API that can return a translation for a given key using the dot notation (eg.
get("home.header.title")) - Works well with JSON based translation structures
- Can interpolate values into the translations
- Customizable (choose your own translations loader, how to interpolate values, empty placeholder etc)
- Caches the translations for maximum performance
- Contains a
lit-html directive that automatically updates when the language changes - Approximately 800 bytes minified & gzipped (2kb without)
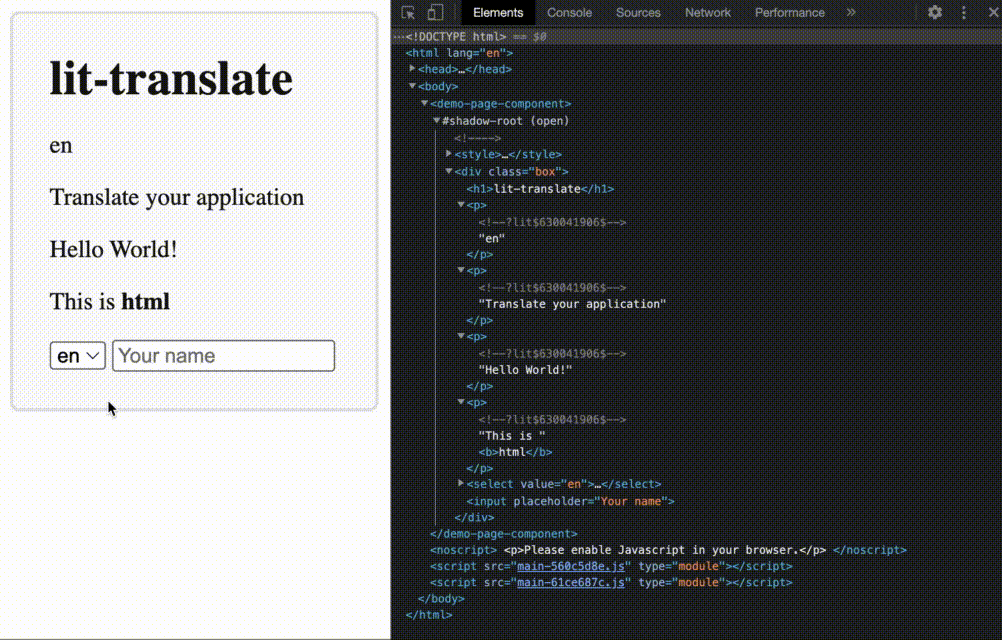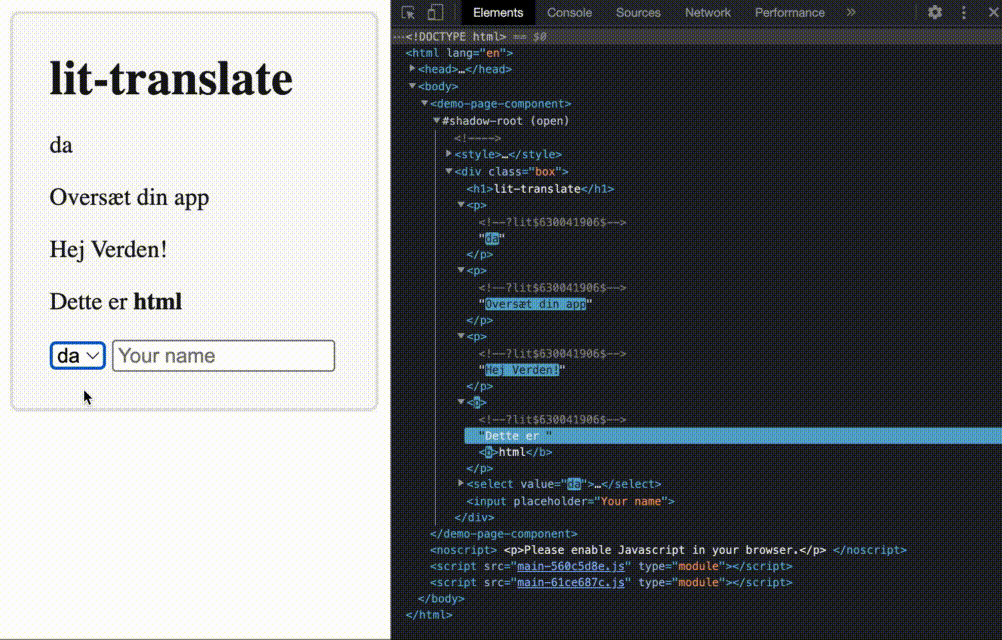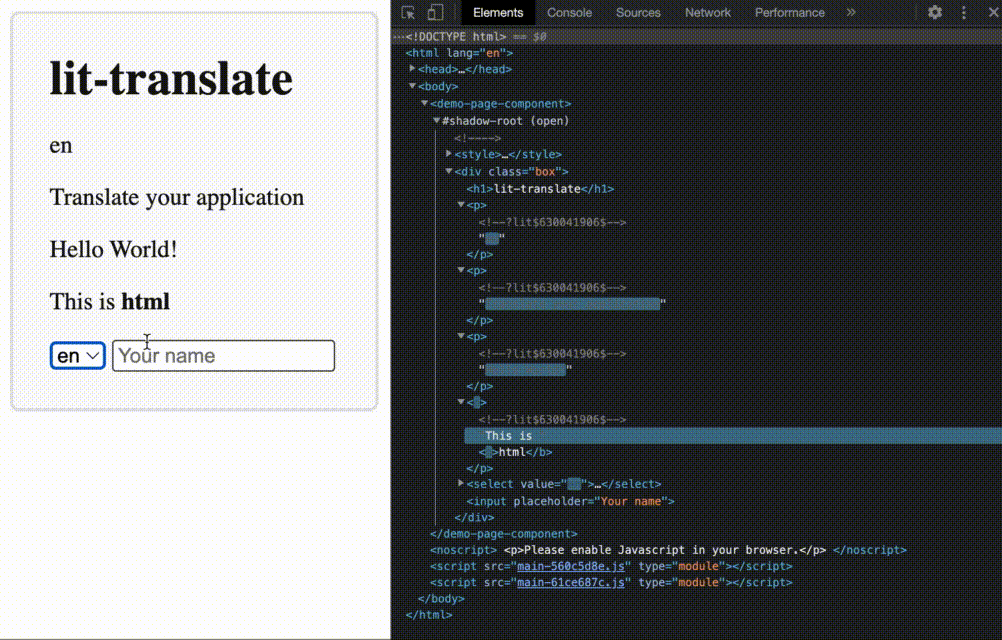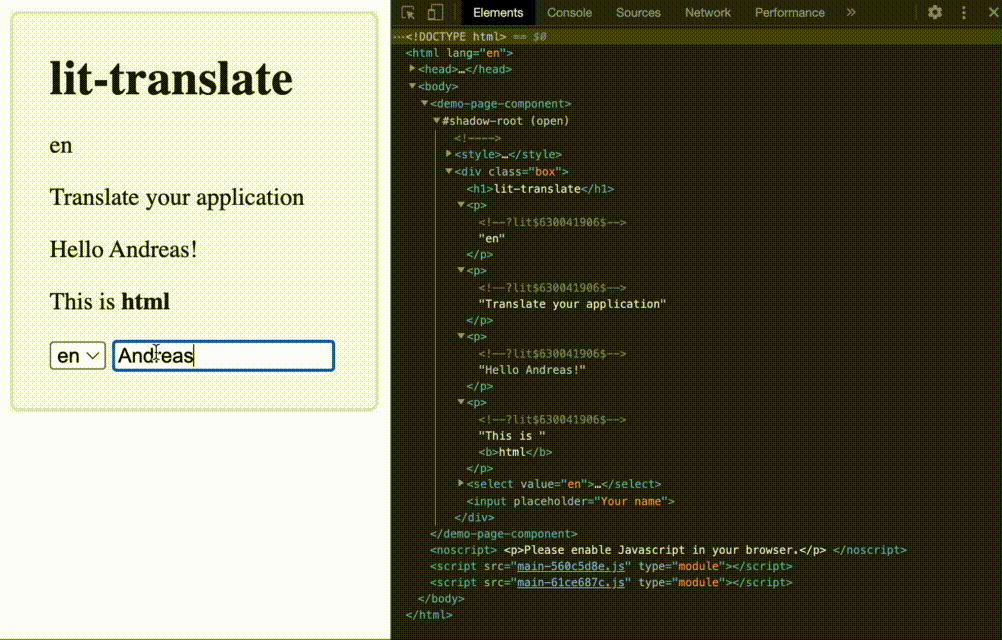
Table of Contents
Installation
npm i @appnest/lit-translate
1. Define the translations
To take advantage of the translation features you need to be able to provide your translations as a JSON structure. You are able to configure how the strings are loaded, but to make things simple we encourage you to maintain your translations in .json files - one for each language you support.
{
"lang": "en",
"header": {
"title": "Hello",
"subtitle": "World"
},
"cta": {
"awesome": "{{ things }} are awesome!",
"cats": "Cats"
}
}
2. Register the translate config
Use the registerTranslateConfig function to register a loader that loads and parses the translations based on a language identifier. In the example below, a loader is registered which loads a .json file with translations for a given language.
registerTranslateConfig({
loader: (lang: LanguageIdentifier) => fetch(`/assets/i18n/${lang}.json`).then(res => res.json())
});
It is possible to use the registerTranslateConfig function to customize almost everything from the library. To learn more you can see step 7.
3. Set the language
Invoke the use function to set a language. This function will use the registered loader from step 1 to load the translations for the language and dispatch a global langChanged event. To avoid fetching the translations again, the translations are stored in a cache for the next time the use function is called with the same parameters.
await use("en");
4. Get the translations
To get a translation use the get function. Give this function a string of keys (using the dot notation) that points to the desired translation in the JSON structure. The example below is based on the translations defined in step 1.
get("lang");
get("header.title");
get("header.subtitle");
5. Interpolate values
Using the get function it is possible to interpolate values. As default, you can simply use the {{ key }} syntax in your translations and provide an object with values replacing those defined in the translations when using the get function. The example below is based on the translations defined in step 1.
get("cta.awesome", { thing: get("cta.cats") ));
6. Use the translate directive together with lit-html
If you are using lit-html you might want to use the translate directive. This directive makes sure to automatically update all of the translated parts when the use function is called and the global langChanged event is dispatched. Note that values have to be returned from a callback due to how the parts are updated.
class MyComponent extends LitElement {
render () {
html`
<h1>${translate("header.title")}</h1>
<p>${translate("header.subtitle")}</p>
<span>${translate("cta.awesome", () => { return { things: get("cta.cats") }})}</span>
`;
}
}
Customize! (advanced)
If you want you can customize almost anything about how your translations are handled by overwriting the configuration hooks. Below is an example on what you might want to customize.
registerTranslateConfig({
loader: (lang: LanguageIdentifier) => fetch(`/assets/i18n/${lang}.json`).then(res => res.json()),
interpolate: (text: string, values: Values) => {
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(values)) {
text = text.replace(new RegExp(`\[\[${key}\]\]`), value);
}
return text;
},
fetchTranslation: (key: string, config: ITranslationConfig) => {
const parts = key.split(".");
let translation: string | object = config.translations || {};
while (parts.length > 0) {
translation = translation[parts.shift()];
if (translation == null) return config.emptyPlaceholder(key, config);
}
return translation.toString();
},
emptyPlaceholder: (key: string, config: ITranslationConfig) => `!${config.lang}.${key}!`
});
🎉 License
Licensed under MIT.









