
Security News
Create React App Officially Deprecated Amid React 19 Compatibility Issues
Create React App is officially deprecated due to React 19 issues and lack of maintenance—developers should switch to Vite or other modern alternatives.
@appnest/lit-translate
Advanced tools
A lightweight blazing-fast internationalization (i18n) library for your next web-based project
This is a lightweight blazing-fast internationalization (i18n) library for your next web-based project. Go here to see a demo https://appnest-demo.firebaseapp.com/lit-translate/.
Features
get("home.header.title"))lit-html directive that automatically updates when the language changes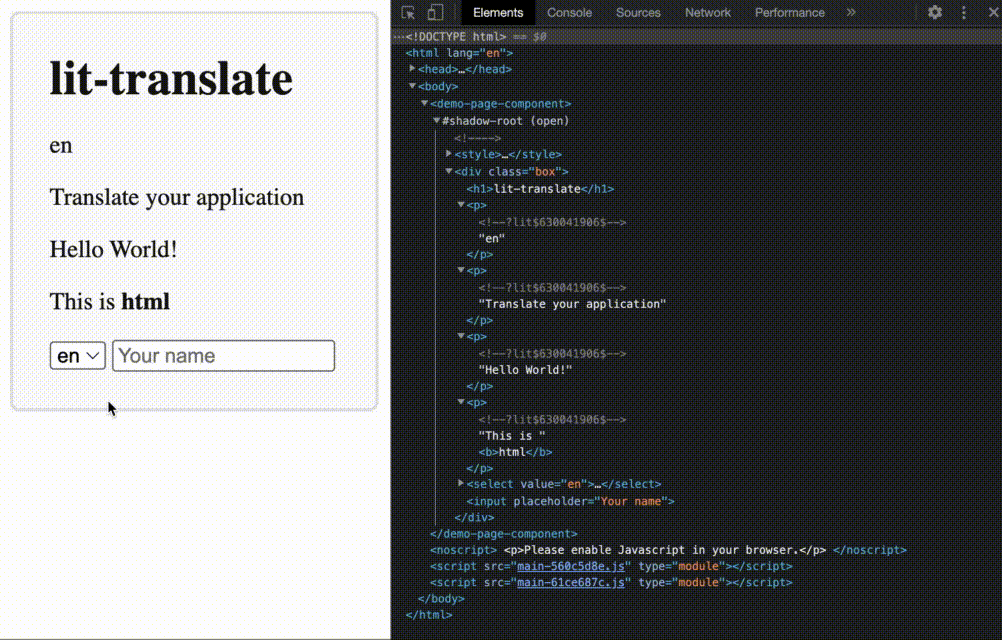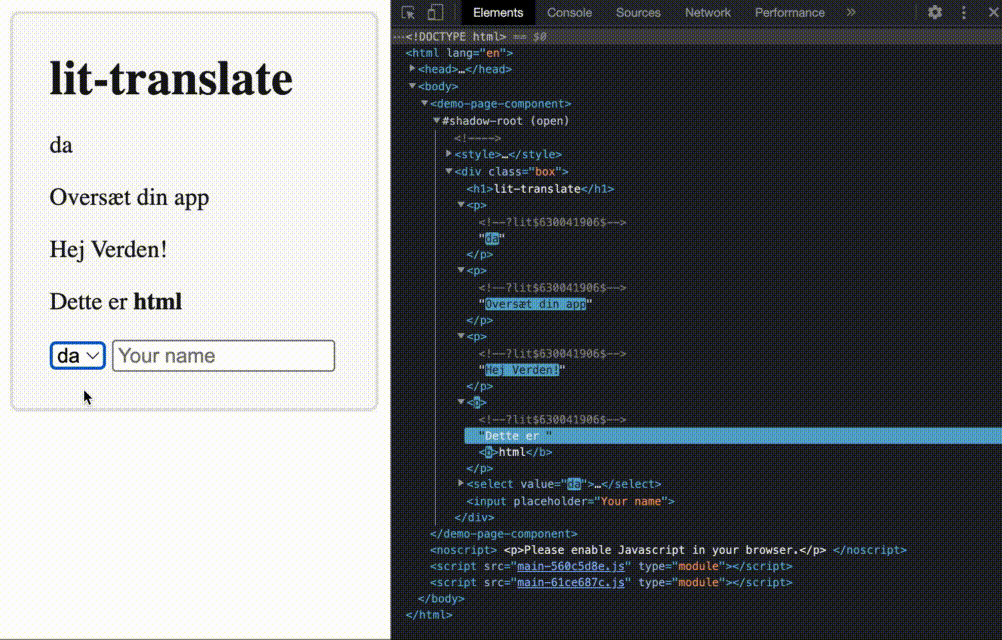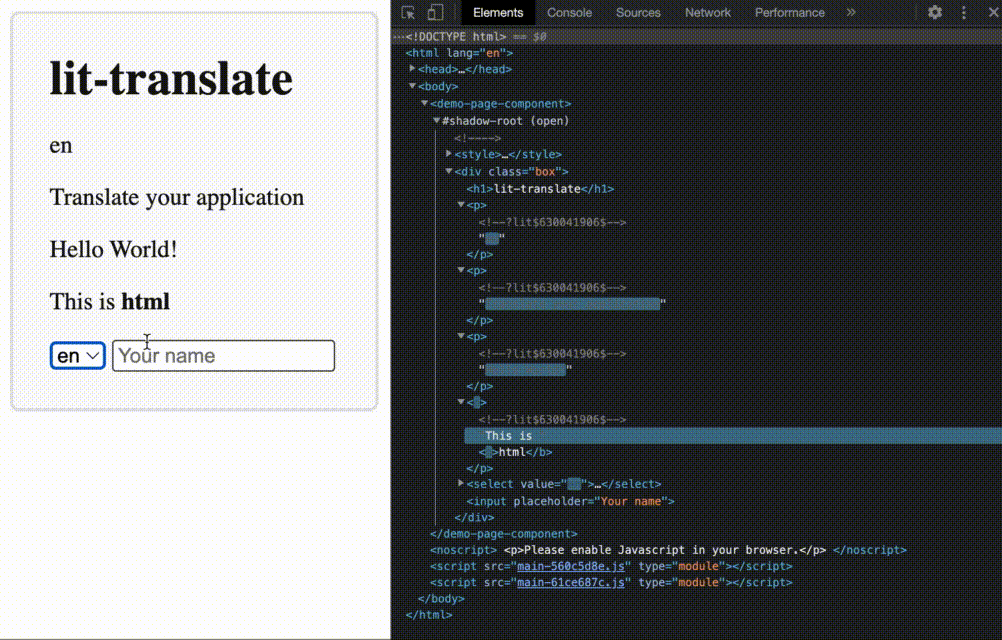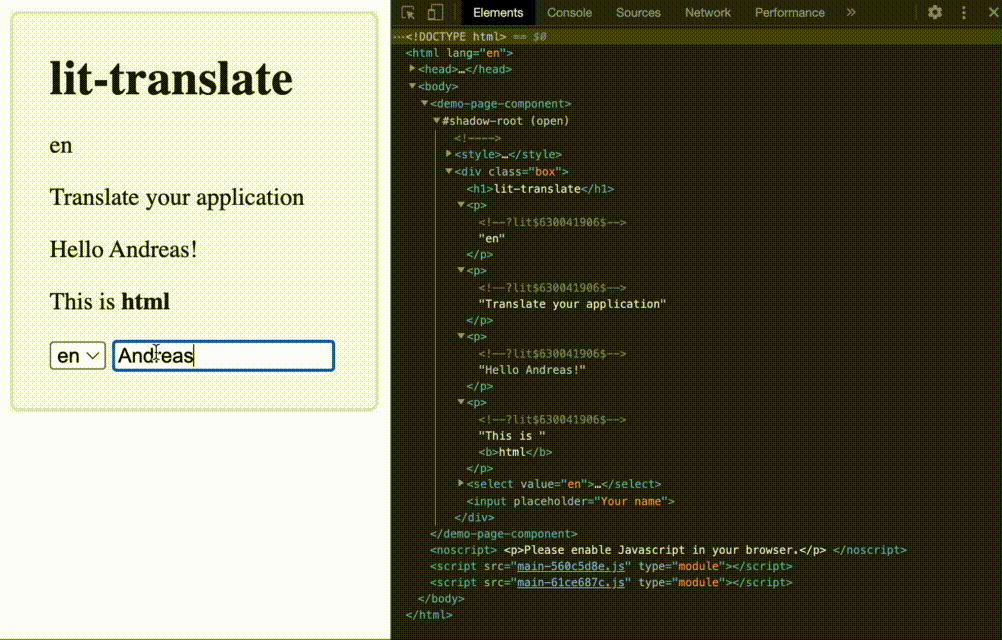
translate directive together with lit-htmlnpm i @appnest/lit-translate
To take advantage of the translation features you need to be able to provide your translations as a JSON structure. You are able to configure how the strings are loaded, but to make things simple we encourage you to maintain your translations in .json files - one for each language you support.
// en.json
{
"header": {
"title": "Hello",
"subtitle": "World"
},
"cta": {
"awesome": "{{ things }} are awesome!",
"cats": "Cats"
}
}
Use the registerTranslateConfig function to register a loader that loads and parses the translations based on a language identifier. In the example below, a loader is registered which loads a .json file with translations for a given language.
import { registerTranslateConfig } from "@appnest/lit-translate";
registerTranslateConfig({
loader: lang => fetch(`/assets/i18n/${lang}.json`).then(res => res.json())
});
It is possible to use the registerTranslateConfig function to customize almost everything from the library. To learn more you can see step 7.
Invoke the use function to set a language. This function will use the registered loader from step 1 to load the translations for the language and dispatch a global langChanged event. To avoid fetching the translations again, the translations are stored in a cache for the next time the use function is called with the same parameters.
import { use } from "@appnest/lit-translate";
use("en");
To get a translation use the get function. Give this function a string of keys (using the dot notation) that points to the desired translation in the JSON structure. The example below is based on the translations defined in step 1.
import { get } from "@appnest/lit-translate";
get("header.title"); // "Hello"
get("header.subtitle"); // "World"
Using the get function it is possible to interpolate values. As default, you can simply use the {{ key }} syntax in your translations and provide an object with values replacing those defined in the translations when using the get function. The example below is based on the translations defined in step 1.
import { get } from "@appnest/lit-translate";
get("cta.awesome", { thing: get("cta.cats") )); // Cats are awesome!
translate directive together with lit-htmlIf you are using lit-html you might want to use the translate directive. This directive makes sure to automatically update all of the translated parts when the use function is called and the global langChanged event is dispatched. Note that values have to be returned from callbacks to refresh the translated values.
import { translate } from "@appnest/lit-translate";
class MyComponent extends LitElement {
render () {
html`
<h1>${translate("header.title")}</h1>
<p>${translate("header.subtitle")}</p>
<span>${translate("cta.awesome", { things: () => get("cta.cats") })}</span>
`;
}
}
If you want you can customize almost anything about how your translations are handled by overwriting the configuration hooks. Below is an example on what you might want to customize.
import { registerTranslateConfig, extract, LanguageIdentifier, Values, Key, ITranslationConfig, ValuesCallback, Translations } from "@appnest/lit-translate";
registerTranslateConfig({
// Loads the language from the correct path
loader: (lang: LanguageIdentifier) => fetch(`/assets/i18n/${lang}.json`).then(res => res.json()),
// Interpolate the values using a [[key]] syntax.
interpolate: (text: string, values: Values | ValuesCallback) => {
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(extract(values))) {
text = text.replace(new RegExp(`\[\[${key}\]\]`), extract(value).toString());
}
return text;
},
// Returns a translation for a given key
getTranslation: (key: Key, config: ITranslationConfig) => {
// Split the key in parts (example: hello.world)
const parts = key.split(".");
// Find the translation by traversing through the strings matching the chain of keys
let translation: string | object = config.translations || {};
while (parts.length > 0) {
translation = (<Translations>translation)[parts.shift()!];
// Do not continue if the translation is not defined
if (translation == null) return config.emptyPlaceholder(key, config);
}
// Make sure the translation is a string!
return translation.toString();
},
// Formats empty placeholders (eg. [da.headline.title])
emptyPlaceholder: (key: Key, config: ITranslationConfig) => `!${config.lang}.${key}!`
});
Sometimes you want to avoid the placeholders being shown initially before any of the translation strings has been loaded. To avoid this issue you might want to defer the first update of the component. Here's an example of what you could do if using lit-element.
import { use, translate } from "@appnest/lit-translate";
@customElement("my-root-component")
export class MyRootComponent extends LitElement {
// Defer the first update of the component until the strings has been loaded to avoid empty strings being shown
private hasLoadedStrings = false;
protected shouldUpdate() {
return this.hasLoadedStrings;
}
// Load the initial language and mark that the strings has been loaded.
async connectedCallback () {
await use("en");
this.hasLoadedStrings = true;
super.connectedCallback();
}
protected render (): TemplateResult {
return html`
<p>${translate("title")}</p>
`;
}
}
Licensed under MIT.
FAQs
A lightweight blazing-fast internationalization (i18n) library for your next web-based project
The npm package @appnest/lit-translate receives a total of 0 weekly downloads. As such, @appnest/lit-translate popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that @appnest/lit-translate demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Create React App is officially deprecated due to React 19 issues and lack of maintenance—developers should switch to Vite or other modern alternatives.

Security News
Oracle seeks to dismiss fraud claims in the JavaScript trademark dispute, delaying the case and avoiding questions about its right to the name.

Security News
The Linux Foundation is warning open source developers that compliance with global sanctions is mandatory, highlighting legal risks and restrictions on contributions.