
Security News
Oracle Drags Its Feet in the JavaScript Trademark Dispute
Oracle seeks to dismiss fraud claims in the JavaScript trademark dispute, delaying the case and avoiding questions about its right to the name.
@descope/angular-sdk
Advanced tools
The Descope SDK for Angular provides convenient access to the Descope for an application written on top of Angular. You can read more on the [Descope Website](https://descope.com).
The Descope SDK for Angular provides convenient access to the Descope for an application written on top of Angular. You can read more on the Descope Website.
Project ID is required for using the SDK. Find it on the project page in the Descope Console.Install the package with:
npm i --save @descope/angular-sdk
Add Descope type definitions to your tsconfig.ts
"compilerOptions": {
"typeRoots": ["./node_modules/@descope"],
<other options>
}
DescopeAuthModule to your applicationapp.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { DescopeAuthModule } from '@descope/angular-sdk';
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
DescopeAuthModule.forRoot({
projectId: '<your_project_id>'
})
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule {}
main.ts
import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app/app.component';
import { DescopeAuthConfig } from '@descope/angular-sdk';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent, {
providers: [
{ provide: DescopeAuthConfig, useValue: { projectId: '<your_project_id>' } }
]
}).catch((err) => console.error(err));
You can use default flows or provide flow id directly to the descope component
app.component.html
<descope-sign-in-flow
(success)="onSuccess()"
(error)="onError()"
></descope-sign-in-flow>
app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html'
})
export class AppComponent {
onSuccess() {
console.log('SUCCESSFULLY LOGGED IN FROM WEB COMPONENT');
}
onError() {
console.log('ERROR FROM LOG IN FLOW FROM WEB COMPONENT');
}
}
<descope
flowId="<your_flow_id>"
(success)="<your_success_function>"
(error)="<your_error_function>"
<!-- theme can be "light", "dark" or "os", which auto select a theme based on the OS theme. Default is "light"
theme="dark"
locale can be any supported locale which the flow's screen translated to, if not provided, the locale is taken from the browser's locale.
locale="en"
debug can be set to true to enable debug mode
debug="true"
tenant ID for SSO (SAML) login. If not provided, Descope will use the domain of available email to choose the tenant
tenant=<tenantId>
Redirect URL for OAuth and SSO (will be used when redirecting back from the OAuth provider / IdP), or for "Magic Link" and "Enchanted Link" (will be used as a link in the message sent to the the user)
redirectUrl=<redirectUrl>
telemetryKey=<telemtry_key>
autoFocus can be true, false or "skipFirstScreen". Default is true.
- true: automatically focus on the first input of each screen
- false: do not automatically focus on screen's inputs
- "skipFirstScreen": automatically focus on the first input of each screen, except first screen
autoFocus="skipFirstScreen"
errorTransformer is a function that receives an error object and returns a string. The returned string will be displayed to the user.
NOTE: errorTransformer is not required. If not provided, the error object will be displayed as is.
Example:
errorTransformer = (error: { text: string; type: string }): string => {
const translationMap: { [key: string]: string } = {
SAMLStartFailed: 'Failed to start SAML flow'
};
return translationMap[error.type] || error.text;
};
...
errorTransformer={errorTransformer}
logger is an object describing how to log info, warn and errors.
NOTE: logger is not required. If not provided, the logs will be printed to the console.
Example:
const logger = {
info: (title: string, description: string, state: any) => {
console.log(title, description, JSON.stringify(state));
},
warn: (title: string, description: string) => {
console.warn(title);
},
error: (title: string, description: string) => {
console.error('OH NOO');
},
}
...
logger={logger}-->
></descope>
All components in the sdk are standalone, so you can use them by directly importing them to your components.
DescopeAuthService and its exposed fields (descopeSdk, session$, user$) to access authentication state, user details and utilitiesThis can be helpful to implement application-specific logic. Examples:
app.component.html
<p *ngIf="!isAuthenticated"> You are not logged in</p>
<button *ngIf="isAuthenticated" (click)="logout()">LOGOUT</button>
<p>User: {{userName}}</p>
app.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { DescopeAuthService } from '@descope/angular-sdk';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.scss']
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
isAuthenticated: boolean = false;
userName: string = '';
constructor(private authService: DescopeAuthService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.authService.session$.subscribe((session) => {
this.isAuthenticated = session.isAuthenticated;
});
this.authService.user$.subscribe((descopeUser) => {
if (descopeUser.user) {
this.userName = descopeUser.user.name ?? '';
}
});
}
logout() {
this.authService.descopeSdk.logout();
}
}
DescopeAuthService provides refreshSession and refreshUser methods that triggers a single request to the Descope backend to attempt to refresh the session or user. You can use them whenever you want to refresh the session/user. For example you can use APP_INITIALIZER provider to attempt to refresh session and user on each page refresh:
app.module.ts
import { APP_INITIALIZER, NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { DescopeAuthModule, DescopeAuthService } from '@descope/angular-sdk';
import { zip } from 'rxjs';
export function initializeApp(authService: DescopeAuthService) {
return () => zip([authService.refreshSession(), authService.refreshUser()]);
}
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
DescopeAuthModule.forRoot({
projectId: '<your_project_id>'
})
],
providers: [
{
provide: APP_INITIALIZER,
useFactory: initializeApp,
deps: [DescopeAuthService],
multi: true
}
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule {}
You can use the same approach with APP_INITIALIZER in standalone mode, by adding it to providers array of the application.
You can also use DescopeInterceptor to attempt to refresh session on each HTTP request that gets 401 or 403 response:
app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import {
HttpClientModule,
provideHttpClient,
withInterceptors
} from '@angular/common/http';
import { DescopeAuthModule, descopeInterceptor } from '@descope/angular-sdk';
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
HttpClientModule,
DescopeAuthModule.forRoot({
projectId: '<your_project_id>',
pathsToIntercept: ['/protectedPath']
})
],
providers: [provideHttpClient(withInterceptors([descopeInterceptor]))],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule {}
DescopeInterceptor:
pathsToIntercept. If not provided it will be used for all requests.Authorization header in Bearer <token> format401 or 403 it automatically attempts to refresh sessionFor more SDK usage examples refer to docs
When developing a full-stack application, it is common to have private server API which requires a valid session token:
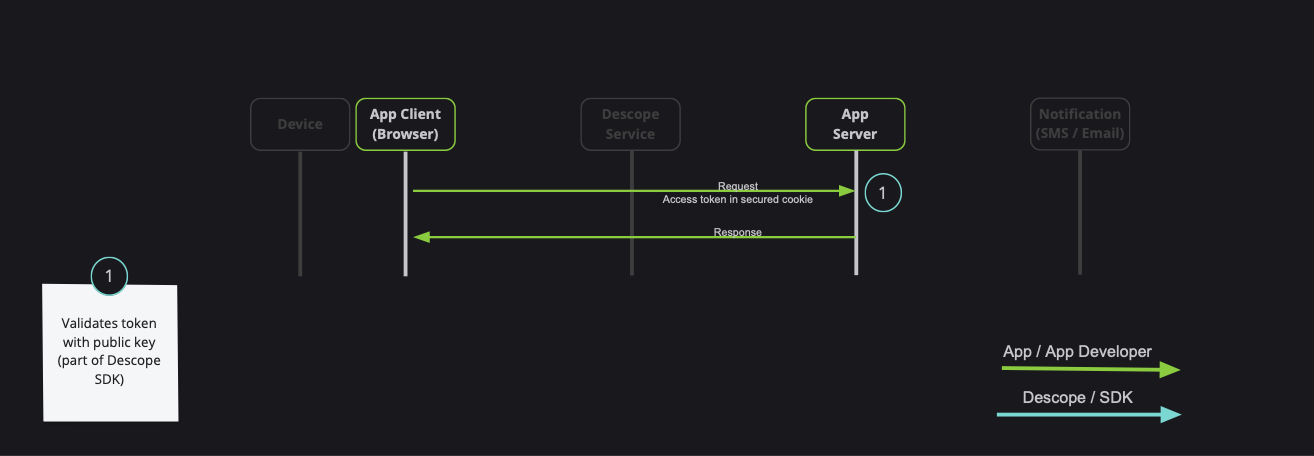
Note: Descope also provides server-side SDKs in various languages (NodeJS, Go, Python, etc). Descope's server SDKs have out-of-the-box session validation API that supports the options described bellow. To read more about session validation, Read this section in Descope documentation.
You can securely communicate with your backend either by using DescopeInterceptor or manually adding token to your requests (ie. by using DescopeAuthService.getSessionToken() helper function)
You can also use the following helper methods on DescopeAuthService to assist with various actions managing your JWT.
getSessionToken() - Get current session token.getRefreshToken() - Get current refresh token.isAuthenticated() - Returns boolean whether user is authenticatedrefreshSession - Force a refresh on current session token using an existing valid refresh token.refreshUser - Force a refresh on current user using an existing valid refresh token.getJwtRoles(token = getSessionToken(), tenant = '') - Get current roles from an existing session token. Provide tenant id for specific tenant roles.getJwtPermissions(token = getSessionToken(), tenant = '') - Fet current permissions from an existing session token. Provide tenant id for specific tenant permissions.Descope SDK is automatically refreshes the session token when it is about to expire. This is done in the background using the refresh token, without any additional configuration.
If the Descope project settings are configured to manage tokens in cookies.
you must also configure a custom domain, and set it as the baseUrl in DescopeAuthModule.
angular-sdk provides a convenient route guard that prevents from accessing given route for users that are not authenticated:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
import { ProtectedComponent } from './protected/protected.component';
import { descopeAuthGuard } from '@descope/angular-sdk';
import { LoginComponent } from './login/login.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'step-up',
component: ProtectedComponent,
canActivate: [descopeAuthGuard],
data: { descopeFallbackUrl: '/' }
},
{ path: 'login', component: LoginComponent },
{ path: '**', component: HomeComponent }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes, { enableTracing: false })],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule {}
If not authenticated user tries to access protected route they will be redirected to descopeFallbackUrl
You can find an example angular app in the examples folder.
To run the examples, create environment.development.ts file in environments folder.
import { Env } from './conifg';
export const environment: Env = {
descopeProjectId: '<your_project_id>'
};
Find your Project ID in the Descope console.
Run the following command in the root of the project to build and run the example:
npm i && npm start
See the following table for customization environment variables for the example app:
| Env Variable | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| descopeFlowId | Which flow ID to use in the login page | sign-up-or-in |
| descopeBaseUrl | Custom Descope base URL | None |
| descopeTheme | Flow theme | None |
| descopeLocale | Flow locale | Browser's locale |
| descopeRedirectUrl | Flow redirect URL for OAuth/SSO/Magic Link/Enchanted Link | None |
| descopeTenantId | Flow tenant ID for SSO/SAML | None |
| descopeDebugMode | "true" - Enable debugger "false" - Disable flow debugger | None |
| descopeStepUpFlowId | Step up flow ID to show to logged in user (via button). e.g. "step-up". Button will be hidden if not provided | None |
| descopeTelemetryKey | String - Telemetry public key provided by Descope Inc | None |
| descopeBackendUrl | Url to your test backend app in case you want to test e2e | None |
Example environment.development.ts file:
import { Env } from './conifg';
export const environment: Env = {
descopeProjectId: '<your_project_id>',
descopeBaseUrl: '<your_base_url>',
descopeFlowId: 'sign-in',
descopeDebugMode: false,
descopeTheme: 'os',
descopeLocale: 'en_US',
descopeRedirectUrl: '<your_redirect_url>',
descopeTelemetryKey: '<your_telemetry_key>',
descopeStepUpFlowId: 'step-up',
descopeBackendUrl: 'http://localhost:8080/protected'
};
If you encounter warning during build of your application:
▲ [WARNING] Module 'lodash.get' used by 'node_modules/@descope/web-component/node_modules/@descope/core-js-sdk/dist/index.esm.js' is not ESM
add lodash.get to allowed CommonJS dependencies in angular.json
"architect": {
"build": {
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:browser",
"options": {
"allowedCommonJsDependencies": ["lodash.get"],
<other_options>
}
<other_config>
}
<other_config>
}
To learn more please see the Descope Documentation and API reference page.
If you need help you can email Descope Support
The Descope SDK for Angular is licensed for use under the terms and conditions of the MIT license Agreement.
FAQs
The Descope SDK for Angular provides convenient access to the Descope for an application written on top of Angular. You can read more on the [Descope Website](https://descope.com).
The npm package @descope/angular-sdk receives a total of 188 weekly downloads. As such, @descope/angular-sdk popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that @descope/angular-sdk demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 4 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Oracle seeks to dismiss fraud claims in the JavaScript trademark dispute, delaying the case and avoiding questions about its right to the name.

Security News
The Linux Foundation is warning open source developers that compliance with global sanctions is mandatory, highlighting legal risks and restrictions on contributions.

Security News
Maven Central now validates Sigstore signatures, making it easier for developers to verify the provenance of Java packages.