What is @ffmpeg/ffmpeg?
@ffmpeg/ffmpeg is a JavaScript package that provides a WebAssembly (Wasm) version of FFmpeg, allowing developers to perform video and audio processing directly in the browser or in Node.js environments. It enables functionalities such as video conversion, audio extraction, and media editing without needing to rely on server-side processing.
What are @ffmpeg/ffmpeg's main functionalities?
Video Conversion
This feature allows you to convert video files from one format to another. The code sample demonstrates converting an MP4 file to an AVI file using FFmpeg commands.
const { createFFmpeg, fetchFile } = require('@ffmpeg/ffmpeg');
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({ log: true });
(async () => {
await ffmpeg.load();
ffmpeg.FS('writeFile', 'input.mp4', await fetchFile('path/to/input.mp4'));
await ffmpeg.run('-i', 'input.mp4', 'output.avi');
const data = ffmpeg.FS('readFile', 'output.avi');
// Do something with the output file
})();
Audio Extraction
This feature allows you to extract audio from a video file. The code sample shows how to extract audio from an MP4 file and save it as an MP3 file.
const { createFFmpeg, fetchFile } = require('@ffmpeg/ffmpeg');
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({ log: true });
(async () => {
await ffmpeg.load();
ffmpeg.FS('writeFile', 'input.mp4', await fetchFile('path/to/input.mp4'));
await ffmpeg.run('-i', 'input.mp4', '-q:a', '0', '-map', 'a', 'output.mp3');
const data = ffmpeg.FS('readFile', 'output.mp3');
// Do something with the output audio file
})();
Video Editing
This feature allows you to perform video editing tasks such as resizing. The code sample demonstrates resizing a video to 320x240 pixels.
const { createFFmpeg, fetchFile } = require('@ffmpeg/ffmpeg');
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({ log: true });
(async () => {
await ffmpeg.load();
ffmpeg.FS('writeFile', 'input.mp4', await fetchFile('path/to/input.mp4'));
await ffmpeg.run('-i', 'input.mp4', '-vf', 'scale=320:240', 'output.mp4');
const data = ffmpeg.FS('readFile', 'output.mp4');
// Do something with the edited video file
})();
Other packages similar to @ffmpeg/ffmpeg
fluent-ffmpeg
fluent-ffmpeg is a Node.js library that provides a fluent API for FFmpeg. It is used for handling video and audio processing tasks. Unlike @ffmpeg/ffmpeg, which runs FFmpeg in a WebAssembly environment, fluent-ffmpeg requires FFmpeg to be installed on the server. It is more suitable for server-side applications where FFmpeg is available.
ffmpeg-static
ffmpeg-static is a package that provides static binaries for FFmpeg. It allows developers to use FFmpeg without needing to install it separately. This package is useful for server-side applications where you want to bundle FFmpeg with your application. Unlike @ffmpeg/ffmpeg, it does not run in a browser environment.
node-ffmpeg
node-ffmpeg is a simple Node.js module to convert video files using FFmpeg. It provides a straightforward API for video conversion and processing. Similar to fluent-ffmpeg, it requires FFmpeg to be installed on the server and is not designed for browser environments like @ffmpeg/ffmpeg.

ffmpeg.wasm









ffmpeg.wasm is a pure Webassembly / Javascript port of FFmpeg. It enables video & audio record, convert and stream right inside browsers.
AVI to MP4 Demo

Try it: https://ffmpegwasm.netlify.app
Installation
Node
$ npm install @ffmpeg/ffmpeg @ffmpeg/core
As we are using experimental features, you need to add flags to run in Node.js
$ node --experimental-wasm-threads transcode.js
Browser
Or, using a script tag in the browser (only works in some browsers, see list below):
SharedArrayBuffer is only available to pages that are cross-origin isolated. So you need to host your own server with Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy: require-corp and Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy: same-origin headers to use ffmpeg.wasm.
<script src="static/js/ffmpeg.min.js"></script>
<script>
const { createFFmpeg } = FFmpeg;
...
</script>
Only browsers with SharedArrayBuffer support can use ffmpeg.wasm, you can check HERE for the complete list.
Usage
ffmpeg.wasm provides simple to use APIs, to transcode a video you only need few lines of code:
const fs = require('fs');
const { createFFmpeg, fetchFile } = require('@ffmpeg/ffmpeg');
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({ log: true });
(async () => {
await ffmpeg.load();
ffmpeg.FS('writeFile', 'test.avi', await fetchFile('./test.avi'));
await ffmpeg.run('-i', 'test.avi', 'test.mp4');
await fs.promises.writeFile('./test.mp4', ffmpeg.FS('readFile', 'test.mp4'));
process.exit(0);
})();
Use other version of ffmpeg.wasm-core / @ffmpeg/core
For each version of ffmpeg.wasm, there is a default version of @ffmpeg/core (you can find it in devDependencies section of package.json), but sometimes you may need to use newer version of @ffmpeg/core to use the latest/experimental features.
Node
Just install the specific version you need:
$ npm install @ffmpeg/core@latest
Or use your own version with customized path
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({
corePath: '../../../src/ffmpeg-core.js',
});
Browser
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({
corePath: 'static/js/ffmpeg-core.js',
});
For the list available versions and their changelog, please check: https://github.com/ffmpegwasm/ffmpeg.wasm-core/releases
Use single thread version
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({
mainName: 'main',
corePath: 'https://unpkg.com/@ffmpeg/core-st@0.11.1/dist/ffmpeg-core.js',
});
Multi-threading
Multi-threading need to be configured per external libraries, only following libraries supports it now:
x264
Run it multi-threading mode by default, no need to pass any arguments.
libvpx / webm
Need to pass -row-mt 1, but can only use one thread to help, can speed up around 30%
Documentation
FAQ
What is the license of ffmpeg.wasm?
There are two components inside ffmpeg.wasm:
@ffmpeg/core contains WebAssembly code which is transpiled from original FFmpeg C code with minor modifications, but overall it still following the same licenses as FFmpeg and its external libraries (as each external libraries might have its own license).
@ffmpeg/ffmpeg contains kind of a wrapper to handle the complexity of loading core and calling low-level APIs. It is a small code base and under MIT license.
Can I use ffmpeg.wasm in Firefox?
Yes, but only for Firefox 79+ with proper header in both client and server, visit https://ffmpegwasm.netlify.app to try whether your Firefox works.
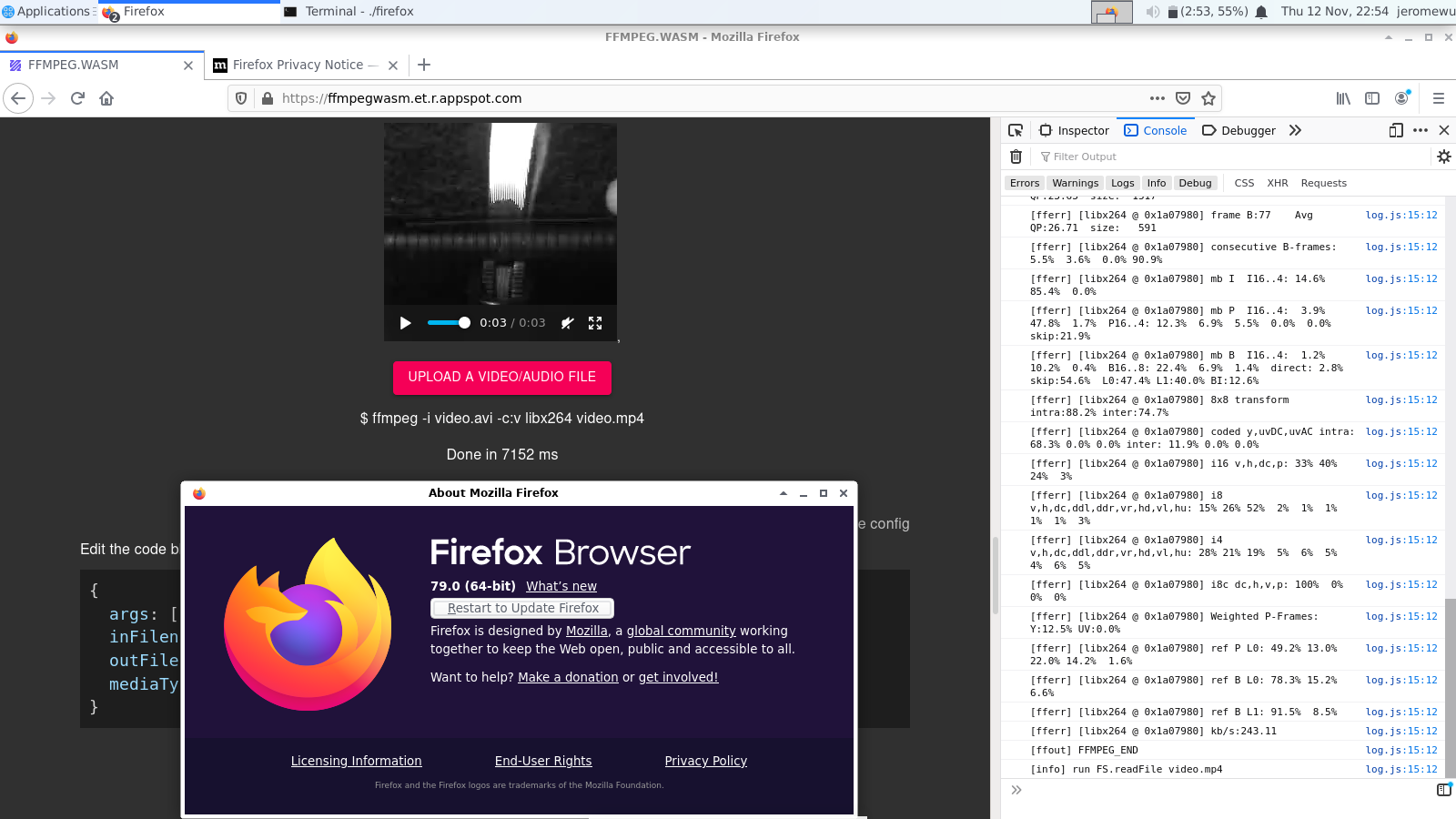
For more details: https://github.com/ffmpegwasm/ffmpeg.wasm/issues/106
What is the maximum size of input file?
2 GB, which is a hard limit in WebAssembly. Might become 4 GB in the future.
How can I build my own ffmpeg.wasm?
In fact, it is ffmpeg.wasm-core most people would like to build.
To build on your own, you can check build.sh inside https://github.com/ffmpegwasm/ffmpeg.wasm-core repository.
Also you can check this series of posts to learn more fundamental concepts:
Why it doesn't work in my local environment?
When calling ffmpeg.load(), by default it looks for http://localhost:3000/node_modules/@ffmpeg/core/dist/ to download essential files (ffmpeg-core.js, ffmpeg-core.wasm, ffmpeg-core.worker.js). It is necessary to make sure you have those files served there.
If you have those files serving in other location, you can rewrite the default behavior when calling createFFmpeg():
const { createFFmpeg } = FFmpeg;
const ffmpeg = createFFmpeg({
corePath: "http://localhost:3000/public/ffmpeg-core.js",
log: true,
});











