
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
@nodebug/blink-diff
Advanced tools
A lightweight image comparison tool
Table of Contents
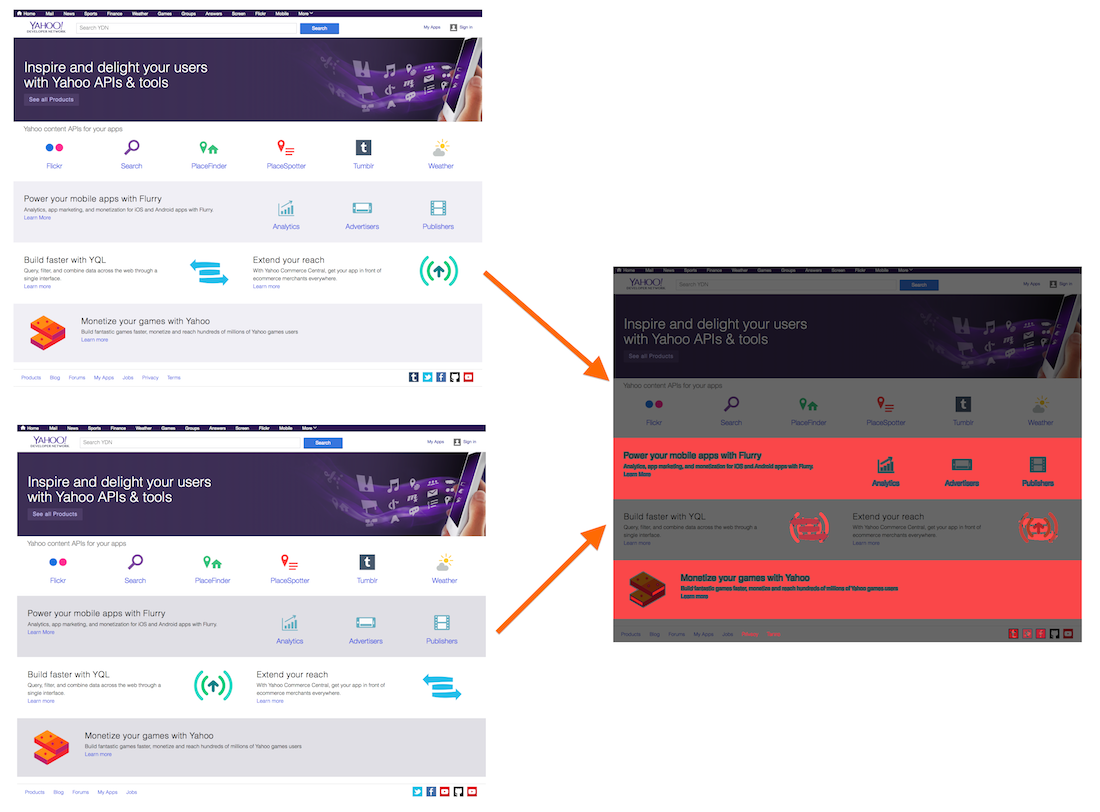
##Image Comparison and Result
##Installation
Install this module with the following command:
npm install blink-diff
Add the module to your package.json dependencies:
npm install --save blink-diff
Add the module to your package.json dev-dependencies:
npm install --save-dev blink-diff
##Usage
The package can be used in two different ways:
###Command-Line usage
The command-line tool can be found in the bin directory. You can run the application with
blink-diff --output <output>.png <image1>.png <image2>.png
Use image1 and image2 as the images you want to compare.
Only PNGs are supported at this point.
The command-line tool exposes a couple of flags and parameters for the comparison:
--verbose Turn on verbose mode
--debug Turn on debug mode - leaving all filters and modifications on the result
--threshold p Number of pixels/percent 'p' below which differences are ignored
--threshold-type t 'pixel' and 'percent' as type of threshold. (default: pixel)
--delta p Max. distance colors in the 4 dimensional color-space without triggering a difference. (default: 20)
--copyImageA Copies first image to output as base. (default: true)
--copyImageB Copies second image to output as base.
--no-copy Doesn't copy anything to output as base.
--output o Write difference to the file 'o'
--filter f Filters f (separated with comma) that will be applied before the comparison.
--no-composition Turns the composition feature off
--compose-ltr Compose output image from left to right
--compose-ttb Compose output image from top to bottom
--hide-shift Hides shift highlighting (default: false)
--h-shift Acceptable horizontal shift of pixel. (default: 0)
--v-shift Acceptable vertical shift of pixel. (default: 0)
--block-out x,y,w,h Block-out area. Can be repeated multiple times.
--version Print version
--help This help
###Object usage
The package can also be used directly in code, without going through the command-line.
Example:
var diff = new BlinkDiff({
imageAPath: 'path/to/first/image', // Use file-path
imageBPath: 'path/to/second/image',
thresholdType: BlinkDiff.THRESHOLD_PERCENT,
threshold: 0.01, // 1% threshold
imageOutputPath: 'path/to/output/image'
});
diff.run(function (error, result) {
if (error) {
throw error;
} else {
console.log(diff.hasPassed(result.code) ? 'Passed' : 'Failed');
console.log('Found ' + result.differences + ' differences.');
}
});
All the parameters that were available in the command-line tool are also available through the class constructor, however they might use slightly different wording. The class exposes additional parameters that are not available from the command-line:
imageAPath Defines the path to the first image that should be compared (required; imageAPath or imageA is required - see example below)imageA Supplies first image that should be compared (required; imageAPath or imageA is required - see example below) - This can be a PNGImage instance or a Buffer instance with PNG dataimageBPath Defines the path to the second image that should be compared (required; imageBPath or imageB is required - see example below)imageB Supplies second image that should be compared (required; imageBPath or imageB is required - see example below) - This can be a PNGImage instance or a Buffer instance with PNG dataimageOutputPath Defines the path to the output-file. If you leaves this one off, then this feature is turned-off.imageOutputLimit Defines when an image output should be created. This can be for different images, similar or different images, or all comparisons. (default: BlinkDiff.OUTPUT_ALL)verbose Verbose output (default: false)thresholdType Type of threshold check. This can be BlinkDiff.THRESHOLD_PIXEL and BlinkDiff.THRESHOLD_PERCENT (default: BlinkDiff.THRESHOLD_PIXEL)threshold Number of pixels/percent p below which differences are ignored (default: 500) - For percentage thresholds: 1 = 100%, 0.2 = 20%delta Distance between the color coordinates in the 4 dimensional color-space that will not trigger a difference. (default: 20)outputMaskRed Red intensity for the difference highlighting in the output file (default: 255)outputMaskGreen Green intensity for the difference highlighting in the output file (default: 0)outputMaskBlue Blue intensity for the difference highlighting in the output file (default: 0)outputMaskAlpha Alpha intensity for the difference highlighting in the output file (default: 255)outputMaskOpacity Opacity of the pixel for the difference highlighting in the output file (default: 0.7 - slightly transparent)outputShiftRed Red intensity for the shift highlighting in the output file (default: 255)outputShiftGreen Green intensity for the shift highlighting in the output file (default: 165)outputShiftBlue Blue intensity for the shift highlighting in the output file (default: 0)outputShiftAlpha Alpha intensity for the shift highlighting in the output file (default: 255)outputShiftOpacity Opacity of the pixel for the shift highlighting in the output file (default: 0.7 - slightly transparent)outputBackgroundRed Red intensity for the background in the output file (default: 0)outputBackgroundGreen Green intensity for the background in the output file (default: 0)outputBackgroundBlue Blue intensity for the background in the output file (default: 0)outputBackgroundAlpha Alpha intensity for the background in the output file (default: undefined)outputBackgroundOpacity Opacity of the pixel for the background in the output file (default: 0.6 - transparent)blockOut Object or list of objects with coordinates that should be blocked before testing.blockOutRed Red intensity for the block-out in the output file (default: 0) This color will only be visible in the result when debug-mode is turned on.blockOutGreen Green intensity for the block-out in the output file (default: 0) This color will only be visible in the result when debug-mode is turned on.blockOutBlue Blue intensity for the block-out in the output file (default: 0) This color will only be visible in the result when debug-mode is turned on.blockOutAlpha Alpha intensity for the block-out in the output file (default: 255)blockOutOpacity Opacity of the pixel for the block-out in the output file (default: 1.0)copyImageAToOutput Copies the first image to the output image before the comparison begins. This will make sure that the output image will highlight the differences on the first image. (default)copyImageBToOutput Copies the second image to the output image before the comparison begins. This will make sure that the output image will highlight the differences on the second image.filter Filters that will be applied before the comparison. Available filters are: blur, grayScale, lightness, luma, luminosity, sepiadebug When set, then the applied filters will be shown on the output image. (default: false)composition Creates as output a composition of all three images (approved, highlight, and build) (default: true)composeLeftToRight Creates comparison-composition from left to right, otherwise it lets decide the app on what is bestcomposeTopToBottom Creates comparison-composition from top to bottom, otherwise it lets decide the app on what is besthShift Horizontal shift for possible antialiasing (default: 2) Set to 0 to turn this off.vShift Vertical shift for possible antialiasing (default: 2) Set to 0 to turn this off.hideShift Uses the background color for "highlighting" shifts. (default: false)cropImageA Cropping for first image (default: no cropping) - Format: { x:, y:, width:, height: }cropImageB Cropping for second image (default: no cropping) - Format: { x:, y:, width:, height: }perceptual Turn the perceptual comparison mode on. See below for more information.gamma Gamma correction for all colors (will be used as base) (default: none) - Any value here will turn the perceptual comparison mode ongammaR Gamma correction for red - Any value here will turn the perceptual comparison mode ongammaG Gamma correction for green - Any value here will turn the perceptual comparison mode ongammaB Gamma correction for blue - Any value here will turn the perceptual comparison mode onExample:
var firstImage = PNGImage.readImage('path/to/first/image', function (err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
var diff = new BlinkDiff({
imageA: srcImage, // Use already loaded image for first image
imageBPath: 'path/to/second/image', // Use file-path to select image
delta: 50, // Make comparison more tolerant
outputMaskRed: 0,
outputMaskBlue: 255, // Use blue for highlighting differences
hideShift: true, // Hide anti-aliasing differences - will still determine but not showing it
imageOutputPath: 'path/to/output/image'
});
diff.run(function (error, result) {
if (error) {
throw error;
} else {
console.log(diff.hasPassed(result.code) ? 'Passed' : 'Failed');
console.log('Found ' + result.differences + ' differences.');
}
});
});
####Cropping
Images can be cropped before they are compared by using the cropImageA or cropImageB parameters. Single values can be left off, and the system will calculate the correct dimensions. However, x/y coordinates have priority over width/height as the position are usually more important than the dimensions - image will also be clipped by the system when needed.
####Perceptual Comparison The perceptual comparison mode considers the perception of colors in the human brain. It transforms all the colors into a human perception color-space, which is quite different to the typical physical bound RGB color-space. There, in the perceptual color-space, the distance between colors is according to the human perception and should therefore closer resemble the differences a human would perceive seeing the images.
####Logging
By default, the logger doesn't log events anywhere, but you can change this behavior by overwriting blinkDiff.log:
var blinkDiff = new BlinkDiff({
...
});
blinkDiff.log = function (text) {
// Do whatever you want to do
};
...
####Block-Out Sometimes, it is necessary to block-out some specific areas in an image that should be ignored for comparisons. For example, this can be IDs or even time-labels that change with the time. Adding block-outs to images may decrease false positives and therefore stabilizes these comparisons.
The color of the block-outs can be selected by the API parameters. However, the block-out areas will not be visible by default - they are hidden even though they are used. To make them visible, turn the debug-mode on.
##Examples
There are some examples in the examples folder, in which I used screenshots of YDN to check for visual regressions (and made some manual modifications to the dom to make differences appear ;-)).
You can find examples for:
YDN_ColorYDN_Missing (including some anti-aliasing)YDN_MultiYDN_SortYDN_Swap (including block-out areas)YDN_UpperAll screenshots were compared to YDN.png, a previously approved screenshot without a regression.
Each of the regressions has the screenshot and the output result, highlighting the differences.
##API-Documentation
Generate the documentation with following command:
npm run docs
The documentation will be generated in the docs folder of the module root.
##Tests
Run the tests with the following command:
npm run test
The code-coverage will be written to the coverage folder in the module root.
##Project Focus There are three types of image comparisons:
Blink-Diff was initially created to compare screenshots. These images are generally low-frequency, meaning larger areas with the same color and less gradients than in photos. The pixel-by-pixel comparison was chosen as it will trigger for differences that a human might not be able to see. We believe that a bug is still a bug even if a human won't see it - a regression might have happened that wasn't intended.
A perceptual comparison would not trigger small differences, possibly missing problems that could get worse down the road.
Pixel-by-pixel comparisons have the reputation of triggering too often, adding manual labor, checking images by hand. Blink-Diff was created to keep this in mind and was optimized to reduce false-positives by taking sub-pixeling and anti-aliasing into account. Additional features like thresholds and the pythagorean distance calculation in the four dimensional color-space makes sure that this won't happen too often. Additionally, filters can be applied to the images, for example to compare luminosity of pixels and not the saturation thereof.
Blink-Diff also supports partially the perceptual comparison that can be turned on when supplying perceptual=true. Then, the colors will be compared in accordance with the human perception and not according to the physical world. High-frequency filters, however, are not yet supported.
##Project Naming The name comes from the Blink comparator that was used in Astronomy to recognize differences in multiple photos, taking a picture of the same area in the sky over consecutive days, months, or years. Most notably, it was used to discover Pluto.
##Contributions Feel free to create an issue or create a pull-request if you have an idea on how to improve blink-diff. We are pretty relaxed on the contribution rules; add tests for your pull-requests when possible, but it is also ok if there are none - we'll add them for you. We are trying to improve blink-diff as much as possible, and this can only be done by contributions from the community.
Also, even if you simply gave us an idea for a feature and did not actually write the code, we will still add you as the Contributor down below since it probably wouldn't be there without you. So, keep them coming!
##Contributors
##Third-party libraries
The following third-party libraries are used by this module:
###Dependencies
###Dev-Dependencies
##License
The MIT License
Copyright 2014-2015 Yahoo Inc.
FAQs
A lightweight image comparison tool
The npm package @nodebug/blink-diff receives a total of 1 weekly downloads. As such, @nodebug/blink-diff popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that @nodebug/blink-diff demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.