
Security News
PyPI’s New Archival Feature Closes a Major Security Gap
PyPI now allows maintainers to archive projects, improving security and helping users make informed decisions about their dependencies.
@thi.ng/rstream
Advanced tools
Reactive streams & subscription primitives for constructing dataflow graphs / pipelines

[!NOTE] This is one of 200 standalone projects, maintained as part of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo and anti-framework.
🚀 Please help me to work full-time on these projects by sponsoring me on GitHub. Thank you! ❤️
Reactive streams & subscription primitives for constructing dataflow graphs / pipelines.
This library provides & uses three key building blocks for reactive programming:
(No value judgments implied - there's room for both approaches!)
merge() /sync())STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
The CloseMode enum has been replaced with a more compact & simple string union
type, see docs and
usage.
Completely revised & improved error handling, stronger
distinction between .subscribe() and .transform() methods & internal
simplification of their implementations.
All error handlers now MUST return a boolean to indicate if the error was recoverable from or should put the subscription into the error state. See error handling for details.
The options given to .transform() and .map() can now include an error
handler:
// transform stream with given transducer(s)
// and forward any errors to `handleError` (user defined fn)
src.transform(xf1, xf2,..., { error: (e) => { ... } });
// or, also new, provide everything as single options object
// (for this version, see note (1) below)
src.transform({ xform: map(...), error: handleError });
.subscribe(sub, xform, opts) signature has been removed and the xform
(transducer) must now be given as part of the options object:import { reactive, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import { filter } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
const src = reactive(1);
// old
src.subscribe(trace("foo"), filter((x) => x < 10), { id: "child-sub" });
// new, see note (1) below
src.subscribe(trace("foo"), { xform: filter((x) => x < 10), id: "child-sub" });
.transformTopic() and updated signatures for .subscribeTopic(), both in
similarity to above.import { pubsub } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import { map } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
type Event = { id: string; value: any; };
const src = pubsub<Event>({ topic: (e) => e.id });
// transform topic stream with given transducer (see note (1) below)
// and forward any errors to `handleError` (user defined fn)
src.transformTopic("foo", map((e) => e.value), { error: handleError })
Notes:
comp().
Other signatures of .transform() method support up to 4 transducers and
composes them automatically.yarn add @thi.ng/rstream
ESM import:
import * as rs from "@thi.ng/rstream";
Browser ESM import:
<script type="module" src="https://esm.run/@thi.ng/rstream"></script>
For Node.js REPL:
const rs = await import("@thi.ng/rstream");
Package sizes (brotli'd, pre-treeshake): ESM: 6.33 KB
Note: @thi.ng/api is in most cases a type-only import (not used at runtime)
56 projects in this repo's /examples directory are using this package:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Interactive image processing (adaptive threshold) | Demo | Source |
 | Large ASCII font text generator using @thi.ng/rdom | Demo | Source |
 | Figlet-style bitmap font creation with transducers | Demo | Source |
 | Interactive & reactive image blurhash generator | Demo | Source |
 | Canvas based dial widget | Demo | Source |
 | Self-modifying, animated typographic grid with emergent complex patterns | Demo | Source |
 | Tool to interactively compute & visualize color contrasts against WCAG threshold | Demo | Source |
 | Probabilistic color theme generator | Demo | Source |
 | Basic crypto-currency candle chart with multiple moving averages plots | Demo | Source |
 | Color palette generation via dominant color extraction from uploaded images | Demo | Source |
 | Interactive inverse FFT toy synth | Demo | Source |
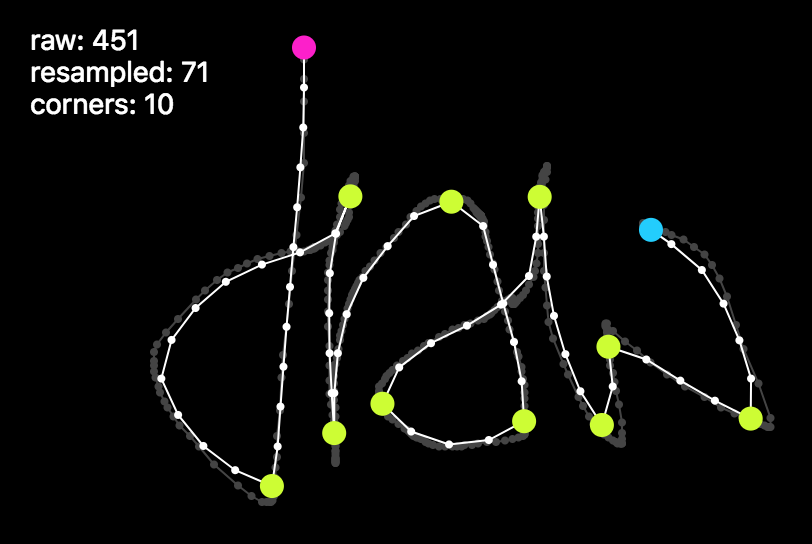 | Mouse gesture / stroke analysis, simplification, corner detection | Demo | Source |
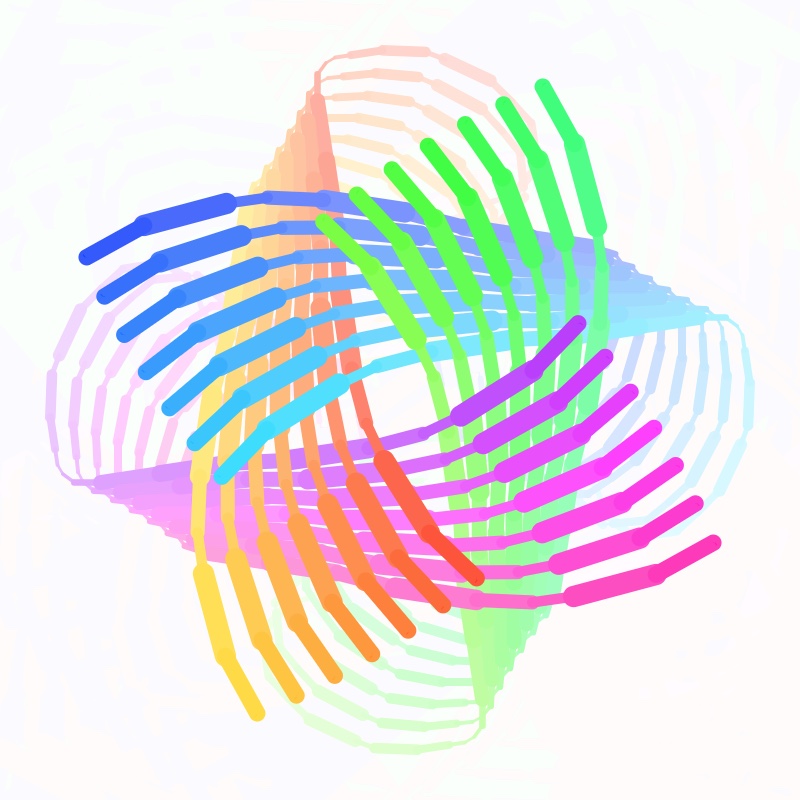 | Interactive pattern drawing demo using transducers | Demo | Source |
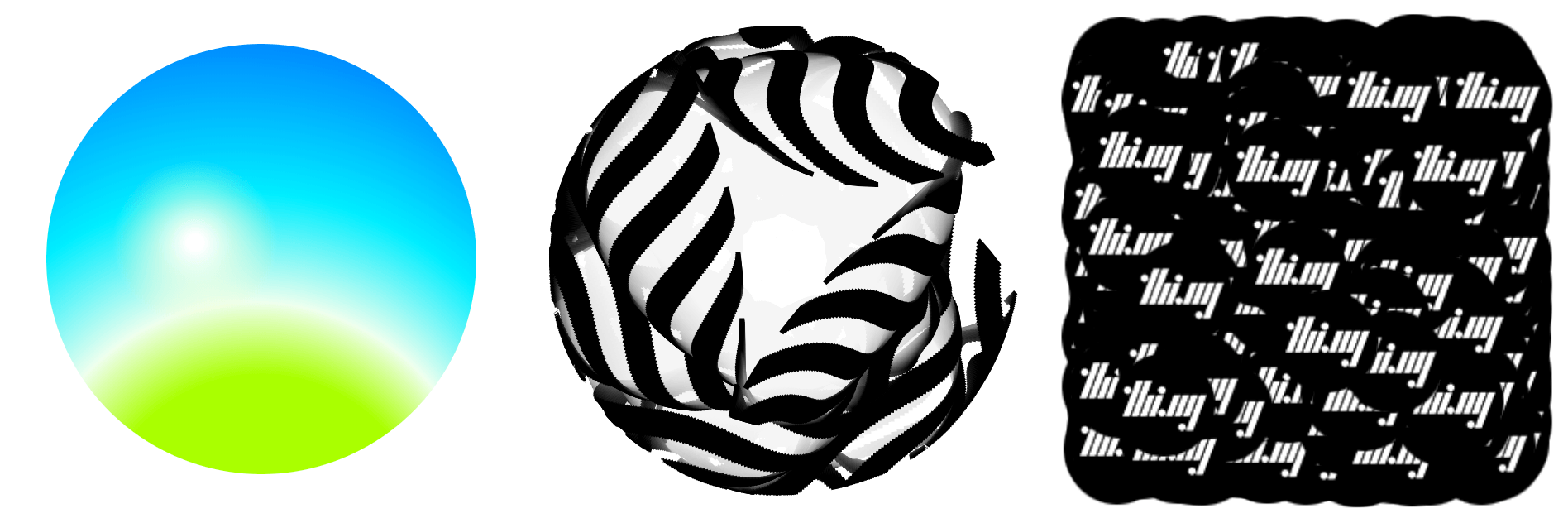 | Various hdom-canvas shape drawing examples & SVG conversion / export | Demo | Source |
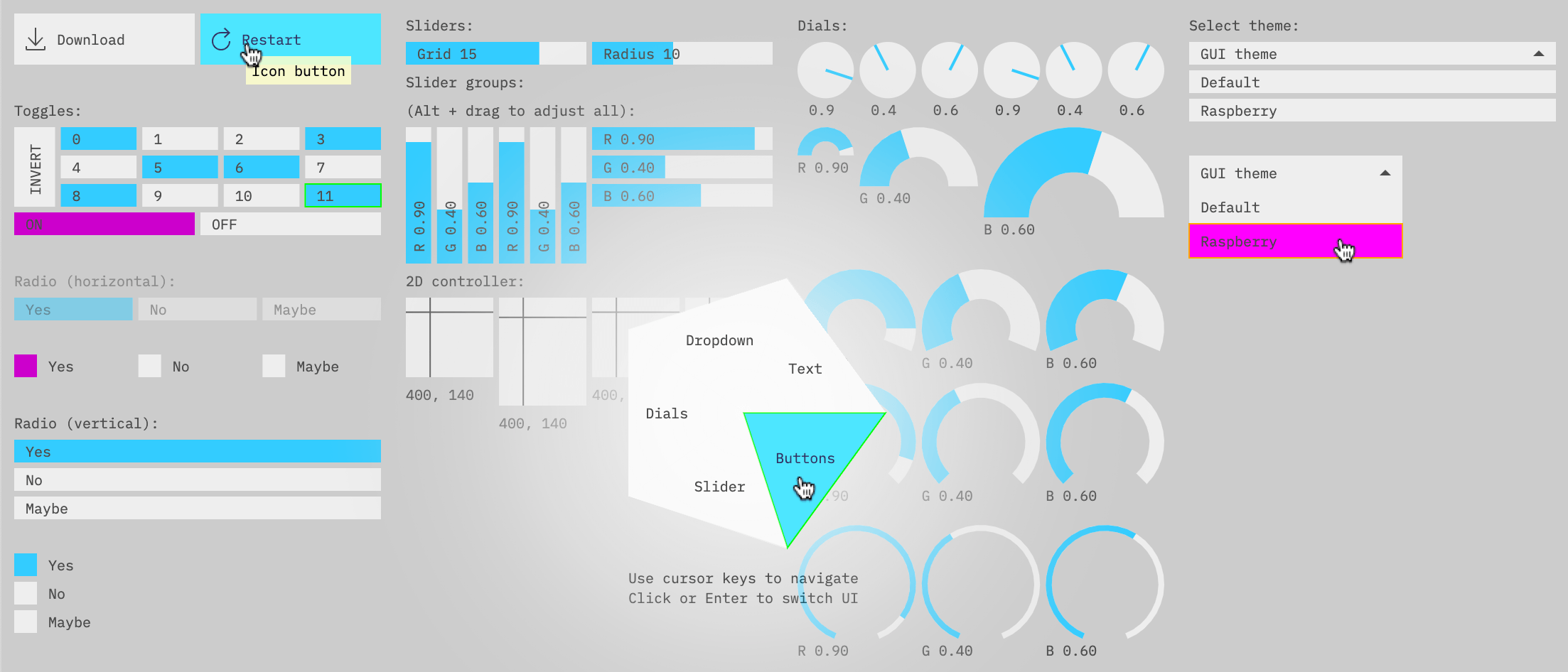 | Canvas based Immediate Mode GUI components | Demo | Source |
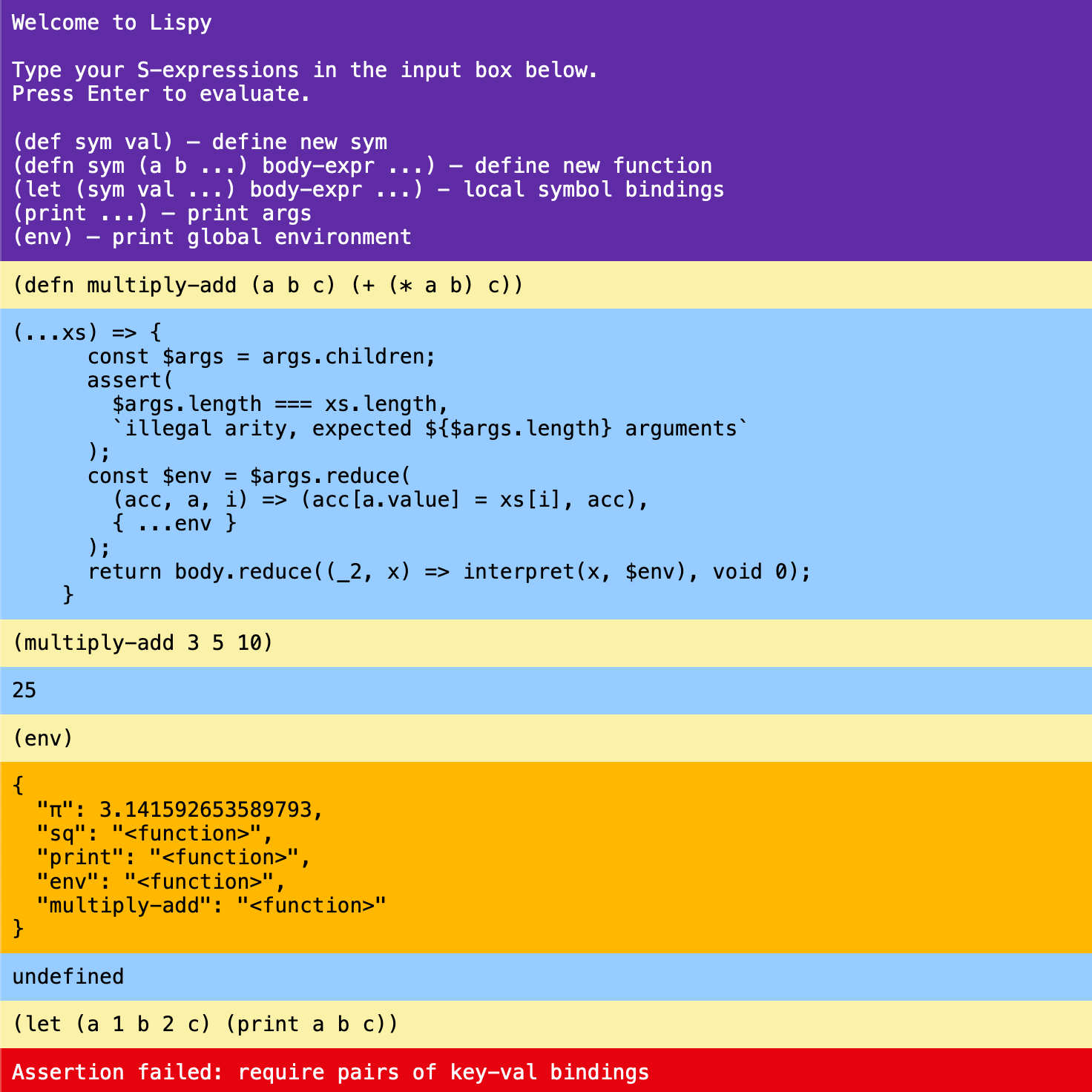 | Browser REPL for a Lispy S-expression based mini language | Demo | Source |
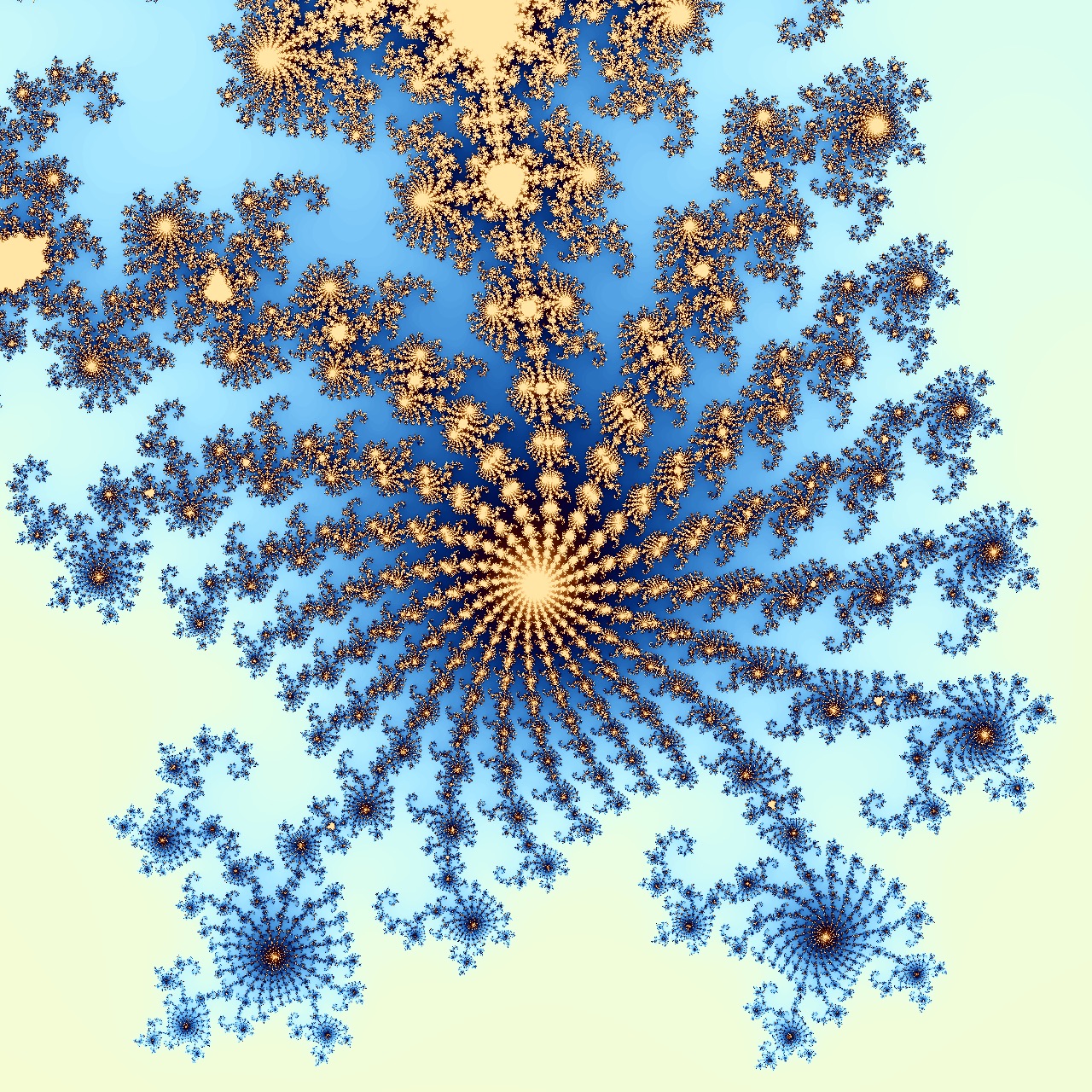 | Worker based, interactive Mandelbrot visualization | Demo | Source |
 | Markdown to Hiccup to HTML parser / transformer | Demo | Source |
 | Mastodon API feed reader with support for different media types, fullscreen media modal, HTML rewriting | Demo | Source |
| Basic rstream-gestures multi-touch demo | Demo | Source | |
 | Parser grammar livecoding editor/playground & codegen | Demo | Source |
| Interactive pixel sorting tool using thi.ng/color & thi.ng/pixel | Demo | Source | |
| RGB waveform image analysis | Demo | Source | |
 | Live coding playground for 2D geometry generation using @thi.ng/pointfree-lang | Demo | Source |
 | Procedural stochastic text generation via custom DSL, parse grammar & AST transformation | Demo | Source |
 | Scroll-based, reactive, multi-param CSS animation basics | Demo | Source |
| Demonstates various rdom usage patterns | Demo | Source | |
 | Minimal rdom-canvas animation | Demo | Source |
 | Dynamically loaded images w/ preloader state | Demo | Source |
 | Basic usage of the declarative rdom-forms generator | Demo | Source |
 | rstream & transducer-based FSM for converting key event sequences into high-level commands | Demo | Source |
 | Basic usage of thi.ng/rdom keyed list component wrapper | Demo | Source |
 | rdom & hiccup-canvas interop test | Demo | Source |
| Full umbrella repo doc string search w/ paginated results | Demo | Source | |
 | rdom powered SVG graph with draggable nodes | Demo | Source |
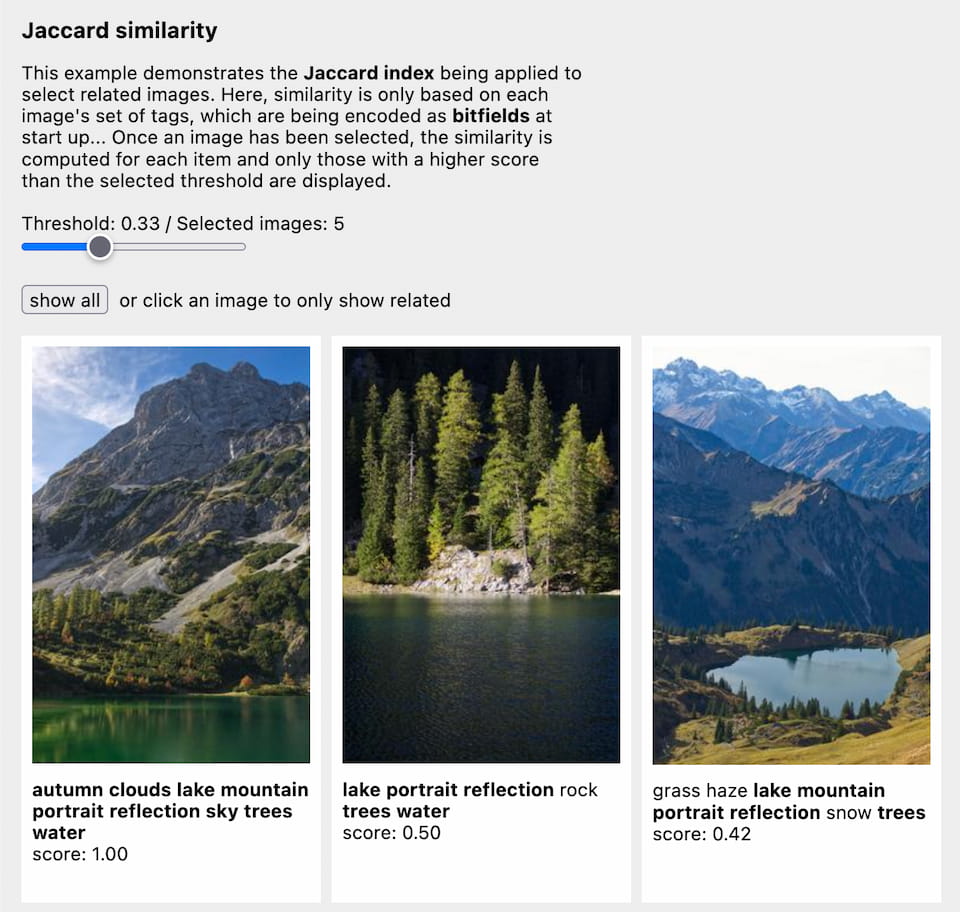 | Responsive image gallery with tag-based Jaccard similarity ranking | Demo | Source |
 | Generative audio synth offline renderer and WAV file export | Demo | Source |
 | Animated Voronoi diagram, cubic splines & SVG download | Demo | Source |
 | Minimal demo of using rstream constructs to form an interceptor-style event loop | Demo | Source |
 | Interactive grid generator, SVG generation & export, undo/redo support | Demo | Source |
| rstream based UI updates & state handling | Demo | Source | |
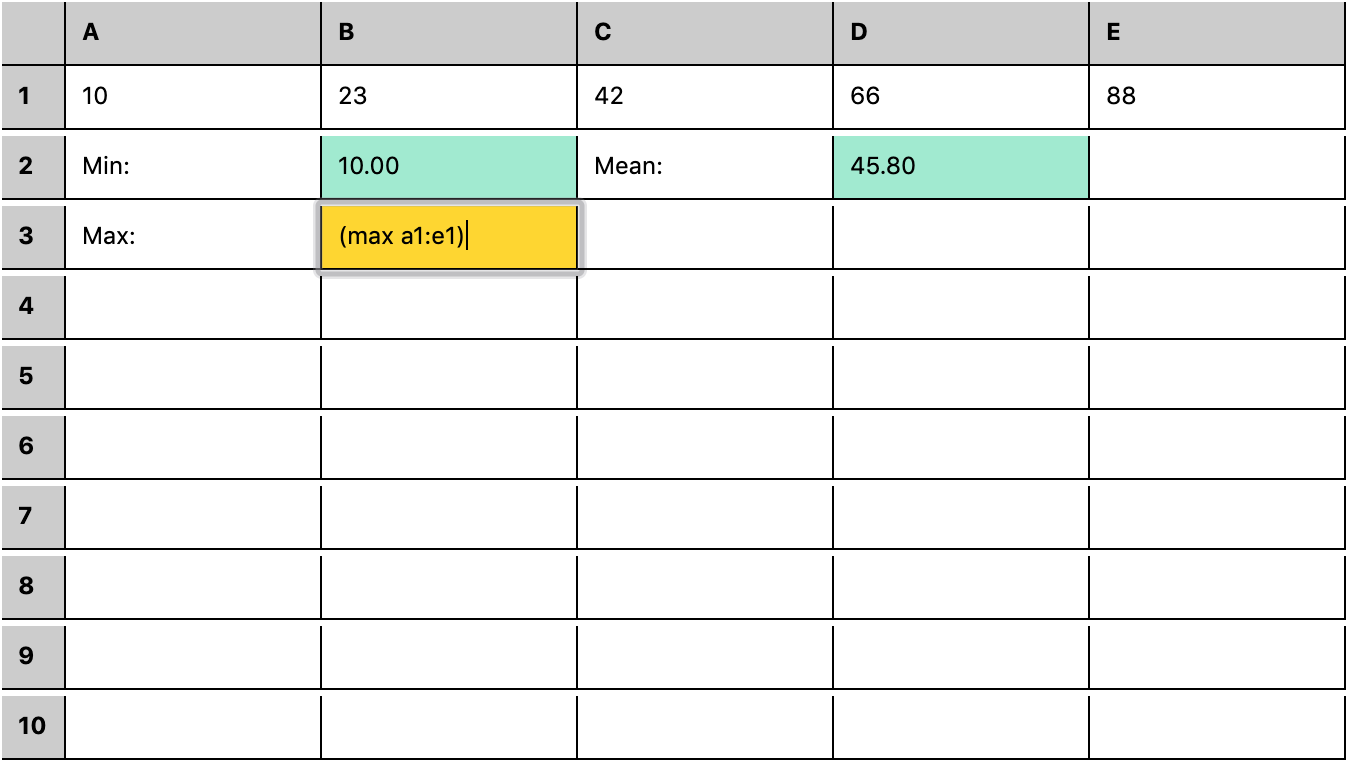 | rstream based spreadsheet w/ S-expression formula DSL | Demo | Source |
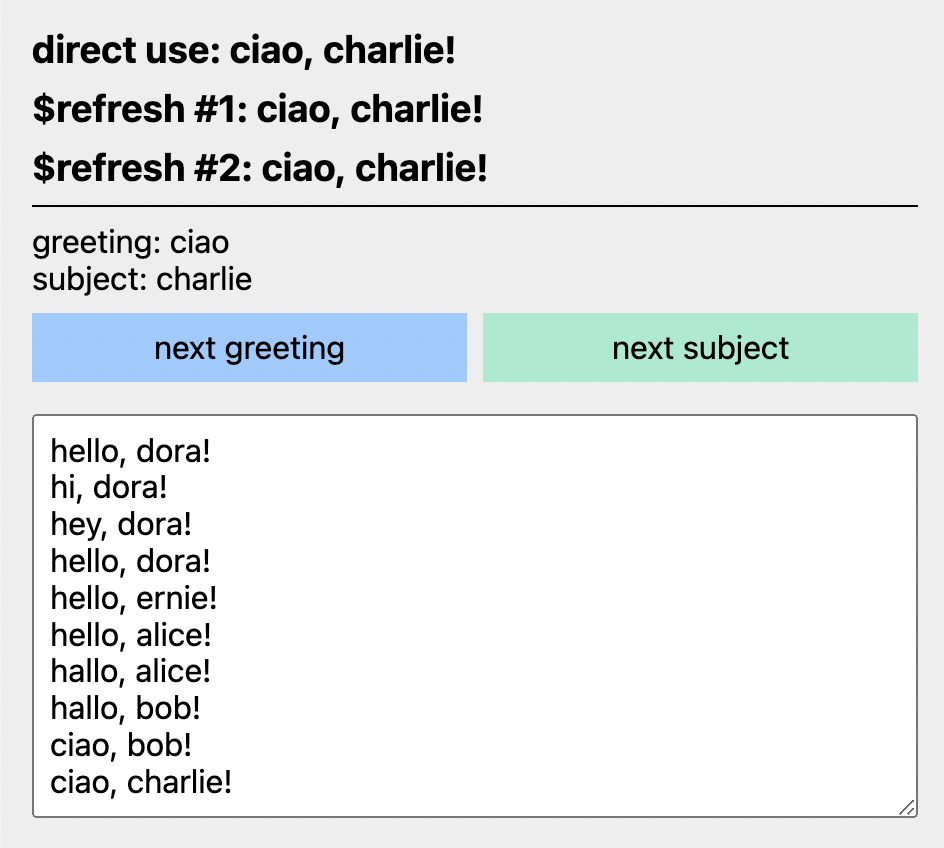 | Minimal rstream sync() example using rdom | Demo | Source |
 | Declarative component-based system with central rstream-based pubsub event bus | Demo | Source |
 | Fork-join worker-based raymarch renderer (JS/CPU only) | Demo | Source |
 | Fitting, transforming & plotting 10k data points per frame using SIMD | Demo | Source |
 | Responsive & reactively computed stacked column layout | Demo | Source |
 | SVG path parsing & dynamic resampling | Demo | Source |
 | hdom based slide deck viewer & slides from my ClojureX 2018 keynote | Demo | Source |
 | thi.ng/rdom & thi.ng/rstream based quiz to guess thi.ng package names | Demo | Source |
 | Multi-layer vectorization & dithering of bitmap images | Demo | Source |
| Transducer & rstream based hdom UI updates | Demo | Source | |
 | Interactive ridge-line plot | Demo | Source |
 | Interactive scatter & line plot of low-discrepancy samples | Demo | Source |
 | rdom & WebGL-based image channel editor | Demo | Source |
 | WebGL cube maps with async texture loading | Demo | Source |
Since version 3.0.0 all stream and subscription factory functions take an optional object of common configuration options with at least these keys (each optional):
interface CommonOpts {
/**
* Internal ID associated with this stream. If omitted, an autogenerated ID
* will be used.
*/
id: string;
/**
* If false or `"never"`, the stream stays active even if all inputs are
* done. If true (default) or `"last"`, the stream closes when the last
* input is done. If `"first"`, the instance closes when the first input is
* done.
*
* @defaultValue "last"
*/
closeIn: CloseMode;
/**
* If false or `"never"`, the stream stays active once there are no more
* subscribers. If true (default) or `"last"`, the stream closes when the
* last subscriber has unsubscribed. If `"first"`, the instance closes when
* the first subscriber disconnects.
*
* @defaultValue "last"
*/
closeOut: CloseMode;
/**
* If true (default), stream caches last received value and pushes it to new
* subscriberswhen they subscribe. If false, calling `.deref()` on this
* stream will always return `undefined`.
*
* @defaultValue true
*/
cache: boolean;
}
Docs: stream()
Creates a new Stream instance, optionally with given StreamSource function
and / or ID. If a src function is provided, the function will be only called
(with the Stream instance as single argument) once the first subscriber has
attached to the stream. If the function returns another function, it will be
used for cleanup purposes if the stream is cancelled, e.g. if the last
subscriber has unsubscribed. Streams are intended as (primarily async) data
sources in a dataflow graph and are the primary construct for the various
from*() functions provided by the package. However, streams can also be
triggered manually (from outside the stream), in which case the user should call
stream.next() to cause value propagation.
import { stream, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
a = stream<number>((s) => {
s.next(1);
s.next(2);
s.done();
});
a.subscribe(trace("a"));
// a 1
// a 2
// a done
// as reactive value mechanism
b = stream<number>();
// or alternatively
// b = subscription();
b.subscribe(trace("b1"));
b.subscribe(trace("b2"));
// external trigger
b.next(42);
// b1 42
// b2 42
Stream (like all other types of Subscription) implements the @thi.ng/api
IDeref interface
which provides read access to a stream's last received value. This is useful for
various purposes, e.g. in combination with @thi.ng/hdom, which supports direct
embedding of streams (i.e. their values) into UI components (and will be deref'd
automatically). If the stream has not yet emitted a value or if the stream is
already done, it will deref to undefined.
Furthermore, all subscription types can be configured (via the cache option)
to NOT retain their last emitted value, in which case .deref() will always
return undefined.
Docs: subscription()
Creates a new Subscription instance, the fundamental datatype & building block
provided by this package (Streams are Subscriptions too). Subscriptions can
be:
IDeref interfaceimport { subscription, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import { filter } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
// as reactive value mechanism (same as with stream() above)
s = subscription<any, any>();
s.subscribe(trace("s1"));
s.subscribe(trace("s2"), filter((x) => x > 25));
// external trigger
s.next(23);
// s1 23
// (s2 doesn't receive value here due to its filter)
s.next(42);
// s2 42
// s1 42
stream() with initial valueDocs: metaStream()
MetaStreams are streams of streams. A MetaStream is a subscription type
which transforms each incoming value into a new stream, subscribes to it (via an
hidden / internal subscription) and then only passes values from that stream to
its own subscribers. If a new value is received, the meta stream first
unsubscribes from the possibly still active stream created from the previous
input, before creating and subscribing to the new stream. Hence this stream type
is useful for cases where streams need to be dynamically and invisibly created &
inserted into an existing dataflow topology without changing it, and with the
guarantee that never more than one of these is active at the same time. Similar
behavior (without the restriction in number) can be achieved using merge()
(see further below).
The user supplied factory function will be called for each incoming value and
is responsible for creating the new stream instances. If the function returns
null / undefined, no further action will be taken (acts like a filter
transducer, i.e. the incoming value is simply ignored).
import { metastream, fromIterable, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import { repeat } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
// transform each received odd number into a stream
// producing 3 copies of that number in the metastream
// even numbers are ignored
a = metastream<number, string>(
(x) => (x & 1)
? fromIterable(repeat("odd: " + x, 3), { delay: 100 })
: null
);
a.subscribe(trace())
a.next(23)
// odd: 23
// odd: 23
// odd: 23
a.next(42) // not odd, ignored by meta factory fn
a.next(43)
// odd: 43
// odd: 43
// odd: 43
The factory function does NOT need to create new streams, but too can merely return other existing streams, and so making the meta stream act like a switch / stream selector.
If the meta stream is the only subscriber to these input streams, you'll need to
use the closeOut: "never" option when creating the inputs. This keeps them
alive and allows for dynamic switching between them.
import { metastream, fromIterable, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import { repeat } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
// infinite inputs
a = fromIterable(
repeat("a"),
{ delay: 1000, closeOut: "never" }
);
b = fromIterable(
repeat("b"),
{ delay: 1000, closeOut: "never" }
);
// stream selector / switch
m = metaStream((x) => x ? a : b);
m.subscribe(trace("meta from: "));
m.next(true);
// meta from: a
m.next(false);
// meta from: b
m.next(true);
// meta from: a
Docs: merge()
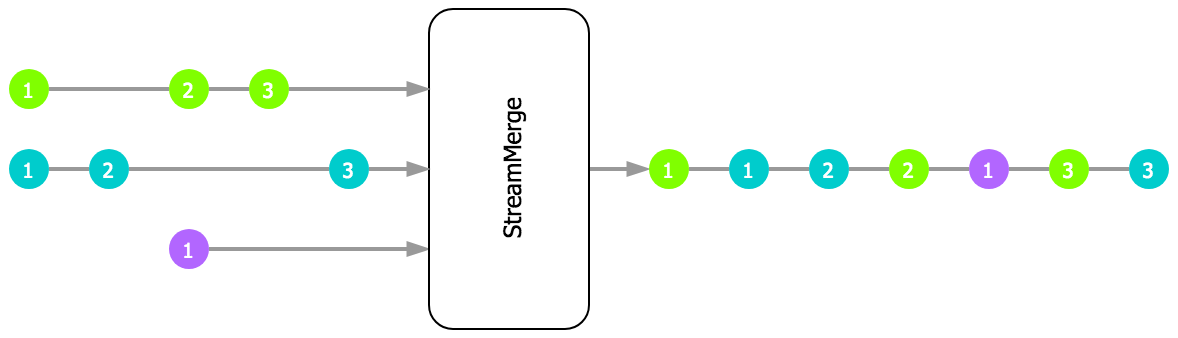
Returns a new StreamMerge instance, a subscription type consuming inputs from
multiple inputs and passing received values on to any subscribers. Input streams
can be added and removed dynamically. By default, StreamMerge calls done()
when the last active input is done, but this behavior can be overridden via the
closeIn
option.
import { merge, fromIterable, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
merge({
// input streams w/ different frequencies
src: [
fromIterable([1, 2, 3], { delay: 10 }),
fromIterable([10, 20, 30], { delay: 21 }),
fromIterable([100, 200, 300], { delay: 7 })
]
}).subscribe(trace());
// 100
// 1
// 200
// 10
// 2
// 300
// 3
// 20
// 30
Use the labeled()
transducer for
each input to create a stream of labeled values and track their provenance:
import { merge, fromIterable, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import { labeled } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
merge({
src: [
fromIterable([1, 2, 3]).transform(labeled("a")),
fromIterable([10, 20, 30]).transform(labeled("b")),
]
}).subscribe(trace());
// ["a", 1]
// ["b", 10]
// ["a", 2]
// ["b", 20]
// ["a", 3]
// ["b", 30]
See StreamMergeOpts for further reference of the various behavior options.
If the StreamMerge receives a Subscription-like value from any of its
inputs, it will not be processed as usual, but instead will be added as new
input to the merge and then automatically remove once that stream is exhausted.
import { merge, stream, fromIterable, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
import { repeat } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
// stream source w/ transducer mapping values to new streams
a = stream().map((x) => fromIterable(repeat(x, 3)));
// simple 1Hz counter
b = fromInterval(1000).map((x) => "b" + x);
merge({ src: [a, b] }).subscribe(trace());
// 0
// 1
// 2
// sent "a" will be transformed into stream via above transducer
// and then auto-added as new input to the StreamMerge
a.next("abc");
// abc
// abc
// abc
// 3
// 4
Docs: sync()
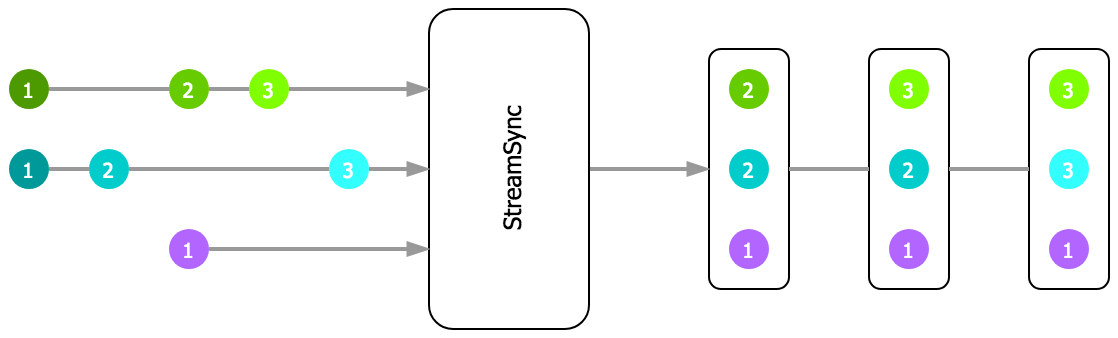
Similar to StreamMerge above, but with extra synchronization of inputs. Before
emitting any new values, StreamSync collects values until at least one has
been received from all inputs. Once that's the case, the collected values are
sent as labeled tuple object to downstream subscribers. Each value in the
emitted tuple objects is stored under their input stream's ID. Only the last
value received from each input is passed on. After the initial tuple has been
emitted, you can choose from two possible behaviors:
reset option is true, every input will have to provide at least
one new value again until another result tuple is produced.Any done inputs are automatically removed. By default, StreamSync calls
done() when the last active input is done, but this behavior can be overridden
via the closeIn
option.
import { sync, stream, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
const a = stream();
const b = stream();
s = sync<any,any>({ src: { a, b } }).subscribe(trace("result: "));
a.next(1);
b.next(2);
// result: { a: 1, b: 2 }
Input streams can be added and removed dynamically and the emitted tuple size adjusts to the current number of inputs (the next time a value is received from any input).
If the reset option is enabled, the last emitted tuple is allowed to be
incomplete, by default. To only allow complete tuples, also set the all option
to false.
The synchronization is done via the
partitionSync()
transducer from the
@thi.ng/transducers
package. See this function's docs for further details.
See StreamSyncOpts for further reference of the various behavior options.
Docs: pubsub()
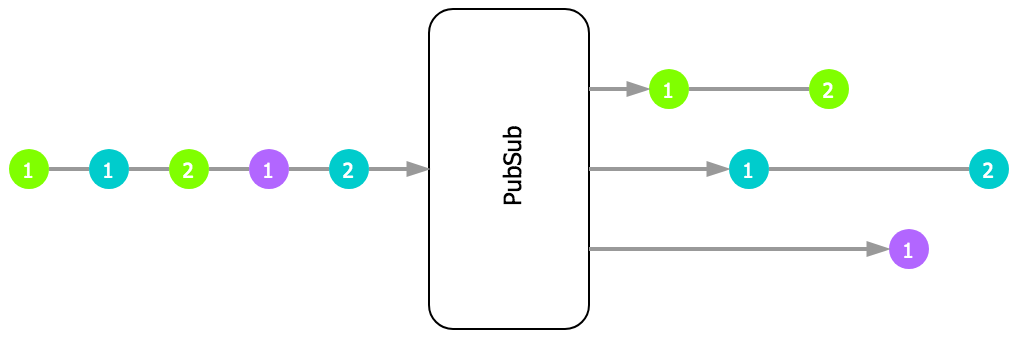
Topic based stream splitter. Applies topic function to each received value and
only forwards it to child subscriptions for returned topic. The actual topic
(return value from topic fn) can be of any type, apart from undefined.
Complex topics (e.g objects / arrays) are allowed and they're matched with
registered topics using @thi.ng/equiv by default (but customizable via equiv
option). Each topic can have any number of subscribers.
If a transducer is specified for the PubSub, it is always applied prior to
passing the input to the topic function. I.e. in this case the topic function
will receive the transformed inputs.
PubSub supports dynamic topic subscriptions and unsubscriptions via
subscribeTopic() and unsubscribeTopic(). However, the standard
subscribe() / unsubscribe() methods are NOT supported (since meaningless
here) and will throw an error! unsubscribe() can only be called WITHOUT
argument to unsubscribe the entire PubSub instance (incl. all topic
subscriptions) from the parent stream.
Docs: bisect()
Returns a new PubSub instance using given predicate pred as boolean topic
function and a & b as subscribers for truthy (a) and falsy b values.
import { bisect, fromIterable, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
fromIterable([1, 2, 3, 4]).subscribe(
bisect((x) => !!(x & 1), trace("odd"), trace("even"))
);
// odd 1
// even 2
// odd 3
// even 4
// odd done
// even done
If a or b need to be subscribed to directly, then a / b MUST be first
created as Subscription (if not already) and a reference kept prior to calling
bisect().
import { bisect, fromIterable, subscription, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
const odd = subscription();
const even = subscription();
odd.subscribe(trace("odd"));
odd.subscribe(trace("odd x10"), tx.map((x) => x * 10));
even.subscribe(trace("even"));
fromIterable([1, 2, 3, 4]).subscribe(bisect((x) => !!(x & 1), odd, even));
// odd x10 10
// odd 1
// even 2
// odd x10 30
// odd 3
// even 4
// odd done
// odd x10 done
// even done
Docs: sidechainPartition()
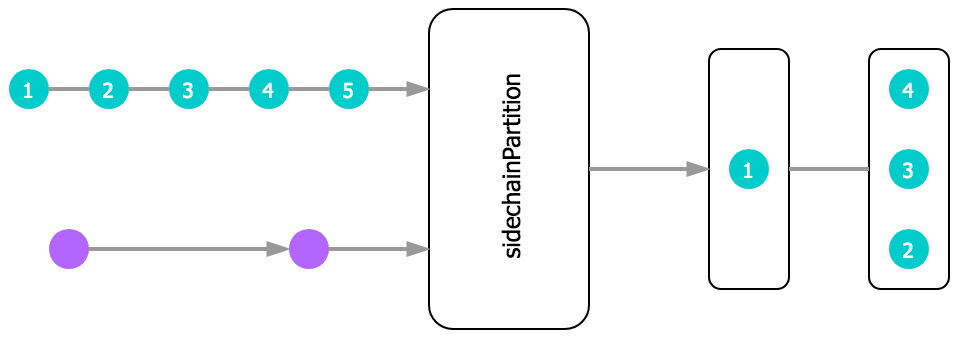
Buffers values from src until side chain fires, then emits buffer (unless
empty) and repeats process until either input is done. By default, the value
read from the side chain is ignored, however the optional predicate can be used
to only trigger for specific values / conditions.
import {
merge, fromEvent, fromRAF,
sidechainPartition, trace
} from "@thi.ng/rstream";
// queue event processing to only execute during the
// requestAnimationFrame cycle (RAF)
sidechainPartition(
// merge various event streams
merge([
fromEvent(document, "mousemove"),
fromEvent(document, "mousedown"),
fromEvent(document, "mouseup")
]),
// sidechain control stream
fromRAF()
).subscribe(trace());
Since v8.0.0 there's
syncRAF(),
which allows the above to be simplified to:
import { merge, fromEvent, syncRAF, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
syncRAF(
merge([
fromEvent(document, "mousemove"),
fromEvent(document, "mousedown"),
fromEvent(document, "mouseup")
])
).subscribe(trace());
Docs: sidechainToggle()
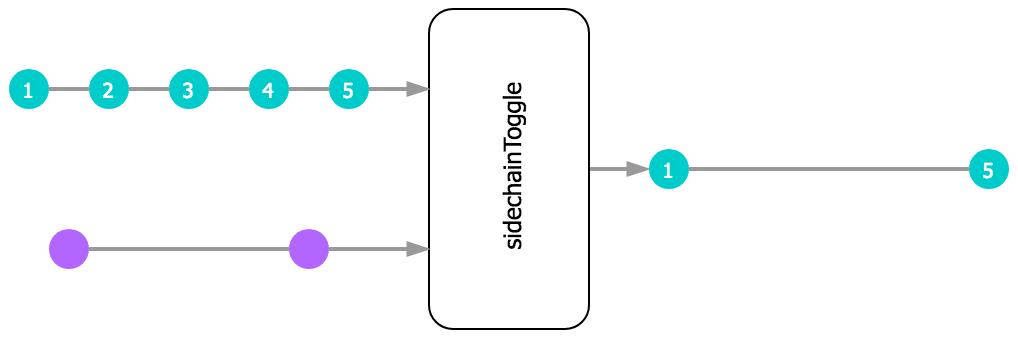
Filters values from input based on values received from side chain. By default, the value read from the side chain is ignored, however the optional predicate can be used to only trigger for specific values/conditions. Every time the predicate fn returns true, the filter will be toggled on/off. Whilst switched off, no input values will be forwarded.
import { sidechainToggle, fromInterval, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
// use slower interval stream to toggle faster main stream on/off
sidechainToggle(fromInterval(500), fromInterval(1000)).subscribe(trace());
// 0
// 3
// 4
// 7
// 8
...
Docs: sidechainTrigger()
Buffers the most recent value received and only forwards it downstream whenever a new control value is received from the sidechain.
import { sidechainTrigger, reactive, stream, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
const src = reactive("payload");
const side = stream();
sidechainTrigger(src, side).subscribe(trace("data:"));
side.next(1);
// data: payload
// every time sidechain triggers
side.next(1);
// data: payload
// only newest value will be buffered
src.next("update #1");
src.next("update #2");
// ...until side chain triggers again
side.next(1);
// data: update #2
Docs: forkJoin()
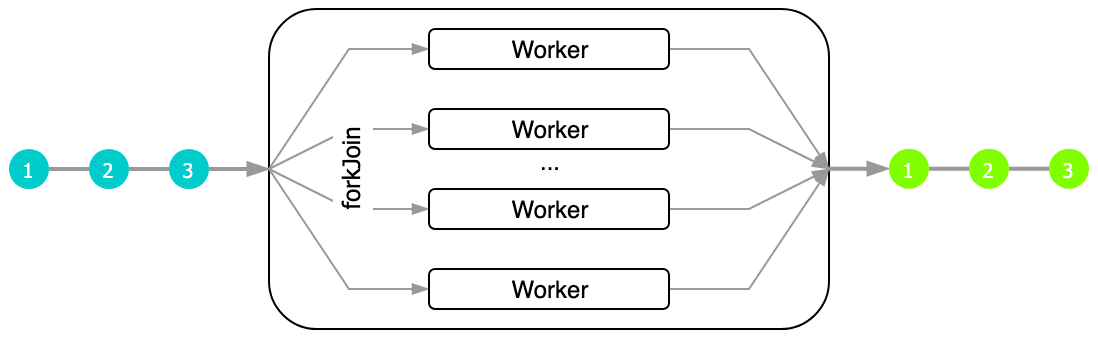
const $self: Worker = <any>self;
self.addEventListener("message", (e) => {
const { buf, factor } = e.data;
$self.postMessage(buf.map((x) => x * factor));
});
import { forkJoin, trace } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
const src = stream<number[]>();
// fork worker jobs & re-join results
forkJoin({
src: src,
// worker job preparation
// this function is called for each worker ID and the results
// of that function are the messages sent to the workers...
fork: (id, numWorkers, buf) => {
const size = (buf.length / numWorkers) | 0;
return {
buf: id < numWorkers - 1
? buf.slice(id * size, (id + 1) * size)
: buf.slice(id * size),
factor: id * 10
};
},
// re-join worker results
join: (parts) => <number[]>Array.prototype.concat.apply([], parts),
// worker script
worker: "./worker.js",
// default: navigator.hardwareConcurrency
numWorkers: 4
}).subscribe(trace("results"));
src.next(new Array(16).fill(1));
// result: [0, 0, 0, 0, 10, 10, 10, 10, 20, 20, 20, 20, 30, 30, 30, 30]
Docs: tunnel()
Delegate stream value processing to workers and pass on their responses to downstream subscriptions. Supports multiple worker instances and worker termination / restart for each new stream value received.
Docs: postWorker()
Send values to workers (incl. optional (inline) worker instantiation)
Docs: fromWorker()
Create value stream from worker messages.
Detailed information, discussion & diagrams about the new error handling can be found in this issue
The ISubscriber interface supports optional error handlers which will be
called if code in the next() or done() handlers throws an error. If no error
handler is defined for a subscriber, the wrapping Subscription's own error
handler will be called, which might put this subscription into an error state
and stop it from receiving new values.
import { subscription, State } from "@thi.ng/rstream";
src = subscription({ next(x) { throw x; } });
// triggers error, caught by subscription wrapper
src.next(1);
// sub-0 unhandled error: 1
src.getState() === State.ERROR
// true
// no error, but also inputs won't be received/processed either
src.next(2)
// another sub with error handler & indicating error could be handled
src = subscription({
next(x) { throw x; },
error(x) { console.warn("eeek", x); return true; }
});
// error caught by given handler
src.next(1)
// eeek 1
// sub still usable, no error
src.getState() !== State.ERROR
// true
// further inputs still accepted
src.next(2)
// eeek 2
If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-rstream,
title = "@thi.ng/rstream",
author = "Karsten Schmidt and others",
note = "https://thi.ng/rstream",
year = 2017
}
© 2017 - 2025 Karsten Schmidt // Apache License 2.0
FAQs
Reactive streams & subscription primitives for constructing dataflow graphs / pipelines
We found that @thi.ng/rstream demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
PyPI now allows maintainers to archive projects, improving security and helping users make informed decisions about their dependencies.

Research
Security News
Malicious npm package postcss-optimizer delivers BeaverTail malware, targeting developer systems; similarities to past campaigns suggest a North Korean connection.

Security News
CISA's KEV data is now on GitHub, offering easier access, API integration, commit history tracking, and automated updates for security teams and researchers.