
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
@transifex/react
Advanced tools
Transifex Native is a full end-to-end, cloud-based localization stack for moderns apps.
React component for localizing React application using Transifex Native.
Related packages:
Learn more about Transifex Native in the Transifex Developer Hub.
Step1: Create a Transifex Native project in Transifex.
Step2: Grab credentials.
Step3: Internationalize the code using the SDK.
Step4: Push source phrases using the @transifex/cli tool.
Step5: Translate the app using over-the-air updates.
No translation files required.
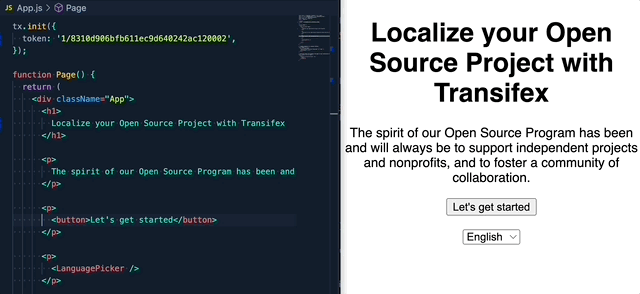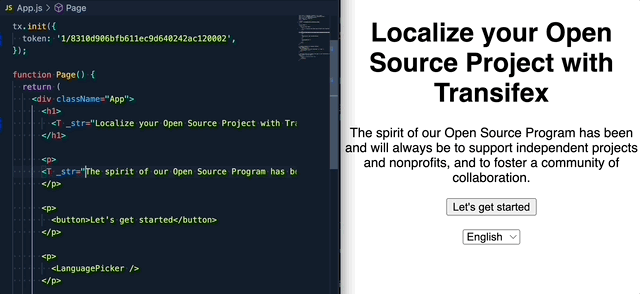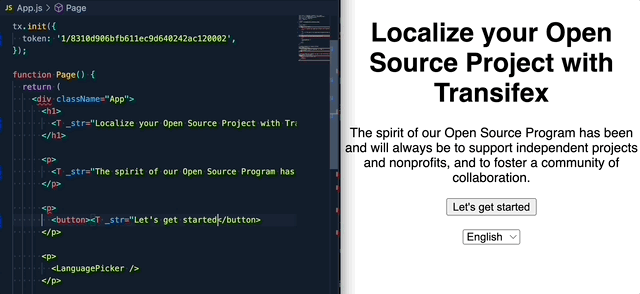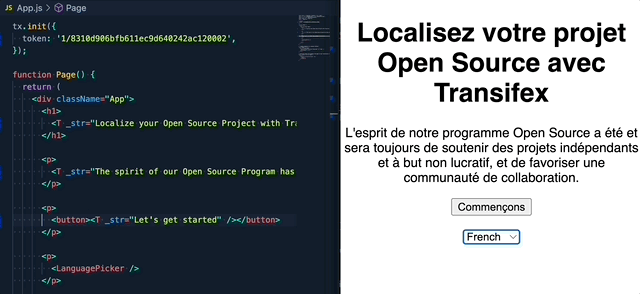
If you are upgrading from the 1.x.x version, please read this migration guide, as there are breaking changes in place.
Install the library and its dependencies using:
npm install @transifex/native @transifex/react --save
T Componentimport React from 'react';
import { T } from '@transifex/react';
function Example() {
return (
<div>
<T _str="Hello world" />
<T _str="Hello {username}" username={user} />
</div>
);
}
Available optional props:
| Prop | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _context | String | String context, affects key generation |
| _key | String | Custom string key |
| _comment | String | Developer comment |
| _charlimit | Number | Character limit instruction for translators |
| _tags | String | Comma separated list of tags |
The T-component can accept React elements as properties and they will be rendered properly, ie this would be possible:
<T
_str="A {button} and a {bold} walk into a bar"
button={<button><T _str="button" /></button>}
bold={<b><T _str="bold" /></b>} />
This will render like this in English:
A <button>button</button> and a <b>bold</b> walk into a bar
And like this in Greek:
Ένα <button>κουμπί</button> και ένα <b>βαρύ</b> μπαίνουν σε ένα μπαρ
Assuming the translations look like this:
| source | translation |
|---|---|
| A {button} and a {bold} walk into a bar | Ένα {button} και ένα {bold} μπαίνουν σε ένα μπαρ |
| button | κουμπί |
| bold | βαρύ |
The main thing to keep in mind is that the _str property to the T-component
must always be a valid ICU messageformat template.
UT Componentimport React from 'react';
import { UT } from '@transifex/react';
function Example () {
return (
<div>
<UT _str="Hello <b>{username}</b>" username={user} />
<p>
<UT _str="Hello <b>{username}</b>" _inline username={user} />
</p>
</div>
)
}
UT has the same behaviour as T, but renders source string as HTML inside a
div tag.
Available optional props: All the options of T plus:
| Prop | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _inline | Boolean | Wrap translation in span |
Note: If you supply React elements as properties to the UT component, it
will misbehave by rendering [object Object]. Only use React elements as
properties with the T component.
useT hookMakes the current component re-render when a language change is detected and returns a t-function you can use to translate strings programmatically.
You will most likely prefer to use the T or UT components over this, unless
for some reason you want to have the translation output in a variable for
manipulation.
import React from 'react';
import { useT } from '@transifex/react';
function Capitalized() {
const t = useT();
const message = t('Hello world');
return <span>{message.toUpperCase()}</span>;
}
useLanguages hookReturns a state variable that will eventually hold the supported languages of the application. Makes an asynchronous call to the CDS.
import React from 'react';
import { useLanguages } from '@transifex/react';
function LanguageList () {
const languages = useLanguages();
return (
<ul>
{languages.map(({ code, name }) => (
<li key={code}>
<strong>{code}</strong>: {name}
</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
useLocale hookReturns a state variable with the currently selected locale.
import React from 'react';
import { useLocale } from '@transifex/react';
function DisplayLocale () {
const locale = useLocale();
return (
<p>Currently selected locale is {locale}</p>
);
}
useTX hookReturns a state variable with the Native instance.
import React from 'react';
import { useTX } from '@transifex/react';
function SetLocale () {
const tx = useTX();
return (
<button onClick={() => tx.setCurrentLocale('el')}>
Set to Greek
</button>
);
}
LanguagePicker componentRenders a <select> tag that displays supported languages and switches the
application's selected language on change.
Uses useLanguages and useLocale internally.
import React from 'react';
import { T, LanguagePicker } from '@transifex/react';
function App () {
return (
<div>
<T _str="This is a translatable message" />
<LanguagePicker />
</div>
);
}
Accepts properties:
className: The CSS class that will be applied to the <select> tagIf you want something different than a <select>, it should be easy to write
your own language picker using useLanguages:
import React from 'react';
import { tx } from '@transifex/native';
import { useLanguages, useLocale } from '@transifex/react';
function MyLanguagePicker () {
const languages = useLanguages();
const locale = useLocale();
return (
<>
{languages.map(({ code, name }) => (
<button key={code} onClick={() => tx.setCurrentLocale(code)}>
{name} {locale === code ? '(selected)' : ''}
</button>
))}
</>
);
}
useTranslations hook - aka Lazy LoadingFetches translations tagged with a specific combination of tags when a component first renders. This way, you can pull translations from the CDS in batches and only when needed:
tx.init({ token: ..., filterTags: 'home' });
export default function App() {
return (
<>
<T _str="This will be translated as soon as possible" _tags="home" />
{someCondition() && <Inner />}
</>
);
}
function Inner() {
useTranslations('inner');
return <T
_str="This will be translated when the inner component is rendered"
_tags="inner" />;
}
The hook returns a boolean state variable called ready that you can use to
handle a loading state:
function Inner() {
const { ready } = useTranslations('inner');
if (!ready) { return 'Loading...'; }
return <T
_str="This will be translated when the inner component is rendered"
_tags="inner" />;
}
If you don't handle the loading state, the source string will be rendered first and then replaced with the translation when it becomes available.
You can also use the hook in parent components that don't need the tagged translations themselves. This will make the translations available sooner for child components that may potentially need them:
tx.init({ token: ..., filterTags: 'home' });
export default function App() {
const { ready: innerReady } = useTranslations('inner');
return (
<>
<T _str="This will be translated as soon as possible" _tags="home" />
{someCondition() && <Inner ready={innerReady} />}
</>
);
}
function Inner({ ready }) {
if (!ready) { return 'Loading...'; }
return <T
_str="This will be translated when the inner component is rendered"
_tags="inner" />;
}
TXProvider providerIf you need to use more than one Transifex Native instances - like for example if you have a component library - you can use this provider to pass the desired instance to the children components.
import { tx, createNativeInstance } from '@transifex/native';
import { TXProvider, LanguagePicker, T } from '@transifex/react';
const myOtherTXInstance = createNativeInstance();
myOtherTXInstance.init({ token: 'othertoken' })
tx.init({
token: 'token',
});
// Make tx aware of the other instances so they can be synced when changing
// language
tx.controllerOf(myOtherTXInstance);
export default function App() {
return (
<>
<LanguagePicker />
<TXProvider instance={myOtherTXInstance}>
<T _str="Hello {username}" username="John" />
</TXProvider>
<T _str="Hello World" />
</>
);
}
Licensed under Apache License 2.0, see LICENSE file.
FAQs
i18n React framework using Transifex Native
We found that @transifex/react demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.