Security News
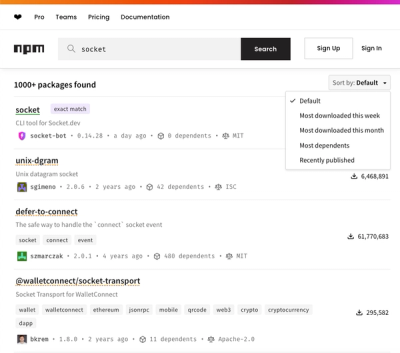
npm Updates Search Experience with New Objective Sorting Options
npm has a revamped search experience with new, more transparent sorting options—Relevance, Downloads, Dependents, and Publish Date.
Build scalable REST APIs using the open source tools and standards you already know.
Baucis enables you to build scalable REST APIs using the open source tools and standards you and your team already know.
Baucis is tested with over 130 Mocha.js tests. Baucis is used in production by at least one Fortune 500 company.
Donations via gittip.com welcome.
Check the change log for info on all the latest features.
Like Baucis and Philemon of old, the module provides REST to the weary traveler. Baucis is not the same as Bacchus.

David Rijckaert - Philemon and Baucis Giving Hospitality to Jupiter and Mercury
To install:
npm install baucis
An example of creating a REST API from a couple Mongoose schemata:
var Vegetable = new mongoose.Schema({ name: String });
var Fruit = new mongoose.Schema({ name: String });
// Note that Mongoose middleware will be executed as usual
Vegetable.pre('save', function () { ... });
// Register the schemata
mongoose.model('vegetable', Vegetable);
mongoose.model('fruit', Fruit);
// Create the API routes
baucis.rest('vegetable');
baucis.rest('fruit');
// Create the app and listen for API requests
var app = express();
app.use('/api', baucis());
app.listen(80);
Later, make requests:
| HTTP Verb | /vegetables | /vegetables/:id |
|---|---|---|
| GET | Get all or a subset of documents | Get the addressed document |
| POST | Creates new documents and sends them back. You may post a single document or an array of documents. | n/a |
| PUT | n/a | Update the addressed document |
| DELETE | Delete all or a subset of documents | Delete the addressed object |
| Header Field | Notes |
|---|---|
| ETag | Used for HTTP caching based on response body. Supported out-of-the-box by Express. |
| Last-Modified | Used for HTTP caching. Can be set automatically by Baucis. Pass lastModified: 'foo' to baucis.rest in order to set the path to be used (currently it must be a Date). GET requests to the collection set this to the latest date out of all documents returned by the query. |
| Accept | Set to application/json for all responses. |
| Allow | Set automatically, correctly removing HTTP verbs when those verbs have been disabled by e.g. passing put: false to baucis.rest. Example: Allow: HEAD, GET, POST. |
| Location | Set to the URL of the created/edited entity for PUT and POST responses. |
| Link | If relations: true is passed to baucis.rest, this header will be set with various related links for all responses. As of v0.5.4, first, last, next, and previous links are added when paging through a collection with limit/skip. |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | Set the Mongoose query's find or remove arguments |
| skip | Don't send the first n matched documents in the response |
| limit | Limit the response document count to n |
| select | Set which fields should be selected for response documents |
| sort | Sort response documents by the given criteria. sort: 'foo -bar'' sorts the collection by foo in ascending order, then by bar in descending order. |
| populate | Set which fields should be populated for response documents. See the Mongoose population documentation for more information. |
| count | May be set to true for GET requests to specify that a count should be returned instead of documents |
| distinct | Set to a path name to query for distinct valuse for that path matching given conditions. |
| hint | Add an index hint to the query (must be enabled per controller). |
| comment | Add a comment to a query (must be enabled per controller). |
It is not permitted to use the select query option to select deselected paths. This is to allow a mechanism for hiding fields from client software.
The select option of populate is disallowed. Only paths deselected at the model level will be deselected in populate queries.
You can deselect paths in the schema definition using select: false or in the controller options using select: '-foo' and your server middleware will be able to select these fields as usual using query.select, while preventing the client from selecting the field.
baucis.restbaucis.rest returns an instance of the controller created to handle the schema's API routes.
var controller = baucis.rest({ ... });
For simple controllers, only the schema name need be passed.
var controller = baucis.rest('robot');
Controllers are Express apps; they may be used as such.
var controller = baucis.rest('robot');
// Add middleware before API routes
controller.use('/qux', function (request, response, next) {
// Do something cool…
next();
});
controller.get('/readme', function (request, response, next) {
// Send a readme document about the resource (for example)
next();
});
// Do other stuff...
controller.set('some option name', 'value');
controller.listen(3000);
Customize them with plain old Express/Connect middleware, including pre-existing modules like passport. Middleware can be registered like so:
controller.request(function (request, response, next) {
if (request.isAuthenticated()) return next();
return response.send(401);
});
Baucis adds middleware registration functions for three stages of the request cycle:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| request | This stage of middleware will be called after baucis applies defaults based on the request, but before the Mongoose query is generated |
| query | This stage of middleware will be called after baucis applies defaults to the Mongoose query object, but before the documents or count are retrieved from the database. The query can be accessed in your custom middleware via request.baucis.query. Query middleware cannot be added explicitly for POST and will be ignored when added for POST implicitly. |
| documents | This stage of middleware will be called after baucis executes the query, but before the documents or count are sent in the response. The documents/count can be accessed in your custom middleware via request.baucis.documents. |
Each of these functions has three forms:
To apply middleware to all API routes, just pass the function or array to the method for the appropriate stage:
controller.request(function (request, response, next) {
if (request.isAuthenticated()) return next();
return response.send(401);
});
controller.documents(function (request, response, next) {
if (typeof request.baucis.documents === 'number') return next();
if (!Array.isArray(request.baucis.documents)) return next();
request.baucis.documents.pop();
next();
});
To add middleware that applies only to specific HTTP verbs, use the second form. It adds a paramater that must contain a space-delimted list of HTTP verbs that the middleware should be applied to.
controller.query('head get put', function (request, response, next) {
request.baucis.query.sort('-created');
next();
});
The final form is the most specific. The first argument lets you specify whether the middleware applies to document instances (paths like /foos/:id) or to collection requests (paths like /foos).
controller.request('instance', 'head get del', middleware);
controller.request('collection', 'post', middleware);
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| singular | The name of the schema, as registered with mongoose.model. |
| plural | This will be set automatically using the lingo module, but may be overridden by passing it into baucis.rest. |
| model | The name of the mongoose model. This will be set to the value of singular by default (and vice versa). A mongoose model may also be passed in. |
| basePath | Defaults to /. Used for embedding a controller in another controller. |
| publish | Set to false to not publish the controller's endpoints when baucis() is called. |
| select | Select or deselect fields for all queries e.g. 'foo +bar -password' |
| relations | Set to true to add various relationship headers for paging, etc. |
| findBy | Use another field besides _id for entity queries. |
| lastModified | Set the Last-Modified HTTP header using the given field. Currently this field must be a Date. |
| allow push | BYPASSES VALIDATION Allow using X-Baucis-Update-Operator to push to a document's path. |
| allow pull | BYPASSES VALIDATION Allow using X-Baucis-Update-Operator to pull from a document's path. |
| allow set | BYPASSES VALIDATION Allow using X-Baucis-Update-Operator to set a document's path. |
| allow hints | Allow sending an index hint from the client. |
| allow comments | Allow sending a query comment from the client. |
| head, get, post, put, del | May be set to false to disable those HTTP verbs completely for the controller |
| locking | Enable optimistic locking. Requires that all PUTs must send the document version (__v) and will send a 409 response if there is a version conflict. |
An example of embedding a controller within another controller
var subcontroller = baucis.rest({
singular: 'bar',
basePath: '/:fooId/bars',
publish: false
});
subcontroller.query(function (request, response, next) {
// Only retrieve bars that are children of the given foo
request.baucis.query.where('parent', request.params.fooId);
next();
});
var controller = baucis.rest('foo');
// Embed the subcontroller at /foos/:fooId/bars
controller.use(subcontroller);
Want to check it out now? Install the plugin:
npm install --save baucis-swagger
Next, download the swagger-ui client.
git clone git@github.com:wordnik/swagger-ui.git
open swagger-ui/dist/index.html
Then, create your API with the swagger option enabled:
var baucis = require('baucis');
var swagger = require('baucis-swagger');
app.use('/api', baucis());
Point the swagger client at your API. Something like:
http://localhost:8012/api/api-docs
Now you have documentation and a test client!
To customize the swagger definition, simply alter the controler's swagger data directly:
var controller = baucis.rest('sauce');
controller.swagger.apis.push({
'path': '/sauces/awesome',
'description': 'Awesome sauce.',
'operations': [
{
'httpMethod': 'GET',
'nickname': 'getAwesomeSauce',
'responseClass': 'Sauce',
'summary': 'Carolina BBQ Sauce.'
}
]
});
controller.swagger.models may also be directly modified.
Versioning is implemented using semver. Supported releases are specified when calling baucis(). The release(s) that a controller belongs to are specified with the versions controller option.
baucis.rest({ singular: 'cat', versions: '0.0.1' });
baucis.rest({ singular: 'cat', versions: '>0.0.1 <1.0.0' });
baucis.rest({ singular: 'cat', versions: '~1' });
baucis.rest({ singular: 'cat', versions: '>2.0.0' });
app.use('/api', baucis({ releases: [ '0.0.1', '0.0.2', '1.0.0', '1.1.0', '2.0.0' ]}));
Later, make requests and set the API-Version header to a semver range, such as ~1, >2 <3, *, etc. Baucis will use the highest release number that satisfies the range.
API versioning is almost stable. Names of controller parameters or request header may change.
As of v0.16.0 baucis takes full advantage of Node streams internally to offer even more performance, especially when dealing with large datasets. Both outgoing and incoming documents are streamed! This means that large datasets do not need to be completely loaded into RAM before sending or receiving documents.
Instead of accessing request.body or request.baucis.documents, you can add a transform stream to the incoming or outgoing document pipeline.
As a shortcut, a map function can be passed in. It will be used to create a map stream internally.
controller.request(function (request, response, next) {
request.baucis.incoming(function (doc, callback) {
doc.name = 'Feverfew';
callback(null, doc);
});
next();
});
Passing in through streams is also allowed. Here's an example using the through module to create a stream that checks for a forbidden sort of whiskey and alters the name of incoming (POSTed) documents.
controller.request(function (request, response, next) {
request.baucis.incoming(through(function (doc) {
if (doc.whiskey === 'Canadian') {
// Errors will be passed off to `next` later, and the stream will
// be stopped.
this.emit('error', new Error('Too smooth.'));
return;
}
doc.name = 'SHAZAM';
this.queue(doc);
}));
next();
});
Here's an example of how a stream that interacts with outgoing documents may be added:
controller.request(function (request, response, next) {
request.baucis.outgoing(through(function (doc) {
if (doc.owner !== request.user) {
// Errors will be passed off to `next` later, and the stream will
// be stopped.
this.emit('error', baucis.errors.Forbidden());
return;
}
delete doc.password;
this.queue(doc);
}));
next();
});
Migration notes:
request.body is present, the incoming request will be parsed before being streamed, negating many of the benefits of streaming. However, especiall when POSTing only one new document at a time, this is not an issue. If you want to POST many objects at once, using the default streaming behavior is highly recommened.request.baucis.documents for non-streaming access is being considered, however, so this feature and related areas are a bit unstable at the moment.© 2012-2014 William P. Riley-Land
FAQs
Build scalable REST APIs using the open source tools and standards you already know.
The npm package baucis receives a total of 17 weekly downloads. As such, baucis popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that baucis demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
npm has a revamped search experience with new, more transparent sorting options—Relevance, Downloads, Dependents, and Publish Date.

Security News
A supply chain attack has been detected in versions 1.95.6 and 1.95.7 of the popular @solana/web3.js library.

Research
Security News
A malicious npm package targets Solana developers, rerouting funds in 2% of transactions to a hardcoded address.