botstream
stream-based bot micro framework
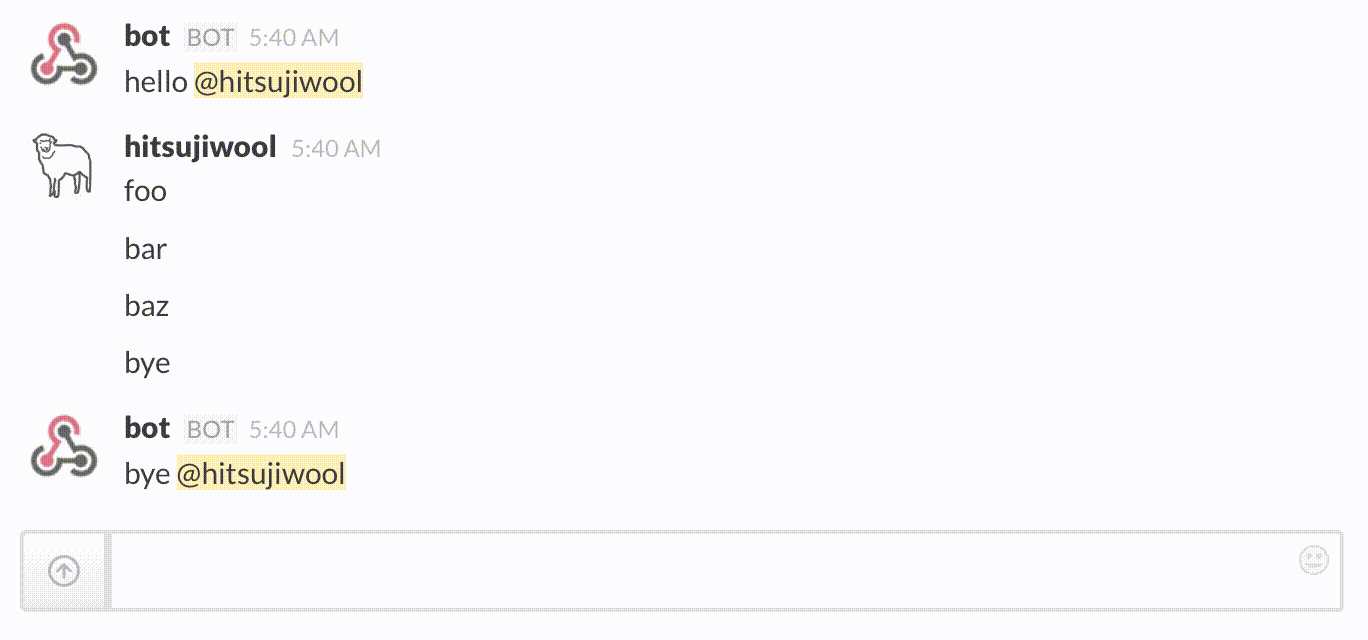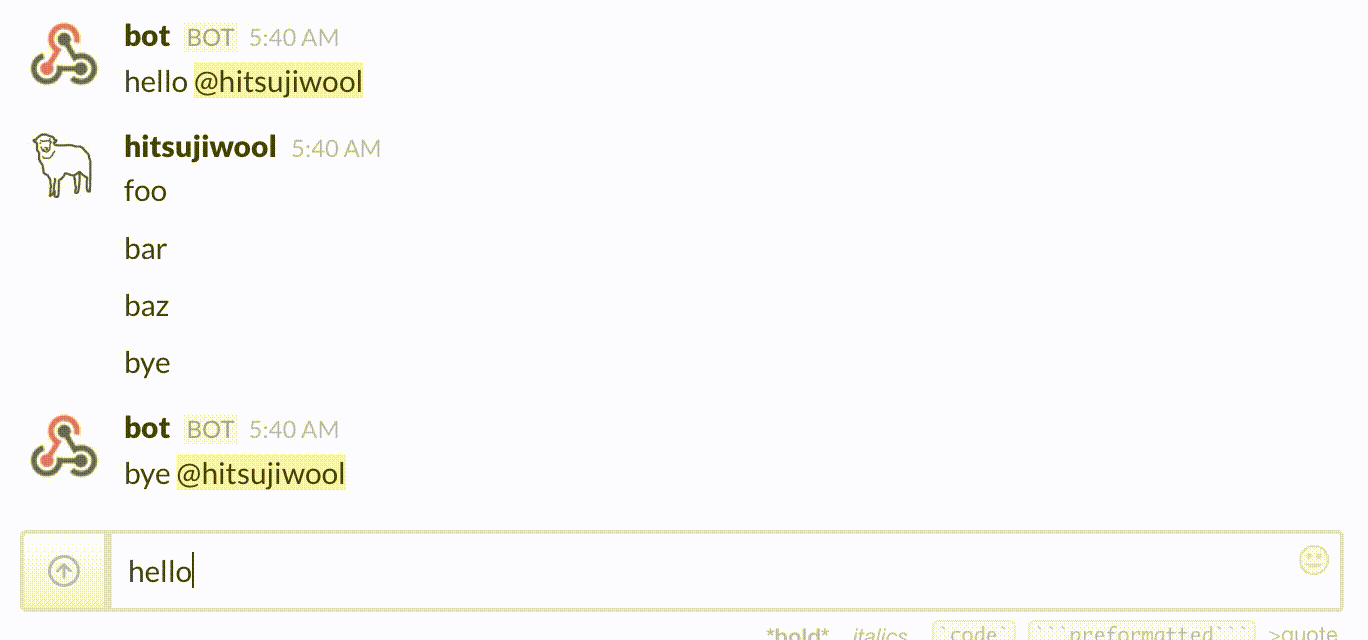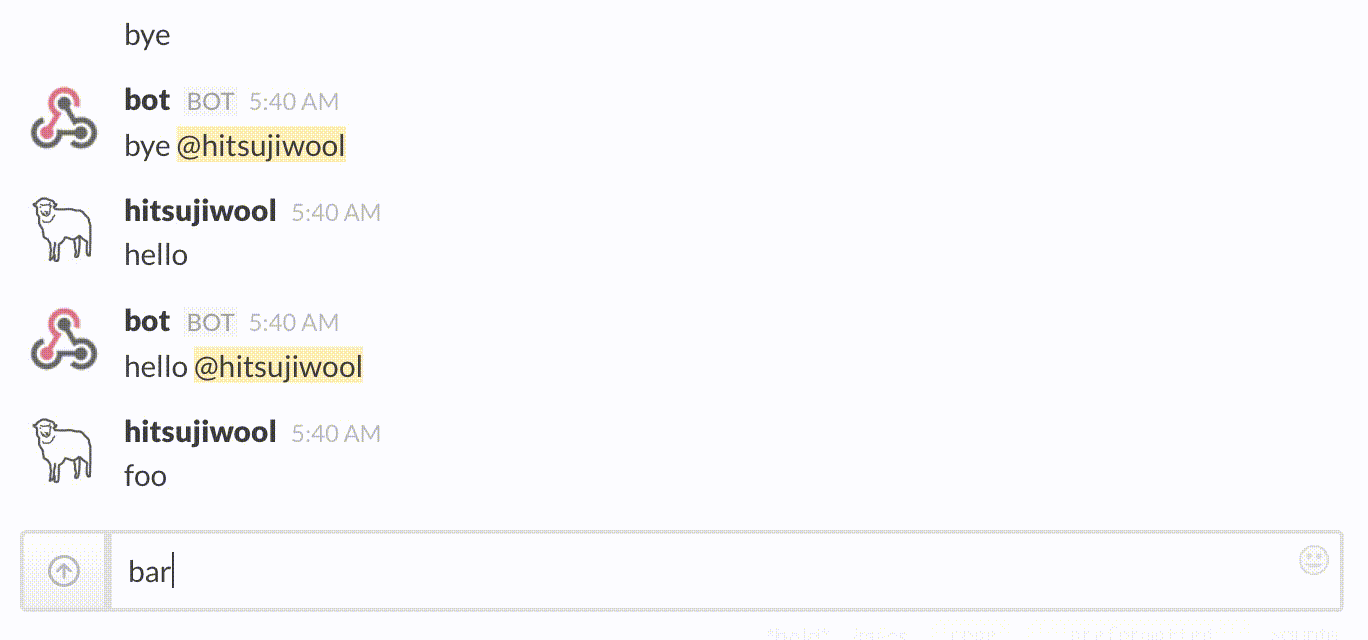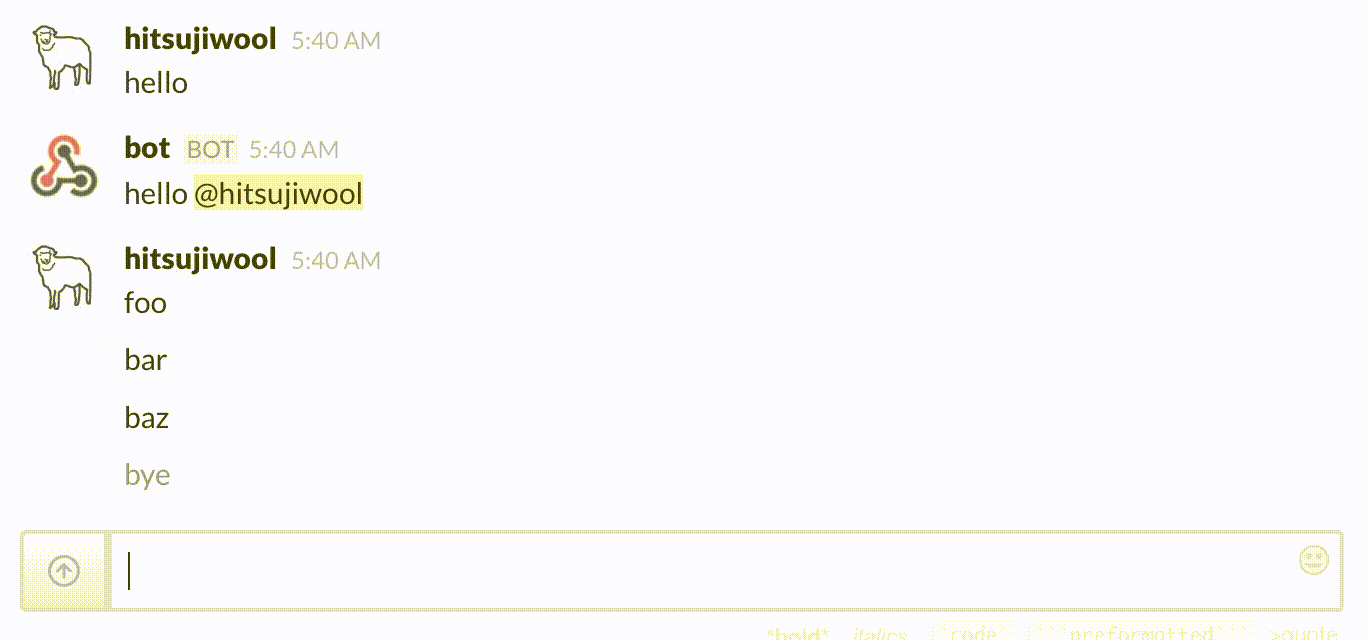
Example
1. Define Message Parser (from slack)
Parse slack outgoing webhooks POST payload and convert it to an event object with properties user and input.
var parse = require('querystring').parse;
var through = require('through');
function slackParser(options) {
var buffer = [];
return through(function(data) {
buffer.push(data.toString('utf8'));
}, function() {
var parsed = parse(buffer.join(''));
if (parsed.user_name !== 'slackbot') {
this.queue({
user: parsed.user_name,
input: parsed.text
});
}
this.queue(null);
});
};
2. Define Actions
Here we define some rules to compose the outgoing message. Action must be defined as a function which returns a through (both readable and writable) stream.
function hello() {
return through(function(event) {
event.output = "hello " + event.user;
this.queue(event);
});
}
function bye() {
return through(function(event) {
event.output = "bye " + event.user;
this.queue(event);
});
}
3. Define Outgoing (to slack)
Convert event object to slack response format.
function slackOutgoing() {
return through(function(event) {
this.queue(JSON.stringify({ text: event.output }));
});
};
4. Register Actions
Integrate all the functions into a botstream application.
var botstream = require('botstream');
var actions = botstream.select()
.case(/hello/, hello)
.case(/bye/, bye)
.default();
var bot = botstream.app(slackParser)
.register(actions)
.register(slackOutgoing);
5. Mount to HTTP(S)
Pipe it from/to existing application. Whatever application which implements stream interface is available.
app.post('/bot', function(req, res) {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
req.pipe(bot.stream()).pipe(res);
});




