
Research
Security News
Quasar RAT Disguised as an npm Package for Detecting Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.
chrome-cookies-secure-ts
Advanced tools
Extract encrypted Google Chrome cookies for a url on a Mac or Linux
Extract encrypted Google Chrome cookies for a url on Mac OS X, Windows, or Linux
npm install chrome-cookies-secure
url should be a fully qualified url, e.g. https://www.example.com/path
format is optional and can be one of the following values:
| format | description |
|---|---|
| curl | Netscape HTTP Cookie File contents usable by curl and wget |
| jar | cookie jar compatible with request |
| set-cookie | Array of Set-Cookie header values |
| header | cookie header string, similar to what a browser would send |
| puppeteer | an array of objects that can be loaded into puppeteer using the setCookie(...) method |
| object | (default) Object where key is the cookie name and value is the cookie value. These are written in order so it's possible that duplicate cookie names will be overriden by later values |
If format is not specified, object will be used as the format by default.
Cookie order tries to follow RFC 6265 - Section 5.4, step 2 as best as possible.
const chrome = require('chrome-cookies-secure');
chrome.getCookies('https://www.example.com/path/', function(err, cookies) {
console.log(cookies);
});
const request = require('request');
const chrome = require('chrome-cookies-secure');
chrome.getCookies('https://www.example.com/', 'jar', function(err, jar) {
request({url: 'https://www.example.com/', jar: jar}, function (err, response, body) {
console.log(body);
});
});
const chrome = require('chrome-cookies-secure');
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
const url = 'https://www.yourUrl.com/';
const getCookies = (callback) => {
chrome.getCookies(url, 'puppeteer', function(err, cookies) {
if (err) {
console.log(err, 'error');
return
}
console.log(cookies, 'cookies');
callback(cookies);
}, 'yourProfile') // e.g. 'Profile 2'
}
getCookies(async (cookies) => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({
headless: false
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.setCookie(...cookies);
await page.goto(url);
await page.waitFor(1000);
browser.close();
});
const chrome = require('chrome-cookies-secure');
const url = 'https://www.yourUrl.com/';
const myFunction = async () => {
const cookies = await chrome.getCookiesPromised(url, 'puppeteer', 'Profile 28')
// ..... Use the cookies
}
On OS X, this module requires Keychain Access to read the Google Chrome encryption key. The first time you use it, it will popup this dialog:
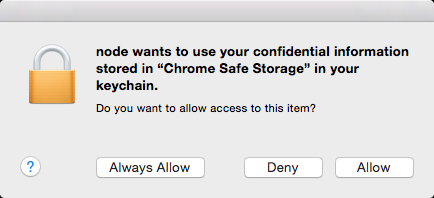
The SQLite database that Google Chrome stores its cookies is only persisted to every 30 seconds or so, so this can explain while you'll see a delay between which cookies your browser has access to and this module.
This software is free to use under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for license text and copyright information.
FAQs
Extract encrypted Google Chrome cookies for a url on a Mac or Linux
We found that chrome-cookies-secure-ts demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.

Security News
Research
A supply chain attack on Rspack's npm packages injected cryptomining malware, potentially impacting thousands of developers.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers discovered a malware campaign on npm delivering the Skuld infostealer via typosquatted packages, exposing sensitive data.