
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Packages Inject SSH Backdoors via Typosquatted Libraries
Socket’s threat research team has detected six malicious npm packages typosquatting popular libraries to insert SSH backdoors.
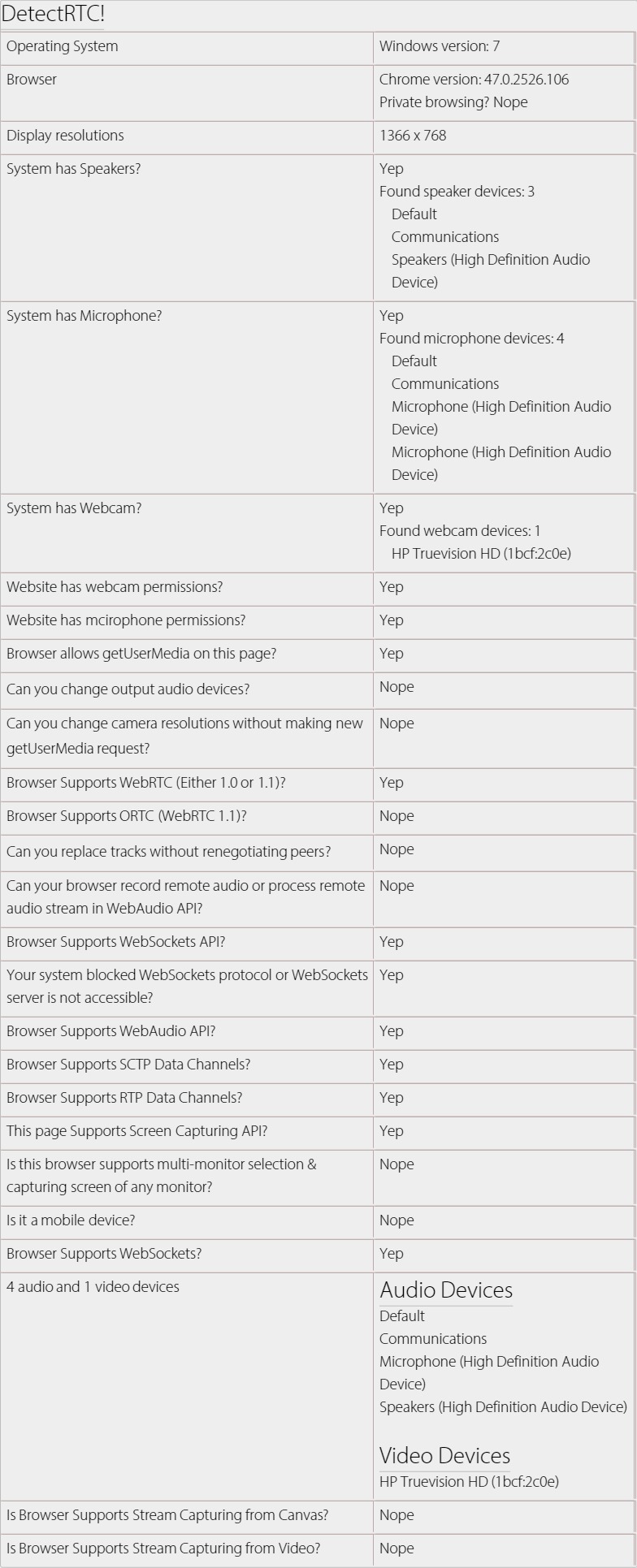
A tiny JavaScript library that can be used to detect WebRTC features e.g. system having speakers, microphone or webcam, screen capturing is supported, number of audio/video devices etc.
if (DetectRTC.isWebRTCSupported === false) {
alert('Please use Chrome or Firefox.');
}
if (DetectRTC.hasWebcam === false) {
alert('Please install an external webcam device.');
}
if (DetectRTC.hasMicrophone === false) {
alert('Please install an external microphone device.');
}
if (DetectRTC.hasSpeakers === false && (DetectRTC.browser.name === 'Chrome' || DetectRTC.browser.name === 'Edge')) {
alert('Oops, your system can not play audios.');
}
A tiny JavaScript library that can be used to detect WebRTC features e.g. system having speakers, microphone or webcam, screen capturing is supported, number of audio/video devices etc.
It is MIT Licenced, which means that you can use it in any commercial/non-commercial product, free of cost.
npm install detectrtc --production
# or via "bower"
bower install detectrtc
DetectRTC.isSetSinkIdSupported // (implemented)
DetectRTC.isRTPSenderReplaceTracksSupported // (implemented)
DetectRTC.isORTCSupported // (implemented)
DetectRTC.isRemoteStreamProcessingSupported // (implemented)
DetectRTC.isWebsiteHasWebcamPermissions // (implemented)
DetectRTC.isWebsiteHasMicrophonePermissions // (implemented)
DetectRTC.audioInputDevices // (implemented)
DetectRTC.audioOutputDevices // (implemented)
DetectRTC.videoInputDevices // (implemented)
// Below API are NOT implemented yet
DetectRTC.browser.googSupportedFlags.googDAEEchoCancellation
DetecRTC.browser.googSupportedFlags.echoCancellation
DetectRTC.isMediaHintsSupportsNewSyntax
node server.js
# or
npm start
# and open:
http://127.0.0.1:9001
# or
http://localhost:9001
var DetectRTC = require('detectrtc');
console.log(DetectRTC.browser);
DetectRTC.load(function() {
console.log(DetectRTC);
});
Or try npm-test.js:
cd node_modules
cd detectrtc
# npm test
# or
node npm-test.js
<script src="./node_modules/detectrtc/DetectRTC.js"></script>
<!-- or bower -->
<script src="./bower_components/detectrtc/DetectRTC.js"></script>
<!-- or CDN link (suggested) -->
<script src="https://cdn.webrtc-experiment.com/DetectRTC.js"></script>
<!-- or RawGit (if CDN fails) -->
<script src="https://cdn.rawgit.com/muaz-khan/DetectRTC/master/DetectRTC.js"></script>
You can even link specific versions:
<script src="https://github.com/muaz-khan/DetectRTC/releases/download/1.3.6/DetectRTC.js"></script>
// for node.js users
var DetectRTC = require('detectrtc');
// non-nodejs users can skip above line
// below code will work for all users
DetectRTC.load(function() {
DetectRTC.hasWebcam; // (has webcam device!)
DetectRTC.hasMicrophone; // (has microphone device!)
DetectRTC.hasSpeakers; // (has speakers!)
DetectRTC.isScreenCapturingSupported; // Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Edge and Android
DetectRTC.isSctpDataChannelsSupported;
DetectRTC.isRtpDataChannelsSupported;
DetectRTC.isAudioContextSupported;
DetectRTC.isWebRTCSupported;
DetectRTC.isDesktopCapturingSupported;
DetectRTC.isMobileDevice;
DetectRTC.isWebSocketsSupported;
DetectRTC.isWebSocketsBlocked;
DetectRTC.checkWebSocketsSupport(callback);
DetectRTC.isWebsiteHasWebcamPermissions; // getUserMedia allowed for HTTPs domain in Chrome?
DetectRTC.isWebsiteHasMicrophonePermissions; // getUserMedia allowed for HTTPs domain in Chrome?
DetectRTC.audioInputDevices; // microphones
DetectRTC.audioOutputDevices; // speakers
DetectRTC.videoInputDevices; // cameras
DetectRTC.osName;
DetectRTC.osVersion;
DetectRTC.browser.name === 'Edge' || 'Chrome' || 'Firefox';
DetectRTC.browser.version;
DetectRTC.browser.isChrome;
DetectRTC.browser.isFirefox;
DetectRTC.browser.isOpera;
DetectRTC.browser.isIE;
DetectRTC.browser.isSafari;
DetectRTC.browser.isEdge;
DetectRTC.browser.isPrivateBrowsing; // incognito or private modes
DetectRTC.isCanvasSupportsStreamCapturing;
DetectRTC.isVideoSupportsStreamCapturing;
DetectRTC.DetectLocalIPAddress(callback);
});
DetectRTC.versionDetectRTC is supporting version property since 1.3.6.
``javascript if(DetectRTC.version === '1.3.6') { alert('We are using DetectRTC version 1.3.6'); }
# Why `load` method?
If you're not detecting audio/video input/output devices then you can skip this method.
`DetectRTC.load` simply makes sure that all devices are captured and valid result is set for relevant properties.
# How to fix devices' labels?
You need to check for `device.isCustomLabel` boolean. If this boolean is `true` then assume that DetectRTC given a custom label to the device.
You must getUserMedia request whenever you find `isCustomLabel===true`. getUserMedia request will return valid device labels.
```javascript
if (DetectRTC.MediaDevices[0] && DetectRTC.MediaDevices[0].isCustomLabel) {
// it seems that we did not make getUserMedia request yet
navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({
audio: true,
video: true
}).then(function(stream) {
var video;
try {
video = document.createElement('video');
video.muted = true;
video.src = URL.createObjectURL(stream);
video.style.display = 'none';
(document.body || document.documentElement).appendChild(vide);
} catch (e) {}
DetectRTC.load(function() {
DetectRTC.videoInputDevices.forEach(function(device, idx) {
// ------------------------------
// now you get valid label here
console.log(device.label);
// ------------------------------
});
// release camera
stream.getTracks().forEach(function(track) {
track.stop();
});
if (video && video.parentNode) {
video.parentNode.removeChild(video);
}
});
});
} else {
DetectRTC.videoInputDevices.forEach(function(device, idx) {
console.log(device.label);
});
}
Demo: https://jsfiddle.net/cf90az9q/
<script src="https://cdn.webrtc-experiment.com/DetectRTC/CheckDeviceSupport.js"></script>
<script>
function selectSecondaryCamera() {
checkDeviceSupport(function() {
var secondDevice = videoInputDevices[1];
if(!secondDevice) return alert('Secondary webcam is NOT available.');
var videoConstraints = {
deviceId: secondDevice.deviceId
};
if(!!navigator.webkitGetUserMedia) {
videoConstraints = {
mandatory: {},
optional: [{
sourceId: secondDevice.deviceId
}]
}
}
navigator.getUserMedia = navigator.mozGetUserMedia || navigator.webkitGetUserMedia;
navigator.getUserMedia({ video: videoConstraints }, function(stream) {
//
}, function(error) {
alert(JSON.stringify(error));
});
});
}
</script>
For further tricks & usages:
mkdir DetectRTC
cd DetectRTC
git clone git://github.com/muaz-khan/DetectRTC.git ./
# install grunt for code style verifications
npm install grunt-cli
# install all dependencies
npm install --save-dev
# verify your changes
# npm test # or "grunt"
grunt
# Success? Make a pull request!
Check tests here: https://travis-ci.org/muaz-khan/DetectRTC
DetectRTC.js is released under MIT licence . Copyright (c) Muaz Khan.
FAQs
A tiny JavaScript library that can be used to detect WebRTC features e.g. system having speakers, microphone or webcam, screen capturing is supported, number of audio/video devices etc.
The npm package detectrtc receives a total of 29,098 weekly downloads. As such, detectrtc popularity was classified as popular.
We found that detectrtc demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket’s threat research team has detected six malicious npm packages typosquatting popular libraries to insert SSH backdoors.

Security News
MITRE's 2024 CWE Top 25 highlights critical software vulnerabilities like XSS, SQL Injection, and CSRF, reflecting shifts due to a refined ranking methodology.

Security News
In this segment of the Risky Business podcast, Feross Aboukhadijeh and Patrick Gray discuss the challenges of tracking malware discovered in open source softare.