
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
eslint-kit
Advanced tools
✨ All-in-one solution for configuring ESLint in all of your projects ✨
The README on main branch can contain some unreleased changes.
Go to release/latest branch to see the actual README for the latest version from NPM.
no-console rule, you will get warnings during the development. This kind of checks is useful when linting code for the production (CI environment, precommit hooks), but useless in development. ESLint Kit has allowDebug option to solve this problem.ESLint Kit is solving all these problems by providing many small presets, each performing a specific task.
You can select presets by using configure function in your .eslintrc.cjs file:
const { configure, presets } = require('eslint-kit')
module.exports = configure({
mode: 'only-errors',
presets: [
presets.imports(),
presets.typescript(),
presets.prettier(),
presets.node(),
presets.react({ version: '18.0' }),
],
extend: {
rules: {
'some-rule': 'off'
}
}
})
eslint-kit dependencies are automatically updated. The configs are covered with tests, and each package update is tested. Broken plugins/rules/configs will not be deployed and will stuck at the review process, waiting for the fix by a developers.
eslint-kit package contains all the dependencies you might need. The only exception are eslint and prettier - they should be installed separately to work properly (executing yarn eslint and so on).
The ESLint Kit presets try to contain only the best-practice rules to make overwriting as rare as possible. But you can still easily override them by using extend property.
npx eslint-kit-cli@latest
Or if you want to use exactly 11 version of eslint-kit:
npx eslint-kit-cli@^11
Learn more about eslint-kit-cli
NPM:
npm install -D eslint-kit@^11.0.0 eslint@^8.56.0 prettier@^3.0.0
Yarn:
yarn add -D eslint-kit@^11.0.0 eslint@^8.56.0 prettier@^3.0.0
After installing, add the .eslintrc.cjs file in your project root:
const { configure, presets } = require('eslint-kit')
module.exports = configure({
presets: [],
})
Now, just select the presets you need. The full information about them is located in Presets section.
You can also set up your editor if you haven't already.
configure({
// (optional) Project root
root: __dirname,
// (optional) Base ESLint Config to extend from
// May be used in monorepos to declare shared ESLint Kit options for all packages
// See "Extends" section for more info
extends: '../../base.eslintrc.cjs',
// Also accepts ESLint Config object, but only if it was created using ESLint Kit
extends: require(path.resolve(__dirname, '../../base.eslintrc.cjs')),
// (optional) Allow debug
// Very good option for development
// See "Allow Debug" section for more info
allowDebug: false,
// (optional) Mode
// See "Linting Modes" section for more info
mode: 'default',
// (optional) ESLint Kit presets
presets: [],
// (optional) Custom eslint config
// It gets merged with presets at the end
extend: { rules: { /* ... */ } }
})
unicorn, 'sonarjs', and @stylistic/eslint-plugin plugins@babel/eslint-parserimport-x and simple-import-sort pluginsjsconfig and tsconfigconfigure({
presets: [
presets.imports({
// (optional) Imports sort settings
sort: {
// (optional) Add newline between import groups
newline: false,
// (optional) Define groups for sorting (see below)
groups: [/* ... */]
},
// (optional) Alias settings
alias: {
// (optional) Base path for all aliases
// Defaults to './'
root: './src',
// (optional) Aliases
// Defaults to empty object
paths: { '@app': './' },
// (optional) A custom path to jsconfig
// Defaults to jsconfig.json
jsconfig: 'jsconfig.json'
}
})
]
})
Under the hood, we use eslint-plugin-simple-import-sort. It provides an option to override sorting groups - check out this section in their README.
These are the default groups values used by eslint-kit:
[
// side effects
['^\\u0000'],
// node.js libraries and scoped libraries
['^(child_process|crypto|events|fs|http|https|os|path)(/.*)?$', '^@?\\w'],
// common aliases (@app, @root, @/, ~/) and anything not matched
['^@app', '^@root', '^~', '^'],
// relative imports
['^\\.'],
]
To define your own groups, just pass it inside using sort.groups.
@typescript-eslint/parser.ts, .mts and .tsx extensionsconfigure({
presets: [
presets.typescript({
// (optional) Project's root
root: './',
// (optional) A path to tsconfig file
tsconfig: 'tsconfig.json',
// (optional) Enforce using `type` insead of `interface`
// Default to `false` in v11, will become `true` in v12, and will be removed in v13
// ESLint Kit CLI will set `true` on bootstrap
enforceUsingType: false,
})
]
})
prettier/prettier from Prettier ESLint pluginconfigure({
presets: [
/*
* Optionally, you can pass the Prettier config
* Note: it will merge and override any options set with .prettierrc files
*/
presets.prettier({
semi: false,
singleQuote: true
// ...
})
]
})
The recommended Prettier config:
{
"semi": false,
"singleQuote": true,
"tabWidth": 2,
"quoteProps": "consistent"
}
node environmentconfigure({
presets: [presets.node()]
})
browser environment and jsx ecma featureconfigure({
presets: [
presets.react({
// (optional) Allows to specify React version
version: 'detect',
// (optional) Allows using JSX without importing `React`
newJSXTransform: false
})
]
})
vue pluginvue-eslint-parser/recommended rules for it@typescript-eslint/parser for <script> blocks when typescript preset is usedbrowser environment and jsx ecma featureexport defaultYou still need to set up your editor / IDE to lint .vue files. You can use this guide from Vue documentation.
configure({
presets: [
presets.vue({
// (optional) Allows to specify Vue version
version: 'detect'
})
]
})
solid plugin and enables /recommended rules/typescript rules when typescript preset is activeconfigure({
presets: [presets.solidJs()]
})
svelte3 plugin and configures ittypescript preset is activeYou still need to set up your editor / IDE to lint .svelte files. You can use this guide from svelte3 plugin repo.
configure({
presets: [
presets.svelte({
// (optional) Disable type checking for .svelte files
noTypeCheck: true
})
]
})
@next/eslint-plugin-next plugin rulesexport defaultnextJs preset doesn't provide React rules, so don't forget to add react preset too. You may omit newJSXTransform, since it's already included in nextJs.
configure({
presets: [presets.react(), presets.nextJs()]
})
export defaultremix preset doesn't provide React rules, so don't forget to add react preset too. You may omit newJSXTransform, since it's already included in remix.
configure({
presets: [presets.react(), presets.remix()]
})
effector plugin and enables /recommended, /scope, and /react rulesconfigure({
presets: [
presets.effector({
// (optional) Enables /future rules
future: false
})
]
})
[!IMPORTANT] The paths from "extend.ignorePatterns", "extend.overrides" and similar options defined in "extends" ESLint config are resolved relative to the current ESLint config
May be used in monorepos to declare shared ESLint Kit options for all packages.
Root .eslintrc.cjs example:
// <root>/base.eslintrc.cjs
const { configure, presets } = require('eslint-kit')
module.exports = configure({
presets: [
presets.imports(),
presets.typescript(),
presets.prettier(),
presets.node(),
],
})
Package .eslintrc.cjs example:
// <root>/libs/my-library/.eslintrc.cjs
const { configure } = require('eslint-kit')
module.exports = configure({
root: __dirname,
extends: '../../base.eslintrc.cjs', // Resolved relative to "root"
})
Also accepts ESLint Config object, but only if it was created using ESLint Kit:
// <root>/libs/my-library/.eslintrc.cjs
const { configure } = require('eslint-kit')
const path = require('path')
module.exports = configure({
extends: require(path.resolve(__dirname, '../../base.eslintrc.cjs')),
})
Internally, the local ESLint Kit options is just merged with the ESLint Kit options from "extends" config.
Some properties are deep merged, but some are simply overwritten.
The complete list of deep merged options:
presetsextendextend.rulesextend.envextend.globalsextend.pluginsextend.settingsextend.overridesYou may find the merging implementation in this source file.
Useful in development mode.
Disables the following rules:
no-debuggerno-consoleno-alerteffector/no-patronum-debugconst { configure, presets } = require('eslint-kit')
module.exports = configure({
allowDebug: process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production",
/* ... */
})
const { configure, presets } = require('eslint-kit')
module.exports = configure({
mode: 'decrease-level',
/* ... */
})
Linting Modes are useful when you want to set similar behavior to a large number of rules.
defaultDo not transform rule levels. This is the default value.
decrease-levelTransform error to warn, and warn to off.
It's useful for incremental adoption: you can focus on fixing only critical issues first.
only-errorsTransform warn to error.
It's useful when you want to completely prevent any warnings to get into your main branch.
only-warnsTransform error to warn.
I have no idea when this may be useful, but ok.
disable-warnsTransform warn to off.
I have no idea when this may be useful, but ok.
Q: ESLint ignores my .eslintrc.cjs, why?
A: It's a regular issue with tools like @vue/cli and create-react-app. Check package.json and remove eslintConfig if you find it. Otherwise, try to restart your editor.
Q: ESLint: TypeError: this.libOptions.parse is not a function
A: Most likely you're using old broken ESLint version. 8.44.0 is tested and can be safely used.
Q: ESLint couldn't determine the plugin "foo" uniquely
A: Most likely your .eslintrc.cjs is located inside some nested project directory, and you have eslint package installed in the high-level node_modules. You can try setting extend.root to true like in the example below:
configure({
presets: [/* ... */],
extend: {
root: true
}
})
Q: In my monorepo, ESLint complains about tsconfig.json (or another file) location. How can I fix it?
A: Just set up root option inside your nested package (workspace) .eslintrc.cjs like in the example below:
configure({
root: __dirname,
presets: [/* ... */]
})
Q: I get another error when using eslint-kit in a monorepo
A: We didn't test monorepos much. They often have different issues with eslint and plugins resolving. And we also don't guarantee that your aliases settings will work in monorepo.
Install ESLint VSCode extension:

Next, select from the following and click on it:
Click on Settings icon:

Select "Keyboard shortcuts"
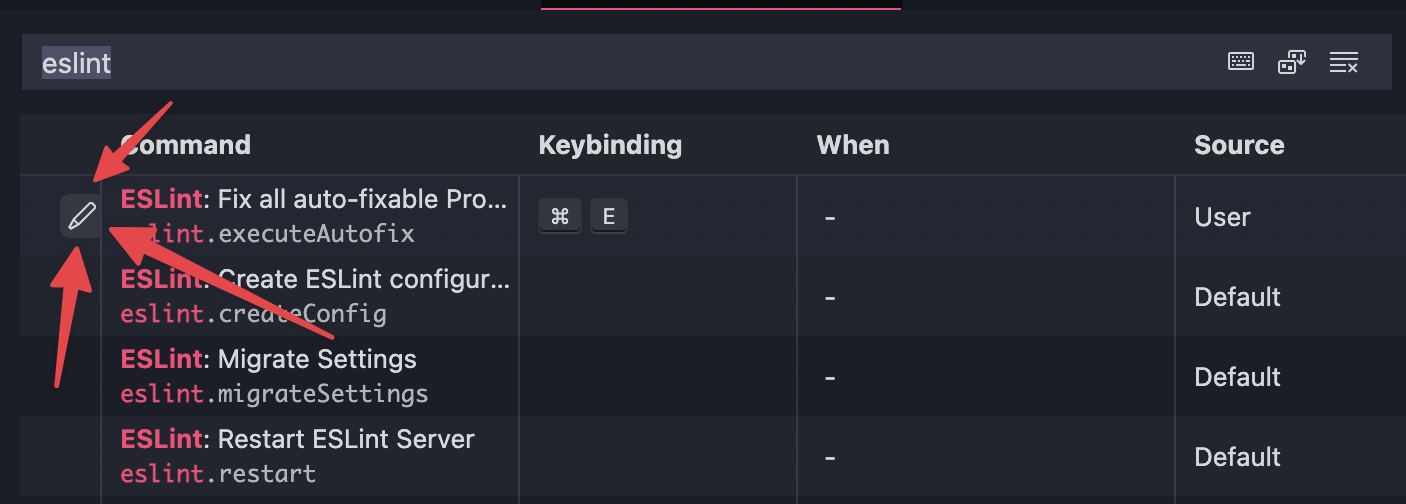
Type "eslint" and click on "edit" button:
Finally, choose the keybind you like.
Click on Settings icon:

Select "Settings"
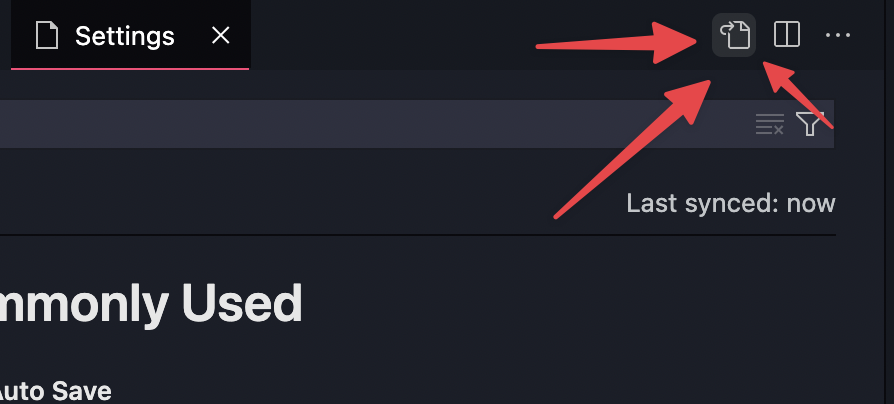
Switch to text mode:
Finally, add the following and save:
{
"eslint.validate": [
"javascript",
"javascriptreact",
"typescript",
"typescriptreact"
],
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll.eslint": true
}
}
feat/, fix/, docs/, refactor/, etc., depending on the changes you want to proposemain branchmain and it will create a new record in the changelog. Then, when the release is finally ready, your changes will be released.The dev branch is main - any developer changes is merged in there. Also, there is a release branch. It always contains the actual published release source code and tag.
All changes are made using Pull Requests - push is forbidden. PR can be merged only after successful test-and-build workflow checks.
When PR is merged, release-drafter workflow creates/updates a draft release. The changelog is built from the merged branch scope (feat, fix, etc) and PR title. When the release is ready - we publish the draft.
Then, the release workflow handles everything:
release branchAlso, this repo has Renovate bot set up to auto-update typescript preset dependencies (they change frequently). The bot creates a PR into main branch and automatically merges it after successful checks.
FAQs
All-in-one solution for configuring ESLint in all of your projects
The npm package eslint-kit receives a total of 754 weekly downloads. As such, eslint-kit popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that eslint-kit demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 0 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.