







Usage
•
Installation
•
Quick start
•
Demos
•
API
•
Perf
•
Changelog
•
FAQ
•
Contributing
📷 The fastest and most versatile JavaScript EXIF reading library.
Try it yourself - demo page & playground.
Features
Works everywhere, parses everything and handles anything you throw at it.
- 🏎️ Fastest EXIF lib: +-1ms per file
- 🗃️ Any input: buffers, url, <img> tag, and more
- 📷 Files: .jpg, .tif, .heic
- 🔎 Segments: TIFF (EXIF, GPS, etc...), XMP, ICC, IPTC, JFIF
- 📑 Reads only first few bytes
- 🔬 Skips parsing tags you don't need
- ✨ Isomorphic: Browser & Node.js
- 🗜️ No dependencies
- 🖼️ Extracts thumbnail
- 💔 Salvages broken files
- 🧩 Modular
- 📚 Customizable tag dictionaries
- 📦 Bundled as UMD/CJS or ESM
- ✔ Tested and benchmarked
- 🤙 Promises
- 🕸 Supports even
IE11 IE10
and more (click to expand)
- XMP Parser - minimalistic, reliable, without dependencies
- XMP Extended
- Multi-segment ICC
- Extracts all ICC tags (RedMatrixColumn, GreenTRC, B2A2, etc...)
- TIFF dictionaries contain less frequently used, non-standard and proprietary TIFF/EXIF tags (only in full bundle)
- Handles UCS2 formatted strings (XPTitle tag), instead of leaving it as a buffer
- Normalizes strings
- Revives dates into Date class instances
- Converts GPS coords from DMS to DD format. From `
GPSLatitude, GPSLatitudeRef tags ([50, 17, 58.57] & "N") to single latitude value (50.29960).
You don't need to read the whole file to tell if there's EXIF in it. And you don't need to extract all the data when you're looking for just a few tags. Exifr just jumps through the file structure, from pointer to pointer. Instead of reading it byte by byte, from beginning to end.
Exifr does what no other JS lib does. It's efficient and blazing fast!
Usage
file can be any binary format (Buffer, Uint8Array, Blob and more), <img> element, string path or url.
options specify what segments and blocks to parse, filters what tags to pick or skip.
| API | Returns | Description |
|---|
exifr.parse(file) | object | Parses IFD0, EXIF, GPS blocks |
exifr.parse(file, true) | object | Parses everything |
exifr.parse(file, ['Model', 'FNumber', ...]) | object | Parses only specified tags |
exifr.parse(file, {options}) | object | Custom settings |
exifr.gps(file) | {latitude, longitude} | Parses only GPS coords |
exifr.orientation(file) | number | Parses only orientation |
exifr.thumbnail(file) | `Buffer | Uint8Array` binary |
exifr.thumbnailUrl(file) | string Object URL | Browser only |
Installation
npm install exifr
Exifr comes in three prebuilt bundles. It's a good idea to start development with full and then scale down to lite, mini, or better yet, build your own around modular core.
import exifr from 'exifr'
import exifr from 'exifr/dist/full.esm.mjs'
var exifr = require('exifr')
<script type="module">import exifr from 'node_modules/exifr/dist/lite.esm.js';</script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/exifr/dist/lite.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/exifr/dist/lite.legacy.umd.js"></script>
Browsers: lite and mini are recommended because of balance between features and file size. UMD format attaches the library to global window.exifr object.
IE & old browsers: legacy builds come bundled with polyfills. Learn more.
Bundles & formats
- full - Contains everything. Intended for use in Node.js.
- lite - Reads JPEG and HEIC. Parses TIFF/EXIF and XMP.
- mini - Stripped down to basics. Parses most useful TIFF/EXIF from JPEGs. Has no tag dictionaries.
Of course, you can use the full version in browser, or use any other build in Node.js.
- ESM - Modern syntax for use in modern browsers and Node.js.
Uses import syntax. - UMD - Universal format for browsers and Node.js.
Supports CJS require('exifr'), AMD/RequireJS and global window.exifr. - legacy UMD - For use in older browsers (up to IE10).
Bundled with polyfills & shims, except for Promise polyfill. Learn more here.
Detailed comparison (click to expand)
| full | lite | mini | core |
|---|
chunked
file readers | BlobReader
UrlFetcher
FsReader
Base64Reader | BlobReader
UrlFetcher | BlobReader | none |
| file parsers | *.jpg
*.heic
*.tif | *.jpg
*.heic | *.jpg | none |
segment
parsers | TIFF (EXIF)
IPTC
XMP
ICC
JFIF | TIFF (EXIF)
XMP | TIFF (EXIF) | none |
| dictionaries | TIFF (+ less frequent tags)
IPTC
ICC | only TIFF keys
(IFD0, EXIF, GPS) | none | none |
| size +- | 60 Kb | 40 Kb | 25 Kb | 15 Kb |
| gzipped | 22 Kb | 12 Kb | 8 Kb | 4 Kb |
| file | full.umd.js
full.esm.js
full.esm.mjs
full.legacy.umd.js | lite.umd.js
lite.esm.js
lite.esm.mjs
lite.legacy.umd.js | mini.umd.js
mini.esm.js
mini.esm.mjs
mini.legacy.umd.js | Learn more |
ESM, .js .mjs .cjs extensions, "main", "module", "type":"module"
TL;DR: All bundles are available in two identical copies. .mjs and .js for ESM. .cjs and .js for UMD. Pick one that works with your tooling or webserver.
(click to expand for more info)
Current state of ESM is complicated. Node.js can already handle ESM files with .mjs extension and modules with "type":"module" in package.json. Turns out the "type":"module" approach alone is not yet ready for production. Some bundlers and tools may work or break with .mjs extension, whereas it's important for Node.js. The same applies to the new .cjs extension (introduced in Node.js 13).
The library is written in ESM, with .mjs extensions and transpiled to both ESM and UMD formats.
The "main" (field in package.json) entry point is now full.umd.cjs but you can still use ESM by explicitly importing full.esm.mjs. "module" field (used by some tools) points to full.esm.mjs.
If your webserver isn't configured to handle .mjs or .cjs files you can use their identical .js clone. For example full.esm.mjs is identical to full.esm.js. So is lite.esm.cjs to lite.esm.js. Just pick one that fits your tools or environment.
Named exports vs default export
Exifr exports both named exports and a default export object containing all the named exports.
This is again due to tooling. You can use import * as exifr from 'exifr' if your tool or env allows it, but import exifr from 'exifr' is recommended and used in examples for simplicity.
Examples
exifr.parse('./myimage.jpg')
.then(output => console.log('Camera:', output.Make, output.Model))
fs.readFile('./myimage.jpg')
.then(exifr.parse)
.then(output => console.log('Camera:', output.Make, output.Model))
Extract only certain tags
let {latitude, longitude} = await exifr.gps('./myimage.jpg')
let num = await exifr.orientation(blob)
let output = await exifr.parse(file, ['ISO', 'Orientation', 'LensModel'])
let output = await exifr.parse(file, {tiff: false, xmp: true})
Extracting thumbnail
let thumbBuffer = await exifr.thumbnail(file)
img.src = await exifr.thumbnailUrl(file)
Web Worker
let worker = new Worker('./worker.js')
worker.postMessage('../test/IMG_20180725_163423.jpg')
worker.onmessage = e => console.log(e.data)
worker.postMessage(arrayBuffer, [arrayBuffer])
importScripts('./node_modules/exifr/dist/lite.umd.js')
self.onmessage = async e => postMessage(await exifr.parse(e.data))
UMD in Browser
<img src="./myimage.jpg">
<script src="./node_modules/exifr/dist/lite.umd.js"></script>
<script>
let img = document.querySelector('img')
window.exifr.parse(img).then(exif => console.log('Exposure:', exif.ExposureTime))
</script>
ESM in Browser
<input id="filepicker" type="file" multiple>
<script type="module">
import exifr from './node_modules/exifr/dist/lite.esm.js'
document.querySelector('#filepicker').addEventListener('change', async e => {
let files = Array.from(e.target.files)
let exifs = await Promise.all(files.map(exifr.parse))
let dates = exifs.map(exif => exif.DateTimeOriginal.toGMTString())
console.log(`${files.length} photos taken on:`, dates)
})
</script>
Demos
and a lot more in the examples/ folder
API
parse(file[, options])
Returns: Promise<object>
Accepts file (in any format), parses it and returns exif object. Optional options argument can be specified.
gps(file)
Returns: Promise<object>
Only extracts GPS coordinates.
Uses pick/skip filters and perf improvements to only extract latitude and longitude tags from GPS block. And to get GPS-IFD pointer it only scans through IFD0 without reading any other unrelated data.
Check out examples/gps.js to learn more.
orientation(file)
Returns: Promise<number>
Only extracts photo's orientation.
thumbnail(file)
Returns: Promise<Buffer|Uint8Array>
Extracts embedded thumbnail from the photo, returns Uint8Array.
Only parses as little EXIF as necessary to find offset of the thumbnail.
Check out examples/thumbnail.html and examples/thumbnail.js to learn more.
thumbnailUrl(file)
Returns: Promise<string>
browser only
Exports the thumbnail wrapped in Object URL. The URL has to be revoked when not needed anymore.
Exifr class
Aforementioned functions are wrappers that internally:
- instantiate
new Exifr(options) class - call
.read(file) to read the file - call
.parse() or .extractThumbnail()
You can instantiate Exif yourself to parse metadata and extract thumbnail efficiently at the same time. In Node.js it's also necessary to close the file with .file.close() if it's read in chunked mode.
let exr = new Exifr(options)
let output = await exr.read(file)
let buffer = await exr.extractThumbnail()
if (exr.file.chunked) await exr.file.close()
file argument
string
BufferArrayBufferUint8ArrayDataViewBlob, File<img> element
options argument
All other and undefined properties are inherited from defaults:
let defaultOptions = {
jfif: false,
tiff: true,
xmp: false,
icc: false,
iptc: false,
ifd0: true,
ifd1: false,
exif: true,
gps: true,
interop: false,
makerNote: false,
userComment: false,
skip: [],
pick: [],
translateKeys: true,
translateValues: true,
reviveValues: true,
sanitize: true,
mergeOutput: true,
silentErrors: true,
chunked: true,
firstChunkSize: undefined,
firstChunkSizeNode: 512,
firstChunkSizeBrowser: 65536,
chunkSize: 65536,
chunkLimit: 5
}
Tag filters
Exifr can avoid reading certain tags, instead of reading but not including them in the output, like other exif libs do. For example MakerNote tag from EXIF block is isually very large - tens of KBs. Reading such tag is a waste of time if you don't need it.
Tip: Using numeric tag codes is even faster than string names because exifr doesn't have to look up the strings in dictionaries.
options.pick
Type: Array<string|number>
Array of the only tags that will be parsed.
Specified tags are looked up in a dictionary. Their respective blocks are enabled for parsing, all other blocks are disabled. Parsing ends as soon as all requested tags are extracted.
{pick: ['ExposureTime', 'FNumber', 'ISO']}
{pick: ['ExposureTime', 'FNumber', 'ISO', 'GPSLatitude']}
{gps: {pick: ['GPSLatitude', 0x0004]}}
options.skip
Type: Array<string|number>
Default: ['MakerNote', 'UserComments']
Array of the tags that will not be parsed.
By default, MakerNote and UserComment tags are skipped. But that is configured elsewhere.
{skip: ['ImageWidth', 'Model', 'FNumber', 'GPSLatitude']}
{exif: {skip: ['ImageUniqueID', 42033, 'SubSecTimeDigitized']}}
Segments & Blocks
EXIF became synonymous for all image metadata, but it's actually just one of many blocks inside TIFF segment. And there are more segment than just TIFF.
APP Segments
Jpeg stores various formats of data in APP-Segments. Heic and Tiff file formats use different structures or naming conventions but the idea is the same, so we refer to TIFF, XMP, IPTC, ICC and JFIF as Segments.
options.tiff type bool|object|Array default: true
TIFF APP1 Segment - Basic TIFF/EXIF tags, consists of blocks: IFD0 (image), IFD1 (thumbnail), EXIF, GPS, Interopoptions.jfif type bool default: false
JFIF APP0 Segment - Additional infooptions.xmp type bool default: false
XMP APP1 Segment - additional XML dataoptions.iptc type bool default: false
IPTC APP13 Segment - Captions and copyrightsoptions.icc type bool default: false
ICC APP2 Segment - Color profile
TIFF IFD Blocks
TIFF Segment consists of various IFD's (Image File Directories) aka blocks.
options.ifd0 (alias options.image) type bool|object|Array default: true
IFD0 - Basic info about the imageoptions.ifd1 (alias options.thumbnail) type bool|object|Array default: false
IFD1 - Info about embedded thumbnailoptions.exif type bool|object|Array default: true
EXIF SubIFD - Detailed info about photooptions.gps type bool|object|Array default: true
GPS SubIFD - GPS coordinatesoptions.interop type bool|object|Array default: false
Interop SubIFD - Interoperability info
Notable TIFF tags
Notable large tags from EXIF block that are not parsed by default but can be enabed if needed.
options.makerNote type: bool default: false
0x927C MakerNote tagoptions.userComment type: bool default: false
0x9286 UserComment tag
XMP
Extracted XMP tags are grouped by namespace. Each ns is separate object in output. E.g. output.xmlns, output.GPano, output.crs, etc...
For XMP Extended see options.multiSegment
Exifr contains minimalistic opinionated XML parser for parsing data from XMP. It may not be 100% spec-compliant, because XMP is based on XML which cannot be translated 1:1 to JSON. The output is opinionated and may alter or simplify the data structure. If the XMP parser doesn't suit you, it can be disabled by setting options.xmp.parse to false. Then a raw XMP string will be available at output.xmp.
Caveats & XML to JSON mapping
- Tags with both attributes and children-value are combined into object.
- Arrays (RDF Containers) with single item are unwrapped. The single item is used in place of the array.
- If
options.mergeOutput:false: Tags of tiff namespace (<tiff:Model>) are merged into output.ifd0. Likewise exif ns is merged into output.exif.
<rdf:Description foo:name="Exifr">
<foo:author>Mike Kovařík</foo:author>
<foo:description xml:lang="en-us">Some string here</foo:description>
<foo:formats><rdf:Seq><rdf:li>jpeg</rdf:li></rdf:Seq></foo:formats>
<foo:segments><rdf:Seq><rdf:li>xmp</rdf:li><rdf:li>tiff</rdf:li><rdf:li>iptc</rdf:li></rdf:Seq></foo:segments>
</rdf:Description>
parses as:
{
name: 'Exifr',
author: 'Mike Kovařík',
description: {lang: 'en-us', value: 'Some string here'},
formats: 'jpeg',
segments: ['xmp', 'tiff', 'iptc']
}
options.multiSegment
Type: bool
Default: false
Enables looking for more than just a single segment of ICC or XMP (XMP Extended).
In some rare cases the photo can contain additional layers, embedded images, or metadata that doesn't fit inside single 64kB (JPEG) segment.
Side effect: Disables chunked reading. The whole file has to be read to locate all segments.
When is it useful:
- VR photos with combination of left/right eye (XMP Extended)
- "Portrait mode" photo that contains depth map (XMP Extended)
- Photos with custom ICC color profile
Sub-options:
options.xmp.multiSegmentoptions.icc.multiSegment
Shortcuts
options.tiff serves as a shortcut for configuring all TIFF blocks:
options.tiff = true enables all TIFF blocks (sets them to true).options.tiff = false disables all TIFF blocks (sets them to false) except for those explicitly set to true in options.options.tiff = {...} applies the same sub-options to all TIFF blocks that are enabled.
options.tiff = false can be paired with any other block(s) to disable all other blocks except for said block.
{interop: true, tiff: false}
{interop: true, ifd0: false, exif: false, gps: false, ifd1: true}
Each TIFF block and the whole tiff segment can also be configured with object or array, much like the options argument.
TIFF blocks automatically inherit from options.tiff and then from options.
{
exif: true, gps: true,
pick: ['FNumber', 'ISO', 'GPSLatitude', 0x0004]
}
{exif: ['FNumber', 'ISO'], gps: ['GPSLatitude', 0x0004]}
{exif: {pick: ['FNumber', 'ISO']}, gps: {pick: ['GPSLatitude', 0x0004]}}
Chunked reader
options.chunked
Type: bool
Default: true
Exifr can read only a few chunks instead of the whole file. It's much faster, saves memory and unnecessary disk reads or network fetches. Works great with complicated file structures - .tif files may point to metadata scattered throughout the file.
How it works: A first small chunk (of firstChunkSize) is read to determine if the file contains any metadata at all. If so, reading subsequent chunks (of chunkSize) continues until all requested segments are found or until chunkLimit is reached.
Supported inputs: Chunked is only effective with Blob, <img> element, string url, disk path, or base64. These inputs are not yet processed or read into memory. Each input format is implemented in a separate file reader class. Learn more about file readers and modularity here.
If you use URL as input: Fetching chunks (implemented in UrlFetcher) from web server uses HTTP Range Requests. Range request may fail if your server does not support ranges, if it's not configured properly or if the fetched file is smaller than the first chunk size. Test your web server or disable chunked reader with {chunked: false} when in doubt.
options.firstChunkSize
Type: number
Default: 512 Bytes in Node / 65536 (64 KB) in browser
Size (in bytes) of the first chunk that probes the file for traces of exif or metadata.
In browser, it's usually better to read just a larger chunk in hope that it contains the whole EXIF (and not just the beginning) instead of loading multiple subsequent chunks. Whereas in Node.js it's preferable to read as little data as possible and fs.read() does not cause slowdowns.
options.chunkSize
Type: number
Default: 65536 Bytes (64 KB)
Size of subsequent chunks that may be read after the first chunk.
options.chunkLimit
Type: number
Default: 5
Max amount of subsequent chunks allowed to read in which exifr searches for data segments and blocks. I.e. failsafe that prevents from reading the whole file if it does not contain all of the segments or blocks requested in options.
This limit is bypassed if multi-segment segments ocurs in the file and if options.multiSegment allows reading all of them.
If the exif isn't found within N chunks (64*5 = 320KB) it probably isn't in the file and it's not worth reading anymore.
Output format
options.mergeOutput
Type: bool
Default: true
Merges all parsed segments and blocks into a single object.
Warning: mergeOutput: false should not be used with translateKeys: false or when parsing both ifd0 (image) and ifd1 (thumbnail). Tag keys are numeric, sometimes identical and may collide.
| mergeOutput: false | mergeOutput: true |
{
Make: 'Google',
Model: 'Pixel',
FNumber: 2,
Country: 'Czech Republic',
xmp: '<x:xmpmeta><rdf:Description>...'
}
| {
ifd0: {
Make: 'Google',
Model: 'Pixel'
},
exif: {
FNumber: 2
},
iptc: {
Country: 'Czech Republic'
},
xmp: '<x:xmpmeta><rdf:Description>...'
}
|
options.sanitize
Type: bool
Default: true
Cleans up unnecessary, untransformed or internal tags (IFD pointers) from the output.
options.silentErrors
Type: bool
Default: true
Error messages are stored at output.errors instead of thrown as Error instances and causing promise rejection.
Failing silently enables reading broken files. But only file-structure related errors are caught.
options.translateKeys
Type: bool
Default: true
Translates tag keys from numeric codes to understandable string names. I.e. uses Model instead of 0x0110.
Most keys are numeric. To access the Model tag use output.ifd0[0x0110] or output.ifd0[272]
Learn more about dictionaries.
Warning: translateKeys: false should not be used with mergeOutput: false. Keys may collide because ICC, IPTC and TIFF segments use numeric keys starting at 0.
| translateKeys: false | translateKeys: true |
{
0x0110: 'Pixel', // IFD0
90: 'Vsetín', // IPTC
64: 'Perceptual', // ICC
desc: 'sRGB IEC61966-2.1', // ICC
} | {
Model: 'Pixel', // IFD0
City: 'Vsetín', // IPTC
RenderingIntent: 'Perceptual', // ICC
ProfileDescription: 'sRGB IEC61966-2.1', // ICC
} |
options.translateValues
Type: bool
Default: true
Translates tag values from raw enums to understandable strings.
Learn more about dictionaries.
| translateValues: false | translateValues: true |
{
Orientation: 1,
ResolutionUnit: 2,
DeviceManufacturer: 'GOOG'
}
| {
Orientation: 'Horizontal (normal)',
ResolutionUnit: 'inches',
DeviceManufacturer: 'Google'
}
|
options.reviveValues
Type: bool
Default: true
Converts dates from strings to a Date instances and modifies few other tags to a more readable format.
Learn more about dictionaries.
| reviveValues: false | reviveValues: true |
{
GPSVersionID: [0x02, 0x02, 0x00, 0x00],
ModifyDate: '2018:07:25 16:34:23',
}
| {
GPSVersionID: '2.2.0.0',
ModifyDate: <Date instance: 2018-07-25T14:34:23.000Z>,
}
|
Advanced APIs
Tips for advanced users. You don't need to read further unless you're into customization and bundlers.
Modularity, Pugin API, Configure custom bundle
This is mostly relevant for Web Browsers, where file size and unused code elimination is important.
The library's functionality is divided into four categories.
- (Chunked) File reader reads different input data structures by chunks.
BlobReader (browser), UrlFetcher (browser), FsReader (Node.js), Base64Reader
See src/file-parsers/.
NOTE: Everything can read everything out-of-the-box as a whole file. But file readers are needed to enable chunked mode. - File parser looks for metadata in different file formats
.jpg, .tiff, .heic
See src/file-parsers/. - Segment parser extracts data from various metadata formats (JFIF, TIFF, XMP, IPTC, ICC)
TIFF/EXIF (IFD0, EXIF, GPS), XMP, IPTC, ICC, JFIF
See src/segment-parsers/. - Dictionary affects the way the parsed output looks.
See src/dicts/.
Each reader, parser and dictionary is a separate file that can be used independently. This way you can configure your own bundle with only what you need, eliminate dead code and save tens of KBs of unused dictionaries.
Check out examples/custom-build.js.
Scenario 1: We'll be handling .jpg files in blob format and we want to extract ICC data in human-readable format. For that we'll need dictionaries for ICC segment.
import * as exifr from 'exifr/src/core.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/file-readers/BlobReader.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/file-parsers/jpeg.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/segment-parsers/icc.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/dicts/icc-keys.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/dicts/icc-values.mjs'
Scenario 2: We want to parse .heic and .tiff photos, extract EXIF block (of TIFF segment). We only need the values to be translated. Keys will be left untranslated but we don't mind accessing them with raw numeric keys - output[0xa40a] instead of output.Sharpness. Also, we're not importing any (chunked) file reader because we only work with Uint8Array data.
import * as exifr from 'exifr/src/core.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/file-parsers/heic.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/file-parsers/tiff.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/segment-parsers/tiff.mjs'
import 'exifr/src/dicts/tiff-exif-values.mjs'
Translation dictionaries, customization
EXIF Data are mostly numeric enums, stored under numeric code. Dictionaries are needed to translate them into meaningful output. But they take up a lot of space (40 KB out of full build's 60 KB). So it's a good idea to make your own bundle and shave off the dicts you don't need.
- Key dict translates object keys from numeric codes to string names (
output.Model instead of output[0x0110]) - Value dict translates vales from enum to string description (
Orientation becomes 'Rotate 180' instead of 3) - Reviver further modifies the value (converts date string to an instance of
Date)
Exifr's dictionaries are based on exiftool.org. Specifically these:
TIFF (EXIF & GPS),
ICC,
IPTC,
JFIF
import exifr from 'exifr'
let exifKeys = exifr.tagKeys.get('exif')
let exifValues = exifr.tagValues.get('exif')
exifKeys.set(0xa409, 'Saturation')
exifValues.set(0xa409, {
0: 'Normal',
1: 'Low',
2: 'High'
})
import exifr from 'exifr'
let gpsRevivers = exifr.tagRevivers.get('gps')
gpsRevivers.set(0x001D, rawValue => {
let [year, month, day] = rawValue.split(':').map(str => parseInt(str))
return new Date(year, month - 1, day)
})
import exifr from 'exifr'
exifr.createDictionary(exifr.tagKeys, 'gps', [
[0x0001, 'LatitudeRef'],
[0x0002, 'Latitude'],
[0x0003, 'LongitudeRef'],
[0x0004, 'Longitude'],
])
import exifr from 'exifr'
exifr.createDictionary(exifr.tagKeys, 'ifd0', [
[0xc7b5, 'DefaultUserCrop'],
[0xc7d5, 'NikonNEFInfo'],
...
])
Usage with Webpack, Parcel, Rollup, Gatsby, etc...
Under the hood exifr dynamically imports Node.js fs module. The import is obviously only used in Node.js and not triggered in a browser. But your bundler may, however, pick up on it and fail with something like Error: Can't resolve 'fs'.
Parcel works out of the box and Webpack should too because of webpackIgnore magic comment added to the library's source code import(/* webpackIgnore: true */ 'fs').
If this does not work for you, try adding node: {fs: 'empty'} and target: 'web' or target: 'webworker' to your Webpack config. Or similar settings for your bundler of choice.
Alternatively, create your own bundle around core build and do not include FsReader in it.
Exifr is written using modern syntax, mainly async/await. You may need to add regenerator-runtime or reconfigure babel.
Performance
Tips for better performance
Here are a few tips for when you need to squeeze an extra bit of speed out of exifr when processing a large amount of files. Click to expand.
Use options.pick if you only need certain tags
Unlike other libraries, exifr can only parse certain tags, avoid unnecessary reads and end when the last picked tag was found.
let {ISO, FNumber} = await exifr.parse(file, {exif: ['ISO', 'FNumber']})
let {ISO, FNumber} = await exifr.parse(file)
Disable options.ifd0 if you don't need the data
Even though IFD0 (Image block) stores pointers to EXIF and GPS blocks and is thus necessary to be parsed to access said blocks. Exifr doesn't need to read the whole IFD0, it just looks for the pointers.
let options = {ifd0: false, exif: true}
let options = {exif: true}
Use exifr.gps() if you only need GPS
If you only need to extract GPS coords, use exifr.gps() because it is fine-tuned to do exactly this and nothing more. Similarly there's exifr.orientation().
exifr.gps(file)
exifr.parse(file, {gps: true})
Cache options object
If you parse multiple files with the same settings, you should cache the options object instead of inlining it. Exifr uses your options to create an instance of Options class under the hood and uses WeakMap to find previously created instance instead of creating q new one each time.
let options = {exif: true, iptc: true}
for (let file of files) exif.parse(file, options)
for (let file of files) exif.parse(file, {exif: true, iptc: true})
File reading: You don't need to read the whole file and parse through a MBs of data. Exifr takes an educated guess to only read a small chunk of the file where metadata is usually located. Each platform, file format, and data type is approached differently to ensure the best performance.
Finding metadata: Other libraries use brute force to read through all bytes until 'Exif' string is found. Whereas exifr recognizes the file structure, consisting of segments (JPEG) or nested boxes (HEIC). This allows exifr to read just a few bytes here and there, to get the offset and size of the segment/box and pointers to jump to the next.
HEIC: Simply finding the exif offset takes 0.2-0.3ms with exifr. Compare that to exif-heic-js which takes about 5-10ms on average. Exifr is up to 30x faster.
Benchmarks
Try the benchmark yourself at benchmark/chunked-vs-whole.js
user reads file 8.4 ms
exifr reads whole file 8.2 ms
exifr reads file by chunks 0.5 ms <--- !!!
only parsing, not reading 0.2 ms <--- !!!
Observations from testing with +-4MB pictures (Highest quality Google Pixel photos. Tested on a mid-range dual-core i5 machine with SSD).
- Node: Parsing after
fs.readFile = 0.3ms - Node: Reading & parsing by chunks = 0.5ms
- Browser: Processing
ArrayBuffer = 3ms - Browser: Processing
Blob = 7ms - Browser:
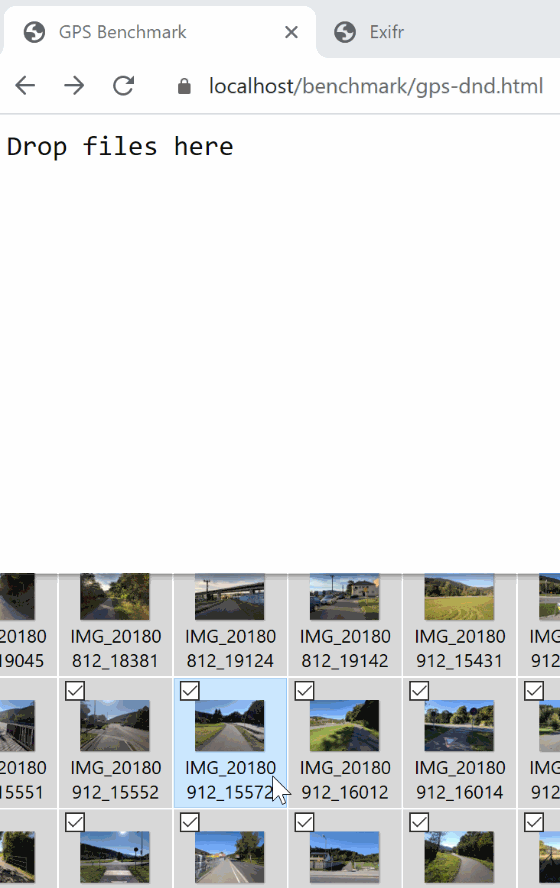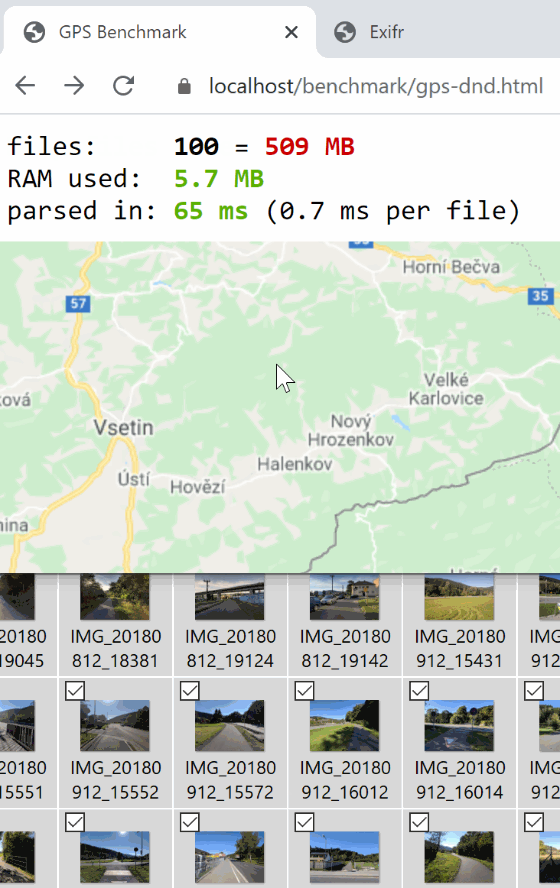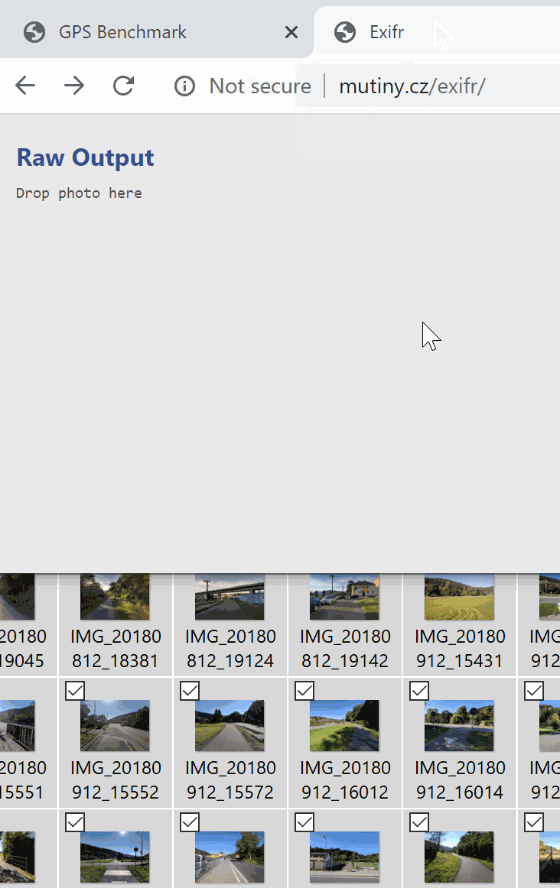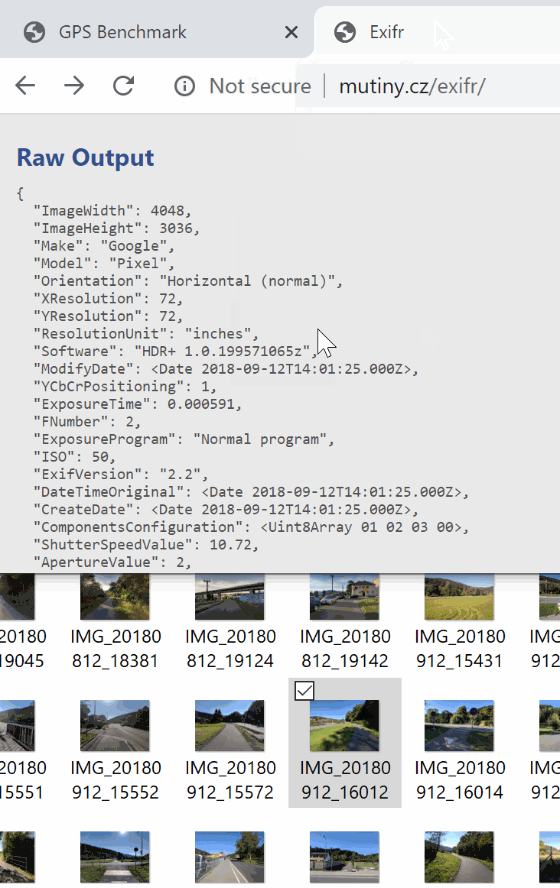
<img> with Object URL = 3ms - Drag-n-dropping gallery of 100 images and extracting GPS data takes about 65ms.
- Phones are about 4x slower. Usually 4-30ms per photo.
Be sure to visit the exifr playground or benchmark/gps-dnd.html, drop in your photos and watch the parsed in timer.
Changelog
For full changelog visit CHANGELOG.md.
Notable changes
- 4.3.0 Package.json's
"main" now points to UMD bundle for better compatibility. - 4.1.0 Started bundling shims and polyfills with
legacy builds. Suppporting IE10. - 4.0.0 Added XMP Parser and XMP Extended support.
- 3.0.0 Major rewrite, added ICC parser, HEIC file support, IE11 back compat, reimplemented chunked reader.
F.A.Q.
Why are there different kB sizes on npm, bundlephobia, and badge in the readme?
TL;DR: Because exifr comes in three bundles, each in three format variants (ESM, UMD, legacy), each in two extensions (.js and .mjs or .mjs) due to tooling. Plus source codes are included.
npm (~1MB, ~65 files): The module includes both src/ and dist/. That's source codes of all the readers, parsers and dictionaries. Multiplied by 3 bundles (full, lite, mini). Then multiplied by 3 bundle formats (ESM, UMD, legacy for IE10) and multiplied by 2 extensions (.mjs+.js or .cjs+.js). But you won't use all of the files. They're there so you can choose what's best for your project, tooling and environment.
bundlephobia (~63/22 kB): Full build is the "main" entry point (in package.json) picked up by Node and bundlephobia. But it's meant for use in Node where size doesn't matter.
badge in readme (~9 kB): The badge points to mini bundle which contains the bare minimum needed to cover the most use-cases (get orientation, coords, exif info, etc...). This is meant for browsers where file size matters.
Contributing
Contributions are welcome in any form. Suggestions, bug reports, docs improvements, new tests or even feature PRs. Don't be shy, I don't bite.
If you're filing an issue, please include:
- The photo that's missing metadata or causing the bug
- Repo or a sandbox (like this one) with minimal code where the bug is reproducible.
There are so many environments, tools and frameworks and I can't know, nor try them all out. Letting me peek into your setup makes tracking down the problem so much easier.
PRs are gladly accepted. Please run tests before you create one:
- in browser by visiting
/test/index.html (uses import maps, you may need to enable experimental flags in your browser) - in Node.js by running
npm run test
License
MIT, Mike Kovařík, Mutiny.cz








