JSON-Patch
A leaner and meaner implementation of JSON-Patch. Small footprint. High performance.

With JSON-Patch, you can:
- apply patches (arrays) and single operations on JS object
- validate a sequence of patches
- observe for changes and generate patches when a change is detected
- compare two objects to obtain the difference
Tested in Firefox, Chrome, Edge, Safari, IE11, Deno and Node.js
Why you should use JSON-Patch
JSON-Patch (RFC6902) is a standard format that
allows you to update a JSON document by sending the changes rather than the whole document.
JSON Patch plays well with the HTTP PATCH verb (method) and REST style programming.
Mark Nottingham has a nice blog about it.
Install
Download as ZIP or install the current version using a package manager (and save it as a dependency):
npm install fast-json-patch --save
Adding to your project
In a web browser
Load the bundled distribution script:
<script src="dist/fast-json-patch.min.js"></script>
In browsers that support ECMAScript modules, the below code uses this library as a module:
<script type="module">
import * as jsonpatch from 'fast-json-patch/index.mjs';
import { applyOperation } from 'fast-json-patch/index.mjs';
</script>
In Node.js
In Node 12+ with --experimental-modules flag, the below code uses this library as an ECMAScript module:
import * as jsonpatch from 'fast-json-patch/index.mjs';
import { applyOperation } from 'fast-json-patch/index.mjs';
In Webpack (and most surely other bundlers based on Babel), the below code uses this library as an ECMAScript module:
import * as jsonpatch from 'fast-json-patch';
import { applyOperation } from 'fast-json-patch';
In standard Node, the below code uses this library as a CommonJS module:
const { applyOperation } = require('fast-json-patch');
const applyOperation = require('fast-json-patch').applyOperation;
Directories
Directories used in this package:
dist/ - contains ES5 files for a Web browsercommonjs/ - contains CommonJS module and typingsmodule/ - contains ECMAScript module and typingssrc/ - contains TypeScript source files
API
function applyPatch<T>(document: T, patch: Operation[], validateOperation?: boolean | Validator<T>, mutateDocument: boolean = true, banPrototypeModifications: boolean = true): PatchResult<T>
Applies patch array on obj.
document The document to patchpatch a JSON-Patch array of operations to applyvalidateOperation Boolean for whether to validate each operation with our default validator, or to pass a validator callbackmutateDocument Whether to mutate the original document or clone it before applyingbanPrototypeModifications Whether to ban modifications to __proto__, defaults to true.
An invalid patch results in throwing an error (see jsonpatch.validate for more information about the error object).
It modifies the document object and patch - it gets the values by reference.
If you would like to avoid touching your patch array values, clone them: jsonpatch.applyPatch(document, jsonpatch.deepClone(patch)).
Returns an array of OperationResult objects - one item for each item in patches, each item is an object {newDocument: any, test?: boolean, removed?: any}.
test - boolean result of the testremove, replace and move - original object that has been removedadd (only when adding to an array) - index at which item has been inserted (useful when using - alias)
-
** Note: It throws TEST_OPERATION_FAILED error if test operation fails. **
-
** Note II: the returned array has newDocument property that you can use as the final state of the patched document **.
-
** Note III: By default, when banPrototypeModifications is true, this method throws a TypeError when you attempt to modify an object's prototype.
-
See Validation notes.
Example:
var document = { firstName: "Albert", contactDetails: { phoneNumbers: [] } };
var patch = [
{ op: "replace", path: "/firstName", value: "Joachim" },
{ op: "add", path: "/lastName", value: "Wester" },
{ op: "add", path: "/contactDetails/phoneNumbers/0", value: { number: "555-123" } }
];
document = jsonpatch.applyPatch(document, patch).newDocument;
function applyOperation<T>(document: T, operation: Operation, validateOperation: boolean | Validator<T> = false, mutateDocument: boolean = true, banPrototypeModifications: boolean = true, index: number = 0): OperationResult<T>
Applies single operation object operation on document.
document The document to patchoperation The operation to applyvalidateOperation Whether to validate the operation, or to pass a validator callbackmutateDocument Whether to mutate the original document or clone it before applyingbanPrototypeModifications Whether to ban modifications to __proto__, defaults to true.index The index of the operation in your patch array. Useful for better error reporting when that operation fails to apply.
It modifies the document object and operation - it gets the values by reference.
If you would like to avoid touching your values, clone them: jsonpatch.applyOperation(document, jsonpatch.deepClone(operation)).
Returns an OperationResult object {newDocument: any, test?: boolean, removed?: any}.
-
** Note: It throws TEST_OPERATION_FAILED error if test operation fails. **
-
** Note II: By default, when banPrototypeModifications is true, this method throws a TypeError when you attempt to modify an object's prototype.
-
See Validation notes.
Example:
var document = { firstName: "Albert", contactDetails: { phoneNumbers: [] } };
var operation = { op: "replace", path: "/firstName", value: "Joachim" };
document = jsonpatch.applyOperation(document, operation).newDocument;
jsonpatch.applyReducer<T>(document: T, operation: Operation, index: number): T
Ideal for patch.reduce(jsonpatch.applyReducer, document).
Applies single operation object operation on document.
Returns the a modified document.
Note: It throws TEST_OPERATION_FAILED error if test operation fails.
Example:
var document = { firstName: "Albert", contactDetails: { phoneNumbers: [ ] } };
var patch = [
{ op:"replace", path: "/firstName", value: "Joachim" },
{ op:"add", path: "/lastName", value: "Wester" },
{ op:"add", path: "/contactDetails/phoneNumbers/0", value: { number: "555-123" } }
];
var updatedDocument = patch.reduce(applyReducer, document);
jsonpatch.deepClone(value: any): any
Returns deeply cloned value.
jsonpatch.escapePathComponent(path: string): string
Returns the escaped path.
jsonpatch.unescapePathComponent(path: string): string
Returns the unescaped path.
jsonpatch.getValueByPointer(document: object, pointer: string)
Retrieves a value from a JSON document by a JSON pointer.
Returns the value.
jsonpatch.observe(document: any, callback?: Function): Observer
Sets up an deep observer on document that listens for changes in object tree. When changes are detected, the optional
callback is called with the generated patches array as the parameter.
Returns observer.
jsonpatch.generate(document: any, observer: Observer, invertible = false): Operation[]
If there are pending changes in obj, returns them synchronously. If a callback was defined in observe
method, it will be triggered synchronously as well. If invertible is true, then each change will be preceded by a test operation of the value before the change.
If there are no pending changes in obj, returns an empty array (length 0).
Example:
var document = { firstName: "Joachim", lastName: "Wester", contactDetails: { phoneNumbers: [ { number:"555-123" }] } };
var observer = jsonpatch.observe(document);
document.firstName = "Albert";
document.contactDetails.phoneNumbers[0].number = "123";
document.contactDetails.phoneNumbers.push({ number:"456" });
var patch = jsonpatch.generate(observer);
Example of generating patches with test operations for values in the first object:
var document = { firstName: "Joachim", lastName: "Wester", contactDetails: { phoneNumbers: [ { number:"555-123" }] } };
var observer = jsonpatch.observe(document);
document.firstName = "Albert";
document.contactDetails.phoneNumbers[0].number = "123";
document.contactDetails.phoneNumbers.push({ number:"456" });
var patch = jsonpatch.generate(observer, true);
jsonpatch.unobserve(document, observer)
jsonpatch.unobserve(document: any, observer: Observer): void
type JsonableObj = { [key:string]: Jsonable };
type JsonableArr = Jsonable[];
type Jsonable = JsonableArr | JsonableObj | string | number | boolean | null;
Destroys the observer set up on document.
Any remaining changes are delivered synchronously (as in jsonpatch.generate). Note: this is different that ES6/7 Object.unobserve, which delivers remaining changes asynchronously.
jsonpatch.compare(document1, document2, invertible)
jsonpatch.compare(document1: Jsonable, document2: Jsonable, invertible = false): Operation[]
type JsonableObj = { [key:string]: Jsonable };
type JsonableArr = Jsonable[];
type Jsonable = JsonableArr | JsonableObj | string | number | boolean | null;
Compares object trees document1 and document2 and returns the difference relative to document1 as a patches array. If invertible is true, then each change will be preceded by a test operation of the value in document1.
If there are no differences, returns an empty array (length 0).
Example:
var documentA = {user: {firstName: "Albert", lastName: "Einstein"}};
var documentB = {user: {firstName: "Albert", lastName: "Collins"}};
var diff = jsonpatch.compare(documentA, documentB);
Example of comparing two object trees with test operations for values in the first object:
var documentA = {user: {firstName: "Albert", lastName: "Einstein"}};
var documentB = {user: {firstName: "Albert", lastName: "Collins"}};
var diff = jsonpatch.compare(documentA, documentB, true);
jsonpatch.validate(patch: Operation[], document?: any, validator?: Function): JsonPatchError
See Validation notes
Validates a sequence of operations. If document parameter is provided, the sequence is additionally validated against the object tree.
If there are no errors, returns undefined. If there is an errors, returns a JsonPatchError object with the following properties:
name String - short error codemessage String - long human readable error messageindex Number - index of the operation in the sequenceoperation Object - reference to the operationtree Object - reference to the tree
Possible errors:
| SEQUENCE_NOT_AN_ARRAY | Patch sequence must be an array |
| OPERATION_NOT_AN_OBJECT | Operation is not an object |
| OPERATION_OP_INVALID | Operation op property is not one of operations defined in RFC-6902 |
| OPERATION_PATH_INVALID | Operation path property is not a valid string |
| OPERATION_FROM_REQUIRED | Operation from property is not present (applicable in move and copy operations) |
| OPERATION_VALUE_REQUIRED | Operation value property is not present, or undefined (applicable in add, replace and test operations) |
| OPERATION_VALUE_CANNOT_CONTAIN_UNDEFINED | Operation value property object has at least one undefined value (applicable in add, replace and test operations) |
| OPERATION_PATH_CANNOT_ADD | Cannot perform an add operation at the desired path |
| OPERATION_PATH_UNRESOLVABLE | Cannot perform the operation at a path that does not exist |
| OPERATION_FROM_UNRESOLVABLE | Cannot perform the operation from a path that does not exist |
| OPERATION_PATH_ILLEGAL_ARRAY_INDEX | Expected an unsigned base-10 integer value, making the new referenced value the array element with the zero-based index |
| OPERATION_VALUE_OUT_OF_BOUNDS | The specified index MUST NOT be greater than the number of elements in the array |
| TEST_OPERATION_FAILED | When operation is test and the test fails, applies to applyReducer. |
Example:
var obj = {user: {firstName: "Albert"}};
var patches = [{op: "replace", path: "/user/firstName", value: "Albert"}, {op: "replace", path: "/user/lastName", value: "Einstein"}];
var errors = jsonpatch.validate(patches, obj);
if (errors.length == 0) {
}
else {
for (var i=0; i < errors.length; i++) {
if (!errors[i]) {
console.log("Valid patch at index", i, patches[i]);
}
else {
console.error("Invalid patch at index", i, errors[i], patches[i]);
}
}
}
OperationResult Type
Functions applyPatch and applyOperation both return OperationResult object. This object is:
{newDocument: any, test?: boolean, removed?: any}
Where:
newDocument: the new state of the document after the patch/operation is applied.test: if the operation was a test operation. This will be its result.removed: contains the removed, moved, or replaced values from the document after a remove, move or replace operation.
Validation Notes
Functions applyPatch, applyOperation, and validate accept a validate/ validator parameter:
- If the
validateOperation parameter is set to false, validation will not occur.
- If set to
true, the patch is extensively validated before applying using jsonpatch's default validation.
- If set to a
function callback, the patch is validated using that function.
If you pass a validator, it will be called with four parameters for each operation, function(operation, index, tree, existingPath) and it is expected to throw JsonPatchError when your conditions are not met.
operation The operation it self.index operation's index in the patch array (if application).tree The object that is supposed to be patched.existingPath the path operation points to.
Overwriting and move Operation
When the target of the move operation already exists, it is cached, deep cloned and returned as removed in OperationResult.
undefineds (JS to JSON projection)
As undefined type does not exist in JSON, it's also not a valid value of JSON Patch operation. Therefore jsonpatch will not generate JSON Patches that sets anything to undefined.
Whenever a value is set to undefined in JS, JSON-Patch methods generate and compare will treat it similarly to how JavaScript method JSON.stringify (MDN) treats them:
If undefined (...) is encountered during conversion it is either omitted (when it is found in an object) or censored to null (when it is found in an array).
See the ECMAScript spec for details.
Specs/tests
Changelog
To see the list of recent changes, see Releases.
4 KB minified and gzipped (12 KB minified)
Performance
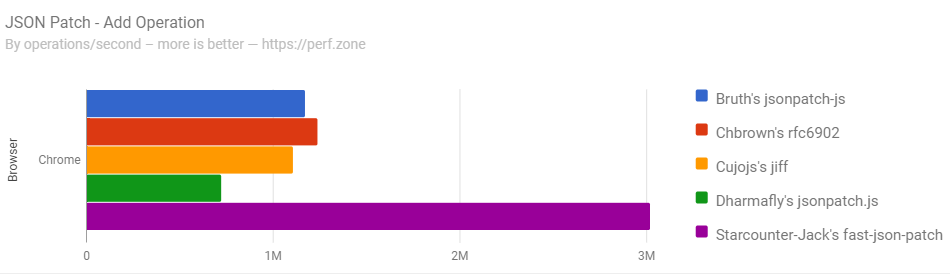
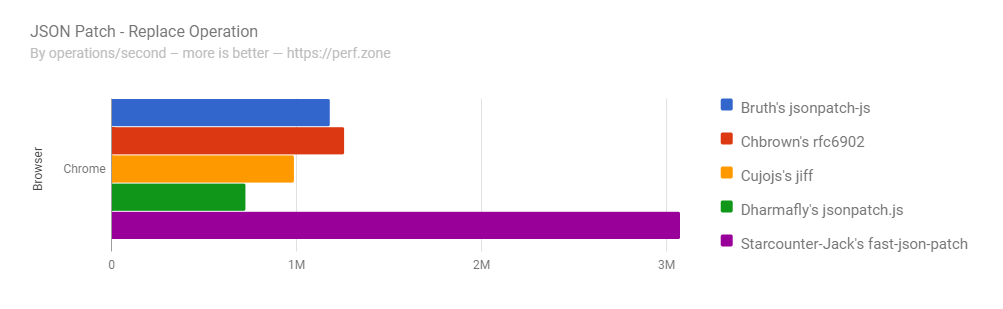
Tested on 29.08.2018. Compared libraries:
We aim the tests to be fair. Our library puts performance as the #1 priority, while other libraries can have different priorities. If you'd like to update the benchmarks or add a library, please fork the perf.zone benchmarks linked above and open an issue to include new results.
License
MIT





