
Security News
Oracle Drags Its Feet in the JavaScript Trademark Dispute
Oracle seeks to dismiss fraud claims in the JavaScript trademark dispute, delaying the case and avoiding questions about its right to the name.
Realtime Geolocation with Firestore & RxJS
:point_right: Live Demo :tv: Video Tutorial
npm install geofirex
# peer dependencies
npm install rxjs firebase
The library is a lightweight client for the Firebase Web SDK that provides tools for wrangling geolocation data in Firestore. You need a Firebase project to get started.
// Init Firebase
import * as firebase from 'firebase/app';
firebase.initializeApp(yourConfig);
// Init GeoFireX
import * as geofirex from 'geofirex';
const geo = geofirex.init(firebase);
Next, add some geolocation data in your database. A collection creates a reference to Firestore (just like the SDK), but with some extra geolocation tools. The point method returns a class that helps you create geolocation data.
const cities = geo.collection('cities');
const point = geo.point(40, -119);
cities.add({ name: 'Phoenix', position: point.data });
Calling point.data returns an object that contains a geohash string and a Firestore GeoPoint. It should look like this in your database. You can name the object whatever you want and even save multiple points on a single document.
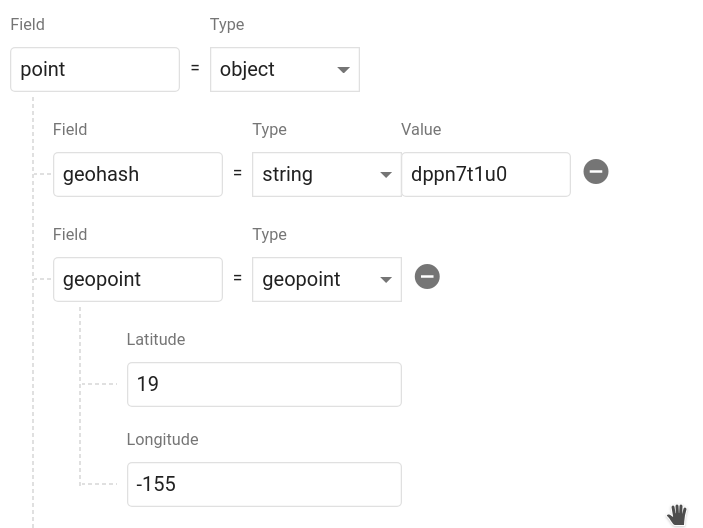
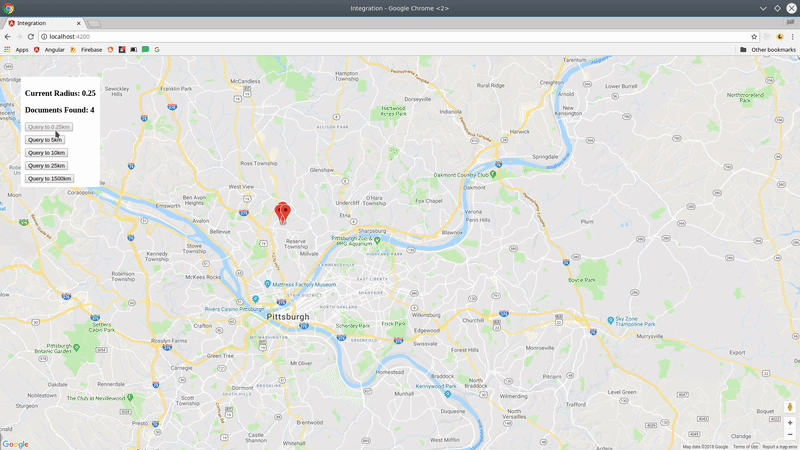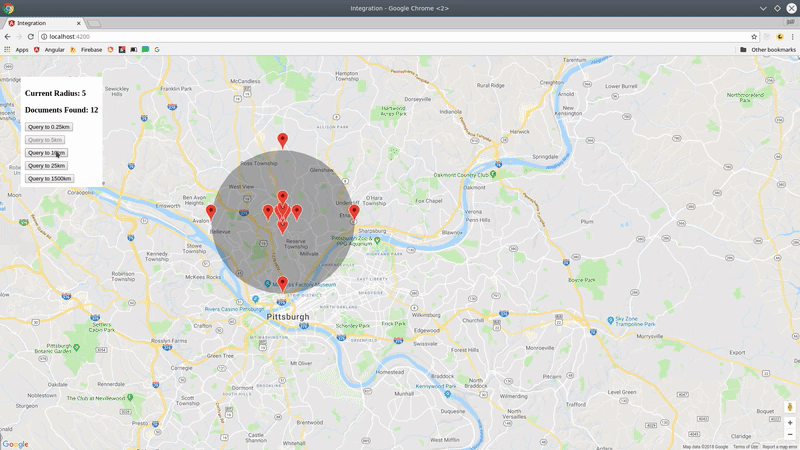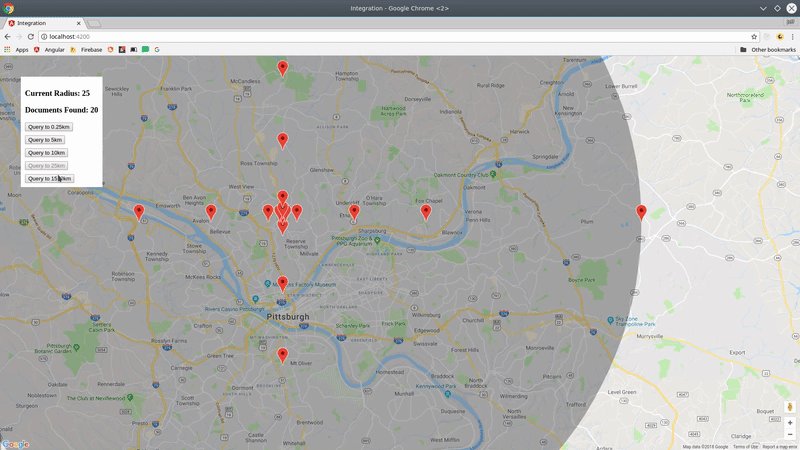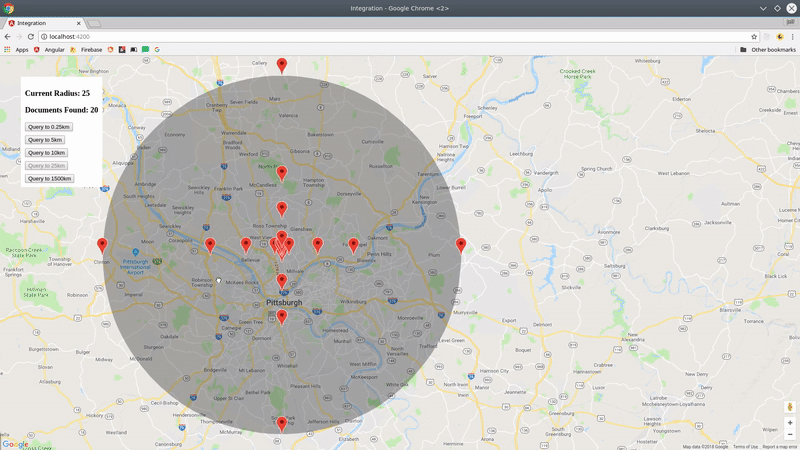
Now let's query Firestore for cities.position within 100km radius of a centerpoint.
const center = geo.point(40.1, -119.1);
const radius = 100;
const field = 'position';
const query = cities.within(center, radius, field);
The query returns a realtime Observable of the document data, plus some useful metadata like distance and bearing from the query centerpoint.
query.subscribe(console.log);
// [{ ...documentData, queryMetadata: { distance: 1.23232, bearing: 230.23 } }]
You now have a realtime stream of data to visualize on a map.
collection(path: string, query? QueryFn)Creates reference to a Firestore collection that can be used to make geo-queries and perform writes If you pass an optional Firestore query function, all subsequent geo-queries will be limited to this subset of documents
Example:
const collection = geo.collection('cities');
collection.within(center: GeoFirePoint, radius: number, field: string)
Query the parent Firestore collection by geographic distance. It will return documents that exist within X kilometers of the centerpoint.
Each doc also contains returns distance and bearing calculated on the query on the queryMetadata property.
Returns: Observable<object[]>
Write data just like you would in Firestore
collection.add(data)
Or use one of the client's conveniece methods
collection.setDoc(id, data) - Set a document in the collection with an ID.collection.setPoint(id, field, lat, lng)- Add a geohash to an existing docIn addition to Geo-Queries, you can also read the collection like you would normally in Firestore, but as an Observable
collection.data()- Observable of document datacollection.snapshot()- Observable of Firestore QuerySnapshotpoint(latitude: number, longitude: number)Returns a GeoFirePoint allowing you to create geohashes, format data, and calculate relative distance/bearing.
Example: const point = geo.point(38, -119)
point.hash Returns a geohash string at precision 9point.geoPoint Returns a Firestore GeoPointpoint.geoJSON Returns data as a GeoJSON Feature<Point>point.coords Returns coordinates as [latitude, longitude]point.data Returns data object suitable for saving to the Firestore databasepoint.distance(latitude, longitude) Haversine distance to a pointpoint.bearing(latitude, longitude) Haversine bearing to a pointThe goal of this package is to facilitate rapid feature development with tools like MapBox, Google Maps, and D3.js. If you have an idea for a useful feature, open an issue.
toGeoJSON OperatorA custom RxJS operator that transforms a collection into a GeoJSON FeatureCollection. Very useful for tools like MapBox that can use GeoJSON to update a realtime data source.
const query = geo.collection('cars').within(...)
query.pipe( toGeoJSON() )
// Emits a single object typed as a FeatureCollection<Geometry>
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [...]
}
getDon't need a realtime stream? Convert any query observable to a promise by wrapping it with get.
import { get } from 'geofirex';
async function getCars {
const query = geo.collection('cars').within(...)
const cars = await get(query)
}
It's possibe to build Firestore collections with billions of documents. One of the main motivations of this project was to make geoqueries possible on a queried subset of data. You can make a regular Firestore query on collection by passing a callback as the second argument, then all geoqueries will scoped these contstraints.
Note: This query requires a composite index, which you will be prompted to create with an error from Firestore on the first request.
Example:
const users = geo.collection('users', ref =>
ref.where('status', '==', 'online')
);
const nearbyOnlineUsers = users.within(center, radius, field);
This package requires RxJS 6.2, but you can still use it with older versions without blowing up you app by installing rxjs-compat.
Example:
npm i rxjs@latest rxjs-compat
DocumentReference.set() called with invalid dataFirestore writes cannot use custom classes, so make sure to call the data getter on the point.
const point = geo.point(40, -50);
// This is an ERROR
ref.add({ location: point });
// This is GOOD
ref.add({ location: point.data });
const radius = new BehaviorSubject(1);
const cities = geo.collection('cities');
const points = this.radius.pipe(
switchMap(rad => {
return cities.within(center, rad, 'point');
})
);
// Now update your query
radius.next(23);
[Latitude, Longitude]The GeoJSON spec formats coords as [Longitude, Latitude] to represent an X/Y plane. However, the Firebase GeoPoint uses [Latitude, Longitude]. For consistency, this libary will always require you to use the latter format.
FAQs
Realtime Firestore GeoQueries with RxJS
The npm package geofirex receives a total of 381 weekly downloads. As such, geofirex popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that geofirex demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Oracle seeks to dismiss fraud claims in the JavaScript trademark dispute, delaying the case and avoiding questions about its right to the name.

Security News
The Linux Foundation is warning open source developers that compliance with global sanctions is mandatory, highlighting legal risks and restrictions on contributions.

Security News
Maven Central now validates Sigstore signatures, making it easier for developers to verify the provenance of Java packages.