
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
jupyterlab-prodigy
Advanced tools
A JupyterLab extension for annotating machine learning training sets using Prodigy
This repo contains a JupyterLab extension for Prodigy, our scriptable annotation tool for creating training data for machine learning models. It lets you run Prodigy within a JupyterLab tab, and annotate as you develop your models and applications. In order to use this extension, you'll need a license for Prodigy – see this page for more details. For questions, please use the Prodigy Support Forum. If you've found a bug, feel free to submit a pull request.
🙏 Special thanks to Jupyter core dev Grant Nestor for helping us build this extension!

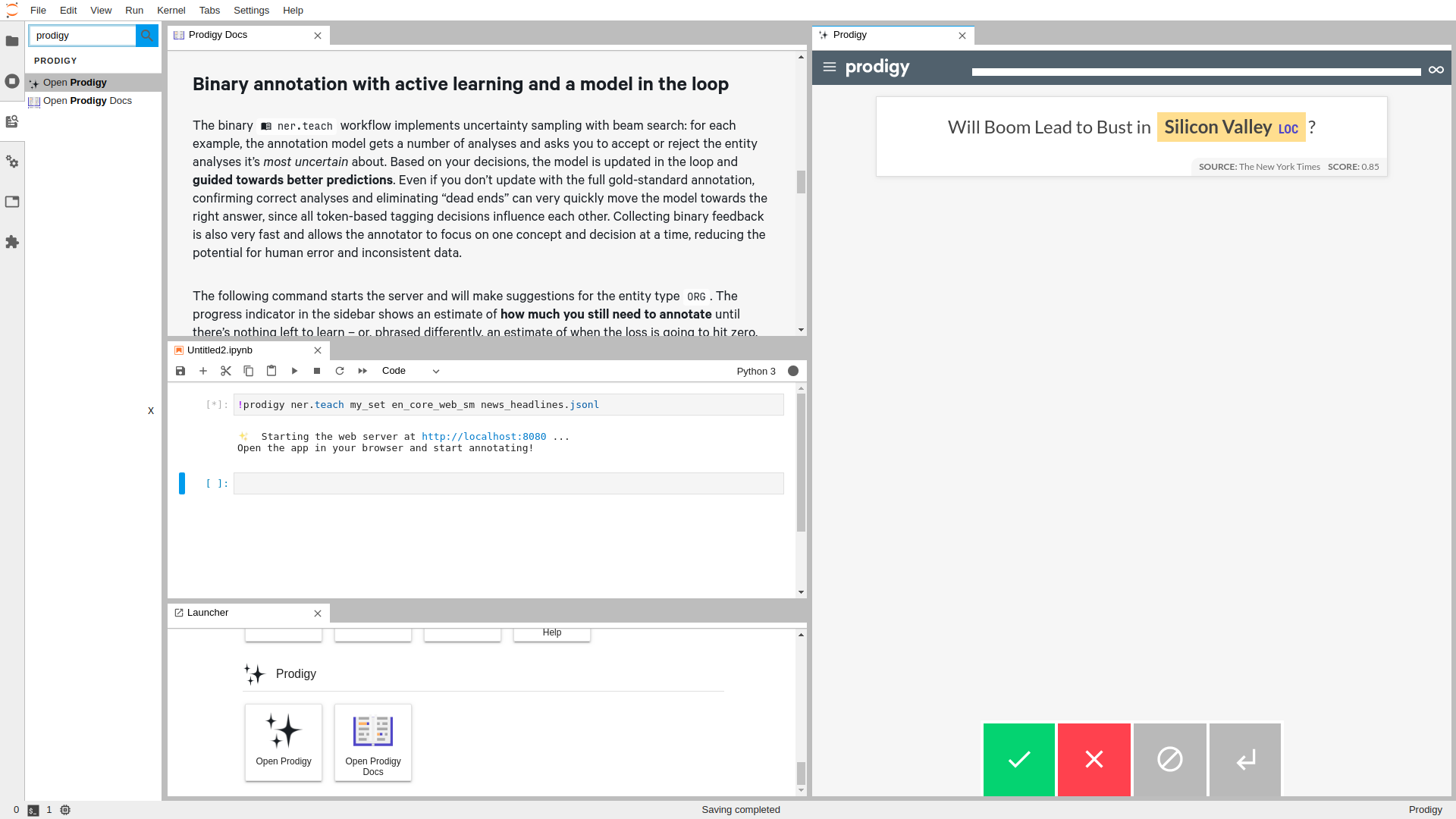
To use this extension, you need JupyterLab >= 3.0.0 and Prodigy.
pip install jupyterlab>=3.0.0
To install the extension, run:
pip install jupyterlab-prodigy
Ensure that the extension is installed and enabled:
jupyter labextension list
To remove the extension, run:
pip uninstall jupyterlab-prodigy
This extension is compatible with Jupyterlab 3.0.0 and above. If you're using
Jupyterlab with versions >=2.0.0 and <3.0.0, then you should install the
3.0.0 version of jupyterlab-prodigy
jupyter labextension install jupyterlab-prodigy@3.0.0
Start a Prodigy session in a terminal, e.g.:
$ prodigy ner.manual my_set blank:en notebooks/news_headlines.jsonl --label PERSON,ORG,PRODUCT
In another terminal session, start JupyterLab:
$ jupyter lab
Then, inside of JupyterLab, open the Commands on the left sidebar, and search/type:
Open Prodigy
Execute it, you will have a new Prodigy panel on the side.
If your Prodigy is being served at a URL different than the default (e.g. behind a reverse proxy) you can configure the URL to use in the settings.
Open the Settings menu, go to Advanced Settings Editor, select the settings for Prodigy Jupyter Extension, and there you can add your custom URL, e.g.:
{
"prodigyConfig": {
"url": "https://prodigy.example.com"
}
}
Note: You will need NodeJS to build the extension package. It is also highly-recommended that you work in a virtual environment when developing.
The jlpm command is JupyterLab's pinned version of
yarn that is installed with JupyterLab. You may use
yarn or npm in lieu of jlpm below.
# Clone the repo to your local environment
# Change directory to the jupyterlab-prodigy directory
# Install dev requirements
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
# Install package in development mode
pip install -e .
# Link your development version of the extension with JupyterLab
jupyter labextension develop . --overwrite
# Rebuild extension Typescript source after making changes
jlpm run build
You can watch the source directory and run JupyterLab at the same time in different terminals to watch for changes in the extension's source and automatically rebuild the extension.
# Watch the source directory in one terminal, automatically rebuilding when needed
jlpm run watch
# Run JupyterLab in another terminal
jupyter lab
With the watch command running, every saved change will immediately be built locally and available in your running JupyterLab. Refresh JupyterLab to load the change in your browser (you may need to wait several seconds for the extension to be rebuilt).
By default, the jlpm run build command generates the source maps for this
extension to make it easier to debug using the browser dev tools. To also
generate source maps for the JupyterLab core extensions, you can run the
following command:
jupyter lab build --minimize=False
pip uninstall jupyterlab-prodigy
See RELEASE
FAQs
A JupyterLab extension for annotating machine learning training sets using Prodigy
The npm package jupyterlab-prodigy receives a total of 6 weekly downloads. As such, jupyterlab-prodigy popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that jupyterlab-prodigy demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.