
Security News
pnpm 10.0.0 Blocks Lifecycle Scripts by Default
pnpm 10 blocks lifecycle scripts by default to improve security, addressing supply chain attack risks but sparking debate over compatibility and workflow changes.
A simple memory monitor which prompts you to slap (kill) processes after they grow too large.
MemSlap is a background daemon for monitoring application memory on macOS. If any processes grow beyond limits you set, they are "slapped" (killed). You can configure which processes have which limits, and if you would like to be prompted by notification first.
You will need to have Node.js installed on your machine before installing MemSlap.
Use npm to install the module (this ships with Node.js). Note that MemSlap is designed to run as a standalone background daemon, so take care to understand where npm installs software. It is recommended you install the module globally using the -g switch:
sudo npm install -g memslap
To see where npm installed the package, you can type npm root -g. This is usually /usr/local/lib/node_modules. Once installed globally, you should have a memslap command in your PATH. Use this to start, stop and otherwise control the daemon. See Command-Line below.
If you want MemSlap to install itself as a LaunchAgent (so it will startup on boot), run this command next:
sudo memslap boot
Note that MemSlap does not run as the root user. It runs as the current user who is logged in. However, we need sudo (root user permissions) to create a LaunchAgent entry.
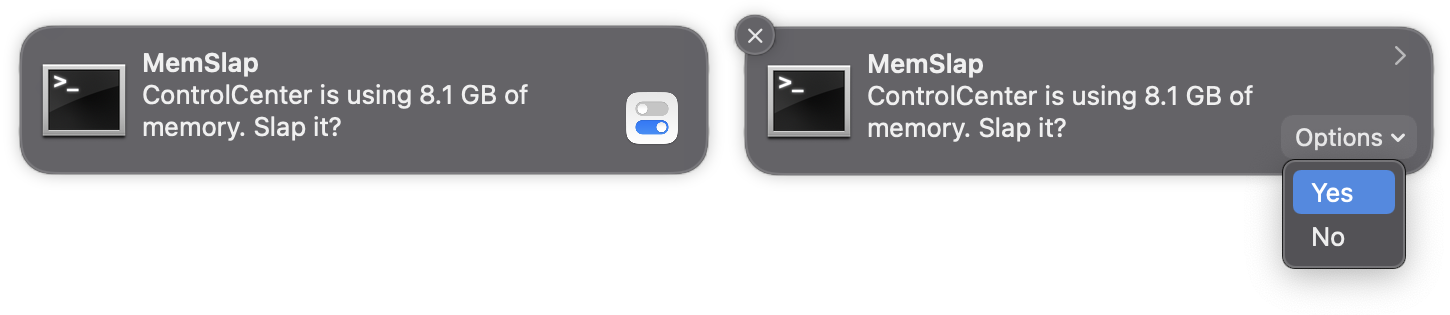
A sample configuration file is provided with MemSlap, which triggers a slap on any process that grows over 5 GB of memory. You will be prompted via notification before any action takes place. Click the notification bubble to kill the process, or ignore it to "snooze" it for 5 minutes. You can also click the little "Options" drop-down menu and select "Yes" to kill immediately, or "No" to snooze.
The configuration for MemSlap is stored in a single JSON file. It lives here on disk:
~/Library/Preferences/memslap.json
Upon initial installation, the default configuration looks like this:
{
"monitors": [
{
"enabled": true,
"name_matches": [".+"],
"max_mem": "5 GB",
"prompt": true,
"sound": "Funk",
"timeout_action": "ignore",
"click_action": "kill",
"snooze_time": "5 minutes",
"signal": "SIGTERM",
"notify": true,
"slap": true
}
],
"log_dir": "Library/Logs",
"log_filename": "memslap.log",
"log_columns": ["hires_epoch", "date", "hostname", "pid", "component", "category", "code", "msg", "data"],
"log_crashes": true,
"crash_filename": "memslap.crash.log",
"pid_file": "Library/Logs/memslap.pid",
"debug_level": 5
}
The config file is split into two sections: a monitors array containing one or more configurations to set rules for application memory limits, and some global configuration properties. See below for details on each.
The monitors property should be an array of objects, with each object representing a set of rules for monitoring applications, and what to do if they exceed limits. Here is an example monitor:
{
"enabled": true,
"name_matches": [".+"],
"name_excludes": ["Photoshop", "Logic"],
"max_mem": "5 GB",
"prompt": true,
"sound": "Funk",
"timeout_action": "ignore",
"click_action": "kill",
"snooze_time": "5 minutes",
"signal": "SIGTERM",
"notify": true,
"slap": true
}
In the above example the monitor will match any processes by name, but it excludes Photoshop and Logic (any processes that match those names). It will slap any processes which use over 5 GB of memory, but it will prompt the user first, using a notification. Feel free to add as many different monitors as you want.
Here are all the properties you can define inside each monitor object:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
enabled | Boolean | (Required) Enables or disables the monitor. |
name_matches | Array | An array of regular expressions to match processes by name. Set to [".+"] to match all. |
name_excludes | Array | An array of regular expressions to exclude processes by name. |
path_matches | Array | An array of regular expressions to match processes by path. |
path_excludes | Array | An array of regular expressions to exclude processes by path. |
max_mem | Mixed | The maximum amount of process memory to allow before slapping. Specify either bytes or a string such as "5 GB". |
prompt | Boolean | Set this to true if you want to be prompted by notification before slapping. |
sound | String | Which system sound to play for the prompt notification. |
timeout_action | String | If the user takes no action on the prompt, this specifies what to do when it times out. Set this to kill to kill by default. |
click_action | String | This specifies what to do if the user clicks on the notification bubble. Set this to kill to kill on click. |
snooze_time | String | How long to "snooze" (disable slaps) for an individual process if a slap is "snoozed" (timed out or user clicks "No"). |
signal | String | Which signal to send to the process to slap it. This defaults to SIGTERM (terminate nicely). |
notify | String | Set this to true to send a notification after a process is slapped. |
slap | Mixed | Set this to true to play a "slap" sound effect when a process is slapped. Or set this to any MP3 file path to use your own sound. |
For matching and excluding processes, case is sensitive, but only one of your regular expressions needs to match. For example:
{
"name_excludes": ["Photoshop", "Logic"]
}
This means that application names matching Photoshop OR Logic will be excluded from slapping.
Here are all the top-level global configuration properties which are not folder specific.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
log_dir | String | The directory in which to place our log files, relative to your home directory. |
log_filename | String | The filename of the MemSlap log file. |
log_columns | Array | An array of log columns to include in the event log. |
log_crashes | Boolean | If set to true, MemSlap will log crashes. |
crash_filename | String | The filename of the crash log, should a crash occur. |
pid_file | String | Path to the PID file used by the control script to start/stop the daemon. Please do not change this. |
debug_level | Integer | A verbosity control for the log file, where 1 is quiet and 10 is very loud indeed. |
See Logging below for more on the MemSlap log.
MemSlap comes with a simple command-line control script called memslap. It should already be available in your PATH, assuming you installed the module via sudo npm install -g memslap. It accepts a single command-line argument to start, stop, and a few other things. Examples:
memslap start
memslap stop
memslap restart
Here is the full command list:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
help | Show usage information. |
start | Start MemSlap as a background service. |
stop | Stop MemSlap and wait until it actually exits. |
restart | Calls stop, then start (hard restart). |
status | Checks whether MemSlap is currently running. |
boot | Install MemSlap as a startup service. |
unboot | Remove MemSlap from the startup services. |
config | Open the MemSlap configuration file using the OS. |
log | Open the current MemSlap log file using the OS. |
debug | Start the service in debug mode (see Debugging below). |
To start MemSlap in debug mode, issue this command:
memslap debug
This will start the service as a foreground process (not a daemon), and echo the event log straight to the console. This is a great way to troubleshoot issues. Hit Ctrl-C to exit.
To upgrade to the latest MemSlap version, you can use the sudo npm update -g memslap command. Your user configuration file will not be touched. Assuming you installed MemSlap globally, and it is currently running, then issue these commands to upgrade to the latest stable:
memslap stop
sudo npm update -g memslap
memslap start
MemSlap isn't for you? No problem, you can remove it with these commands:
memslap stop
sudo memslap unboot
sudo npm remove -g memslap
To remove all traces of the software, you may want to delete these files as well:
rm -v ~/Library/Preferences/memslap.json
rm -v ~/Library/Logs/memslap*
MemSlap uses the logging system built into pixl-server. Essentially there is one combined "event log" which contains debug messages and errors. By default it will log to ~/Library/Logs/memslap.log.
The general logging configuration is controlled by these three top-level global properties:
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
log_dir | String | Directory path where event log will be stored. Can be a fully-qualified path, or relative from your home directory. |
log_filename | String | Event log filename, joined with log_dir. |
debug_level | Integer | Debug logging level, larger numbers are more verbose, 1 is quietest, 10 is loudest. |
Log entries with the category set to debug are debug messages, and have a verbosity level from 1 to 10.
Here is an example log excerpt showing a typical startup with one monitor. In all these log examples the first 4 columns (hires_epoch, date, hostname and pid) are omitted for display purposes. The columns shown are component, category, code, msg, and data.
[MemSlap][debug][2][MemSlap v1.0.0 Starting Up][{"pid":10059,"ppid":10055,"node":"v16.12.0","arch":"arm64","platform":"darwin","argv":["/usr/local/bin/node","/usr/local/lib/node_modules/memslap/lib/main.js","--debug","--echo","--color"],"execArgv":[]}]
[MemSlap][debug][9][Writing PID File: Library/Logs/memslap.pid: 10059][]
[MemSlap][debug][9][Confirmed PID File contents: Library/Logs/memslap.pid: 10059][]
[MemSlap][debug][2][Server IP: 192.168.3.34, Daemon PID: 10059][]
[MemSlap][debug][3][Starting component: MemSlap][]
[MemSlap][debug][3][MemSlap engine starting up][]
[MemSlap][debug][2][Startup complete, entering main loop][]
[MemSlap][debug][9][Running process check][]
[MemSlap][debug][4][Process is being slapped][{"proc":{"pid":9343,"parentPid":1,"name":"Tweetbot","cpu":0,"cpuu":0,"cpus":0,"mem":174899200,"priority":4,"memVsz":410511824,"memRss":170800,"nice":0,"started":"2021-11-22 09:52:46","state":"sleeping","tty":"","user":"jhuckaby","command":"Tweetbot","params":"","path":"/Applications/Tweetbot.app/Contents/MacOS/Tweetbot"},"mon":{"enabled":true,"name_matches":{},"name_excludes":{},"max_mem":157286400,"prompt":true,"sound":"Funk","timeout_action":"ignore","click_action":"kill","snooze_time":300,"signal":"SIGTERM","notify":true,"slap":true}}]
[MemSlap][debug][9][Notify callback fired][{"deliveredAt":"2021-11-22 12:03:00 -0800","activationType":"closed","activationAt":"2021-11-22 12:03:06 -0800","activationValue":"No"}]
[MemSlap][debug][4][User clicked no][]
[MemSlap][debug][5][Process is being snoozed for 300 sec][{"pid":9343,"parentPid":1,"name":"Tweetbot","cpu":0,"cpuu":0,"cpus":0,"mem":174899200,"priority":4,"memVsz":410511824,"memRss":170800,"nice":0,"started":"2021-11-22 09:52:46","state":"sleeping","tty":"","user":"jhuckaby","command":"Tweetbot","params":"","path":"/Applications/Tweetbot.app/Contents/MacOS/Tweetbot"}]
If you are concerned about log file size, and/or you run MemSlap with a high debug_level (verbosity), you might want to enable log rotation. This can be done easily on macOS by creating the following file:
sudo vi /etc/newsyslog.d/memslap.conf
And then paste in these contents:
# logfilename [owner:group] mode count size when flags [/pid_file] [sig_num]
/Users/*/Library/Logs/memslap.log 644 5 * $D0 J
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2021 Joseph Huckaby.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
FAQs
A simple memory monitor which prompts you to slap (kill) processes after they grow too large.
The npm package memslap receives a total of 2 weekly downloads. As such, memslap popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that memslap demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
pnpm 10 blocks lifecycle scripts by default to improve security, addressing supply chain attack risks but sparking debate over compatibility and workflow changes.

Product
Socket now supports uv.lock files to ensure consistent, secure dependency resolution for Python projects and enhance supply chain security.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers have discovered multiple malicious npm packages targeting Solana private keys, abusing Gmail to exfiltrate the data and drain Solana wallets.