
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
react-arcgis
Advanced tools

React-ArcGIS is a library of React components which use the ArcGIS API for JavaScript. React-ArcGIS uses esri-loader internally to load and interact with the AMD ArcGIS API for JavaScript, and provide a base for building mapping applications.
npm i react-arcgis (if you decide you like it, you can even include --save)"react": "*".loadModules from esri-loader as esriPromise so as to not break existing applications.<Map />, <Scene />, <WebMap />, and <WebScene />While having a declarative html-like syntax for doing everything in the ArcGIS API for JavaScript would be great, the surface area of the api is very large, and it is regularly updated with new features and functionality. Rather than attempting to wrap the entire thing in a react-like syntax, I have decided to just handle the essentials, and provide clear examples for how to perform more complex tasks by using the api directly (still within your react app of course).
Because you will be less abstracted from Esri's API, you will actually be in a better position to utilize its full functionality!
Don't forget to load the js api stylesheet! https://js.arcgis.com/4.5/esri/css/main.css
If you need to support browsers lacking a native promise implementation, you will have to add a global Promise constructor polyfill to your project, as react-arcgis does not include one. I recommend es6-promise.
Render a simple map in React:
import * as React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Map } from 'react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<Map />,
document.getElementById('container')
);
Or, render a 3D web-scene:
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Scene } from 'react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<Scene />,
document.getElementById('container')
);
You can also add webmaps and webscenes from ArcGIS Online:
import * as React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { WebMap, WebScene } from 'react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<div style={{ width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}>
<WebMap id="6627e1dd5f594160ac60f9dfc411673f" />
<WebScene id="f8aa0c25485a40a1ada1e4b600522681" />
</div>,
document.getElementById('container')
);
If you want to change the style of the Map or Scene, just give it a class:
import * as React from 'react';
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Scene } from 'react-arcgis';
ReactDOM.render(
<Scene className="full-screen-map" />,
document.getElementById('container')
);
You can also pass properties into the Map, MapView, or SceneView via the viewProperties or mapProperties props:
import * as React from 'react';
import { Map } from 'react-arcgis';
export default (props) => (
<Map
class="full-screen-map"
mapProperties={{ basemap: 'satellite' }}
/>
)
These properties are passed directly to the available properties on the corresponding ArcGIS API classes:
import * as React from 'react';
import { Scene } from 'react-arcgis';
export default (props) => (
<Scene
style={{ width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}
mapProperties={{ basemap: 'satellite' }}
viewProperties={{
center: [-122.4443, 47.2529],
zoom: 6
}}
/>
)
If you want to access the map and view instances directly after they are loaded, pass in an onLoad handler:
import * as React from 'react';
import { Map } from 'react-arcgis';
export default class MakeAMap extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
map: null,
view: null
};
this.handleMapLoad = this.handleMapLoad.bind(this)
}
render() {
return <Map className="full-screen-map" onLoad={this.handleMapLoad} />;
}
handleMapLoad(map, view) {
this.setState({ map, view });
}
}
Don't forget an onFail handler in case something goes wrong:
import * as React from 'react';
import { WebScene } from 'react-arcgis';
export default class MakeAScene extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
status: 'loading'
};
this.handleFail = this.handleFail.bind(this);
}
render() {
return <WebScene className="full-screen-map" id="foobar" onFail={this.handleFail} />;
}
handleFail(e) {
console.error(e);
this.setState({ status: 'failed' });
}
}
The functionality available through the ArcGIS API for JavaScript goes well beyond just rendering maps, and if your application needs to do more with the map than simply show it, you will quickly find that you need access to the rest of Esri's API.
React-arcgis provides the children of <Map />, <Scene />, <WebMap />, and <WebScene /> with access to their parent's map and view instances through props. Combined with esriPromise, we can use this to easily get other functionality from the ArcGIS JS API and use it within our react application.
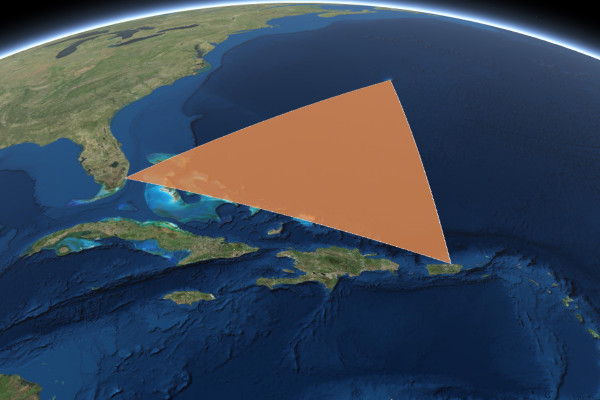
For example, let's convert a Bermuda Triangle graphic from this example into a react component:
import * as React from 'react';
import { esriPromise } from 'react-arcgis';
export default class BermudaTriangle extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
graphic: null
};
}
render() {
return null;
}
componentWillMount() {
esriPromise(['esri/Graphic']).then(([ Graphic ]) => {
// Create a polygon geometry
const polygon = {
type: "polygon", // autocasts as new Polygon()
rings: [
[-64.78, 32.3],
[-66.07, 18.45],
[-80.21, 25.78],
[-64.78, 32.3]
]
};
// Create a symbol for rendering the graphic
const fillSymbol = {
type: "simple-fill", // autocasts as new SimpleFillSymbol()
color: [227, 139, 79, 0.8],
outline: { // autocasts as new SimpleLineSymbol()
color: [255, 255, 255],
width: 1
}
};
// Add the geometry and symbol to a new graphic
const graphic = new Graphic({
geometry: polygon,
symbol: fillSymbol
});
this.setState({ graphic });
this.props.view.graphics.add(graphic);
})).catch((err) => console.error(err));
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.props.view.graphics.remove(this.state.graphic);
}
}
Now we can use the <BermudaTriangle /> component within our <Map />, <Scene />, <WebMap />, or <WebScene />, and the map and view props will automatically be supplied by react-arcgis:
import * as React from 'react';
import { Scene } from 'react-arcgis';
import BermudaTriangle from './BermudaTriangle'; // The Graphic component we just made
export default (props) => (
<Scene class="full-screen-map">
<BermudaTriangle />
</Scene>
)
Anyone is welcome to contribute to this package. My only "rule" is that your contribution must either pass the existing unit tests, or include additional unit tests to cover new functionality.
Here are some commands that may be helpful for development:
npm test: Runs the unit testsnpm run build: Builds the applicationMIT
FAQs
React component library for Esri's ArcGIS API for JavaScript
The npm package react-arcgis receives a total of 151 weekly downloads. As such, react-arcgis popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that react-arcgis demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.