react-xarrows
introduction
Draw arrows between components in React!




main features
- Connect between elements by passing a ref or an id for startElement and endElement.
- Automatic anchoring based on smallest path.
- can add customizable labels
- relatively fast algorithm to find path and to adjust canvas.
- Easily customize the look and behavior of the arrow.
- Written in typescript so you get nice props suggestions(but support js also of course).
found a problem? not a problem! post a new issue(here).
liked my work? please star this repo.
see and fork easily on codesandbox.
installation
with npm npm install react-xarrows.
(or yarn add react-xarrows)
Examples
Demos
see here! codebox of few examples(in this repo at /examples).
simple example:
import React, { useRef } from "react";
import Xarrow from "react-xarrows";
const boxStyle = {
border: "grey solid 2px",
borderRadius: "10px",
padding: "5px",
};
function SimpleExample() {
const box1Ref = useRef(null);
return (
<div
style={{ display: "flex", justifyContent: "space-evenly", width: "100%" }}
>
<div ref={box1Ref} style={boxStyle}>
hey
</div>
<p id="elem2" style={boxStyle}>
hey2
</p>
<Xarrow
start={box1Ref} //can be react ref
end="elem2" //or an id
/>
</div>
);
}
export default SimpleExample;
The API
types definitions
the properties the xarrow component receives is as follow:
export type xarrowPropsType = {
start: refType;
end: refType;
startAnchor?: anchorType | anchorType[];
endAnchor?: anchorType | anchorType[];
label?: labelType | labelsType;
color?: string;
lineColor?: string | null;
headColor?: string | null;
strokeWidth?: number;
headSize?: number;
path: "smooth" | "grid" | "straight";
curveness?: number;
dashness?: boolean | { strokeLen?: number; nonStrokeLen?: number; animation?: boolean | number };
passProps?: React.SVGProps<SVGPathElement>;
extendSVGcanvas?: number;
SVGcanvasProps?: React.SVGAttributes<SVGSVGElement>;
arrowBodyProps?: React.SVGProps<SVGPathElement>;
arrowHeadProps?: React.SVGProps<SVGPathElement>;
divContainerProps?: React.HTMLProps<HTMLDivElement>;
};
export type anchorType = anchorPositionType | anchorCustomPositionType;
export type anchorPositionType = "middle" | "left" | "right" | "top" | "bottom" | "auto";
export type anchorCustomPositionType = {
position: anchorPositionType;
offset: { rightness: number; bottomness: number };
};
export type reactRefType = { current: null | HTMLElement };
export type refType = reactRefType | string;
export type labelsType = { start?: labelType; middle?: labelType; end?: labelType };
export type labelType = JSX.Element;
API flexibility
This API has built in such way that most props can accept different types. you can keep things simple or provide more detailed props for more custom behavior - the API except both(see startAnchor or label properties for good examples).
see typescript types above for detailed descriptions of what type excepts every prop.
Properties
'start' and 'end'
can be a reference to a react ref to html element or string - an id of a DOM element.
'startAnchor' and 'endAnchor'
each anchor can be: "auto" | "middle" | "left" | "right" | "top" | "bottom".
auto will choose automatically the path with the smallest length.
can also be a list of possible anchors. if list is provided - the minimal length anchors will be choose from the list.
you can also offset each anchor passing offset.
examples:
endAnchor="middle" will set the anchor of the end of the line to the middle of the end element.endAnchor= { position: "auto", offset: { rightness: 20 } } will choose automatic anchoring for end anchor but will offset it 20 pixels to the right after normal positioning.endAnchor= ["right", {position: "left", offset: {bottomness: -10}}] only right and left anchors will be allowed for endAnchor, and if the left side connected then it will be offset 10 pixels up.
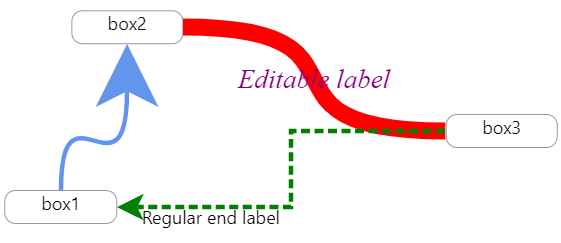
label
can be a string that will default to be at the middle or an object that describes where to place label and how to customize it. see label at xarrowPropsType above.
examples:
label="middleLabel"label=<div style={{ fontSize: "1.3em", fontFamily: "fantasy", fontStyle: "italic" }}>styled middle label</div>label={{ start:"I'm start label",middle: "middleLabel",end:<div style={{ fontSize: "1.3em", fontFamily: "fantasy", fontStyle: "italic" }}>big end label</div> }}
color,lineColor and headColor
color defines color for all the arrow include head. if lineColor or headColor is given so it overrides color specifically for line or head.
examples:
color="red" will change the color of the arrow to red(body and head).headColor="red" will change the color of the head of the arrow to red.lineColor="red" will change the color of the body of the arrow to red.
(NOTE - maybe headColor and lineColor will be combined to color)
strokeWidth and headSize
strokeWidth defines the thickness of the arrow(line and head).
headSize defines how big will be the head relative to the line(set headSize to 0 to make the arrow like a line).
examples:
strokeWidth={15} will make the arrow more thick(body and head).headSize={15} will make the head of the arrow more thick(relative to strokeWidth as well).
path
path can be one of: "smooth" | "grid" | "straight", and it controls the path arrow is drawn, exactly how their name suggest.
examples:
path={"grid"} will draw the line in sharp curves(90 degrees) like grid.
curveness
defines how much the lines curve.
examples:
curveness={false} will make the line straight without curves(exactly like path='straight').curveness={true} will choose default values of curveness.curveness={2} will make Xarrow extra curved.
dashness
can make the arrow dashed and can even animate.
if true default values(for dashness) are choose. if object is passed then default values are choose except what passed.
examples:
dashness={true} will make the line of the arrow to be dashed.dashness={{ strokeLen: 10, nonStrokeLen: 15, animation: -2 }} will make a custom looking dashness.
passing props
The xarrow is fully customizable, and you can pass props to any part of the component.
if unlisted(unknown) property is passed to xarrow so by default it'll be passed down to divConatiner.
passProps
you can pass properties to visible parts(body and head) of the arrow (such event handlers and much more).
this supposed to be enough for most cases.
examples:
passProps= {{onClick: () => console.log("xarrow clicked!")}} - now the arrow will console log a message when clicked.passProps= {{cursor: "pointer"}} - now the cursor will change to pointer style when hovering over Xarrow.passProps= {{pointerEvents: "none"}} - now the user cannot interact with Xarrow via mouse events.
advanced customization
The properties below can be used to customize the arrow even farther:
arrowBodyProps, arrowHeadProps, SVGcanvasProps, divContainerProps
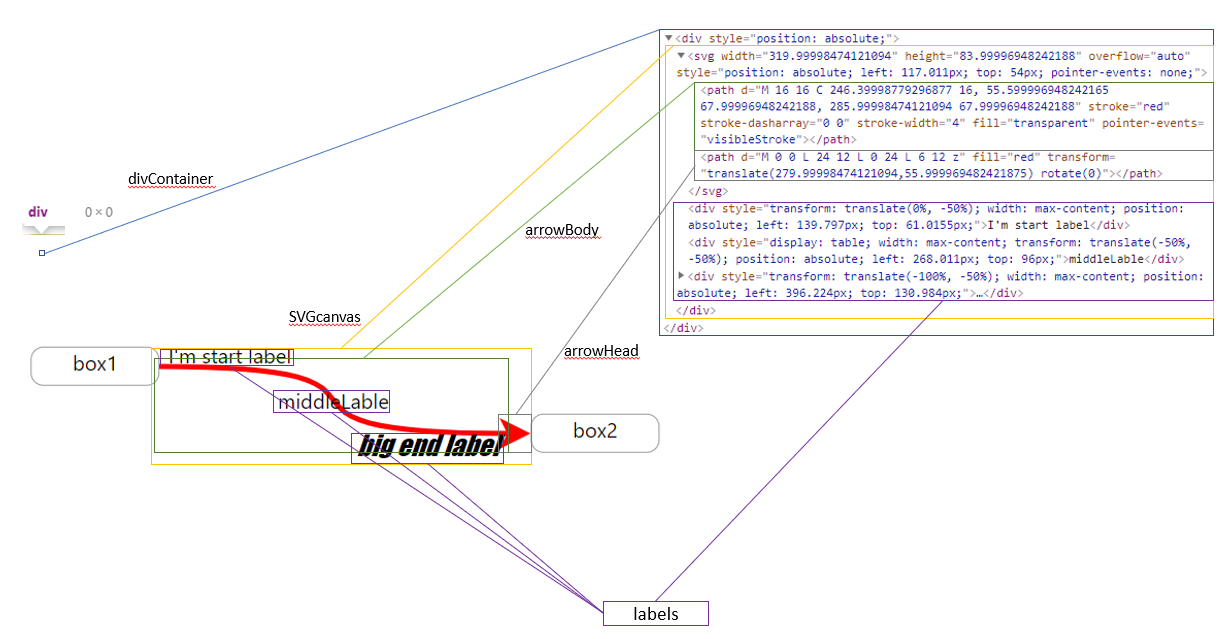
if you wish you can pass props specific part of the component.
divContainerProps - the container which contains the SVG canvas, and the optional labels elements. It takes no place, and located where you normaly placed him in the elements tree(no offset). The SVGcanvas and the labels will be placed in a offset from this div.SVGcanvasProps - the svg canvas which contains arrow head and body.arrowBodyProps - the body of the arrowarrowHeadProps - the arrow head.
Note that arrowBody and arrowHead receives props of svg path element, SVGcanvas receives props of svg element, and divContainerProps of a div element.
examples:
arrowHead = {onClick: () => console.log("head clicked!")} - now only the head will console log a message when clicked.
extendSVGcanvas
will extend the svg canvas at all sides. can be useful if for some reason the arrow(or labels) is cut though to small svg canvas(should be used in advanced custom arrows, for example if you used dx to move one of the labels and at exceeded the canvas).
example: advanced= {{extendSVGcanvas: 30 }} - will extended svg canvas in all sides by 30 pixels.
passProps
default props
default props is as follows:
Xarrow.defaultProps = {
startAnchor: "auto",
endAnchor: "auto",
label: null,
color: "CornflowerBlue",
lineColor: null,
headColor: null,
strokeWidth: 4,
headSize: 6,
path: "smooth",
curveness: 0.8,
dashness: false,
passProps: {},
arrowBodyProps: {},
arrowHeadProps: {},
SVGcanvasProps: {},
divContainerProps: {},
extendSVGcanvas: 0,
};
Versions
See CHANGELOG.md in this repo.








