spritesmith 
Convert images into spritesheets and coordinate maps.
spritesmith is also available as:
A folder of icons processed by spritesmith:






generates a spritesheet:

and a coordinate map:
{
"/home/todd/github/spritesmith/docs/fork.png": {
"x": 0,
"y": 0,
"width": 32,
"height": 32
},
"/home/todd/github/spritesmith/docs/github.png": {
"x": 32,
"y": 0,
"width": 32,
"height": 32
},
}
Do you like spritesmith?
Support us via gratipay or spread word on Twitter
Breaking changes in 1.0.0
We have moved to pixelsmith as the default engine. It is node based and should support your sprites. Any other engines must be installed outside of spritesmith. This will lead to cleaner and faster installations.
We have moved to binary-tree as the default algorithm. We changed this to give the best possible packing out of the box. If you were using top-down as the default, please specify it in your configuration.
Getting started
spritesmith can be installed via npm: npm install spritesmith
var spritesmith = require('spritesmith');
var sprites = ['fork.png', 'github.png', 'twitter.png'];
spritesmith({src: sprites}, function handleResult (err, result) {
result.image;
result.coordinates;
result.properties;
});
Documentation
spritesmith exports a spritesmith function as its module.exports.
If you would like a faster build time or need to support an obscure image format, see params.engine.
If you would like to adjust how images are laid out, see params.algorithm and params.algorithmOpts.
spritesmith(params, callback)
Utility that takes images and generates a spritesheet, coordinate map, and spritesheet info
- params
Object - Container for paramters
- src
String[] - Array of filepaths for images to include in spritesheet - padding
Number - Padding to use between images
- For example if
2 is provided, then there will be a 2px gap to the right and bottom between each image - An example usage of
padding can be found in the Examples section
- engine
String|Object - Optional engine override to use
- engineOpts
Object - Options to pass through to engine for settings
- For example
phantomjssmith accepts timeout via {engineOpts: {timeout: 10000}} - See your engine's documentation for available options
- exportOpts
Mixed - Options to pass through to engine for export
- For example
gmsmith supports quality via {exportOpts: {quality: 75}} - See your engine's documentation for available options
- algorithm
String - Optional algorithm to pack images with
- By default we use
binary-tree which packs images as efficiently as possible - An example usage of
algorithm can be found in the Examples section - For more algorithm options, see the Algorithms section
- algorithmOpts
Object - Optional algorithm options to pass through to algorithm for layout
- For example
top-down supports ignoring sorting via {algorithmOpts: {sort: false}} - See your algorithm's documentation for available options
- callback
Function - Error-first function that receives compiled spritesheet and map
callback should have signature function (err, result)- err
Error|null - If an error occurred, this will be it - result
Object - Container for result items
- image
String - Binary string representation of image - coordinates
Object - Map from filepath to coordinate information between original sprite and spritesheet
filepath will be the same as provided in params.src- [filepath]
Object - Container for coordinate information
- For those keeping track, this is
result.coordinates[filepath] - x
Number - Horizontal position of top-left corner of original sprite on spritesheet - y
Number - Vertical position of top-left corner of original sprite on spritesheet - width
Number - Width of original sprite - height
Number - Height of original sprite
- properties
Object - Container for information about spritesheet
- width
Number - Width of the spritesheet - height
Number - Height of the spritesheet
Algorithms
Images can be laid out in different fashions depending on the algorithm. We use layout to provide you as many options as possible. At the time of writing, here are your options for params.algorithm:
top-down | left-right | diagonal | alt-diagonal | binary-tree |
|---|
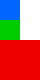 | 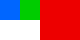 | 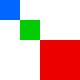 | 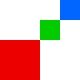 |  |
More information can be found in the layout documentation:
https://github.com/twolfson/layout
Engines
An engine can greatly improve the speed of your build (e.g. canvassmith) or support obscure image formats (e.g. gmsmith).
All spritesmith engines adhere to a common specification and test suite:
https://github.com/twolfson/spritesmith-engine-test
Below is a list of known engines with their tradeoffs:
pixelsmith
pixelsmith is a node based engine that runs on top of get-pixels and save-pixels.
Key differences: Doesn't support uncommon image formats (e.g. tiff) and not as fast as a compiled library (e.g. canvassmith).
phantomjssmith
phantomjssmith is a phantomjs based engine. It was originally built to provide cross-platform compatibility but has since been succeeded by pixelsmith.
Requirements: phantomjs must be installed on your machine and on your PATH environment variable. Visit the phantomjs website for installation instructions.
Key differences: phantomjs is cross-platform and supports all image formats.
canvassmith
canvassmith is a node-canvas based engine that runs on top of Cairo.
Requirements: Cairo and [node-gyp][] must be installed on your machine.
Instructions on how to install Cairo are provided in the [node-canvas wiki][].
[node-gyp][] should be installed via npm:
npm install -g node-gyp
Key differences: canvas has the best performance (useful for over 100 sprites). However, it is UNIX only.
[node-canvas wiki]: (https://github.com/LearnBoost/node-canvas/wiki/_pages
[node-gyp]: https://github.com/TooTallNate/node-gyp/
gmsmith
gmsmith is a gm based engine that runs on top of either Graphics Magick or Image Magick.
Requirements: Either Graphics Magick or Image Magick must be installed on your machine.
For the best results, install from the site rather than through a package manager (e.g. apt-get). This avoids potential transparency issues which have been reported.
Image Magick is implicitly discovered. However, you can explicitly use it via engineOpts
{
engineOpts: {
imagemagick: true
}
}
Key differences: gmsmith allows for configuring image quality whereas others do not.
Examples
Algorithm
This is an example of using a custom layout via the alt-diagonal algorithm.
var fs = require('fs');
var spritesmith = require('spritesmith');
spritesmith({
src: [
__dirname + '/fork.png',
__dirname + '/github.png',
__dirname + '/twitter.png'
],
algorithm: 'alt-diagonal'
}, function handleResult (err, result) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
fs.writeFileSync(__dirname + '/alt-diagonal.png', result.image, 'binary');
result.coordinates, result.properties;
});
Result:

Engine
This is an example of using a custom engine (canvassmith in this case).
{
"dependencies": {
"canvassmith": "~0.2.4"
}
}
var fs = require('fs');
var spritesmith = require('spritesmith');
spritesmith({
src: [
__dirname + '/fork.png',
__dirname + '/github.png',
__dirname + '/twitter.png'
],
engine: require('canvassmith')
}, function handleResult (err, result) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
fs.writeFileSync(__dirname + '/canvassmith.png', result.image, 'binary');
result.coordinates, result.properties;
});
Result:

Padding
This is an example of adding padding between images.
var fs = require('fs');
var spritesmith = require('spritesmith');
spritesmith({
src: [
__dirname + '/fork.png',
__dirname + '/github.png',
__dirname + '/twitter.png'
],
padding: 20
}, function handleResult (err, result) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
fs.writeFileSync(__dirname + '/padding.png', result.image, 'binary');
result.coordinates, result.properties;
});
Result:

Contributing
In lieu of a formal styleguide, take care to maintain the existing coding style. Add unit tests for any new or changed functionality. Lint via npm run lint and test via npm test.
Attribution
GitHub and Twitter icons were taken from Alex Peattie's JustVector Social Icons.
Fork designed by P.J. Onori from The Noun Project
Plus and Equals icons were built using the Ubuntu Light typeface.
License
Copyright (c) 2012-2014 Ensighten
Licensed under the MIT license.








