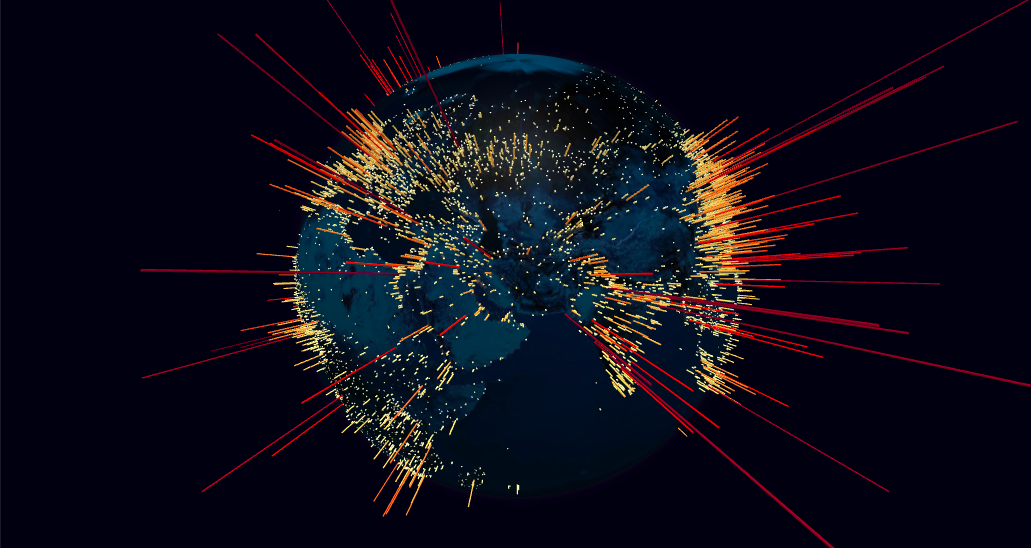
| arcsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of links to represent in the arcs map layer. Each link is displayed as an arc line that rises from the surface of the globe, connecting the start and end coordinates. | [] |
| arcStartLat([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's start latitude coordinate. | startLat |
| arcStartLng([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's start longitude coordinate. | startLng |
| arcEndLat([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's end latitude coordinate. | endLat |
| arcEndLng([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's end longitude coordinate. | endLng |
| arcColor([str, [str, ...] or fn]) | Arc object accessor function or attribute for the line's color. Also supports color gradients by passing an array of colors, or a color interpolator function. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| arcAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the arc's maximum altitude (ocurring at the half-way distance between the two points) in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude (ground line), 1 = globe radius). If a value of null or undefined is used, the altitude is automatically set proportionally to the distance between the two points, according to the scale set in arcAltitudeAutoScale. | null |
| arcAltitudeAutoScale([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the scale of the arc's automatic altitude, in terms of units of the great-arc distance between the two points. A value of 1 indicates the arc should be as high as its length on the ground. Only applicable if arcAltitude is not set. | 0.5 |
| arcStroke([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's diameter, in angular degrees. A value of null or undefined will render a ThreeJS Line whose width is constant (1px) regardless of the camera distance. Otherwise, a TubeGeometry is used. | null |
| arcCurveResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the arc's curve resolution, expressed in how many straight line segments to divide the curve by. Higher values yield smoother curves. | 64 |
| arcCircularResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the radial geometric resolution of each line, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the tube's circumference. Only applicable when using Tube geometries (defined arcStroke). | 6 |
| arcDashLength([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the dashed segments in the arc, in terms of relative length of the whole line (1 = full line length). | 1 |
| arcDashGap([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the gap between dash segments, in terms of relative line length. | 0 |
| arcDashInitialGap([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the initial gap before the first dash segment, in terms of relative line length. | 0 |
| arcDashAnimateTime([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the time duration (in ms) to animate the motion of dash positions from the start to the end point for a full line length. A value of 0 disables the animation. | 0 |
| arcsTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate arc changes involving geometry modifications. A value of 0 will move the arcs immediately to their final position. New arcs are animated by rising them from the ground up. | 1000 |