

advanced-pid
An advanced PID controller in Python. The derivative term can also be used in
practice thanks to built-in first-order filter. Detailed information can be
found here.
Usage is very simple:
from advanced_pid import PID
pid = PID(Kp=2.0, Ki=0.1, Kd=1.0, Tf=0.05)
while True:
timestamp, measurement = system.get_measurement()
reference = 1.0
control = pid(timestamp, reference - measurement)
system.set_input(control)
Complete API documentation can be found
here.
Usage
Biggest advantage of advanced-pid, the derivative term has a built-in first-order
filter.
advanced-pid package includes a toy mass-spring-damper system model for testing:
from advanced_pid import PID
from advanced_pid.models import MassSpringDamper
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from numpy import diff
system = MassSpringDamper(mass=1.0, spring_const=1.0, damping_const=0.2)
system.set_initial_value(initial_position=1.0, initial_velocity=0.0)
pid = PID(Kp=1.0, Ki=0.0, Kd=2.0, Tf=0.5)
time, meas, cont = [], [], []
for i in range(800):
timestamp, measurement = system.get_measurement()
control = pid(timestamp, -measurement)
system.set_input(control)
time.append(timestamp)
meas.append(measurement)
cont.append(control)
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3, 1)
fig.suptitle('Mass-Spring-Damper system')
ax1.set_ylabel('Measured Position [m]')
ax1.plot(time, meas, 'b')
ax1.grid()
ax2.set_ylabel('Force [N]')
ax2.plot(time, cont, 'g')
ax2.grid()
ax3.set_xlabel('Time [s]')
ax3.set_ylabel('Derivative Term')
ax3.plot(time[1:], diff(meas)/diff(time), 'r')
ax3.grid()
plt.show()
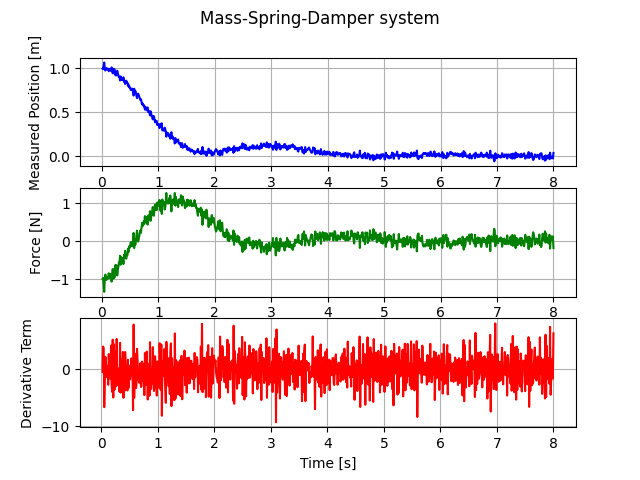
As It can be seen in the figure, derivative term cannot be use without a filter:
Installation
To install, run:
pip3 install advanced-pid
Tests
To run tests, run:
python -m unittest tests.test_pid
License
Licensed under the
MIT License.




