
Security News
Research
Data Theft Repackaged: A Case Study in Malicious Wrapper Packages on npm
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.
Python library for calculating geodesic distance on triangular based surface meshes
Python library to compute geodesic distance over a triangular based surface mesh.
A Cython wrapper of the C++ code by Kirsanov, which is an implementation of the exact geodesic algorithm for triangular mesh first described by Mitchell, Mount and Papadimitriou in 1987.
pygeodesic is similar to other libraries on PyPi (such as gdist and tvb-gdist), but:
A good alternative to pygeodesic is potpourri3d, which uses the heat method and vector heat method to compute geodesic distance over surfaces and point clouds. However, this library does not currently output the geodesic path on the surface.
A C++ compiler is required if you are not installing one of the precompiled wheels. Although pygeodesic is a Cython wrapper, Cython is not required as the cythonized C++ file is also provided.
VTK is used for visualisation in the example notebooks.
Install from PyPi:
pip install pygeodesic
Installation from source (from within folder containing setup.py):
python setup.py install
Loading pygeodesic:
import pygeodesic.geodesic as geodesic
To read the mesh files provided with the original C++ code:
filename = r'data/flat_triangular_mesh.txt'
result = geodesic.read_mesh_from_file(filename)
if result:
points, faces = result
To calculate the geodesic distance and path between two points (the source and the target) on the mesh:
# Initialise the PyGeodesicAlgorithmExact class instance
geoalg = geodesic.PyGeodesicAlgorithmExact(points, faces)
# Define the source and target point ids with respect to the points array
sourceIndex = 25
targetIndex = 97
# Compute the geodesic distance and the path
distance, path = geoalg.geodesicDistance(sourceIndex, targetIndex)
To calculate the geodesic distances from a single point (the source point) to all other points on the mesh:
source_indices = np.array([25])
target_indices = None
distances, best_source = geoalg.geodesicDistances(source_indices, target_indices)
To calculate the geodesic distances from two source points to 3 target points:
source_indices = np.array([25,100])
target_indices = np.array([0,10,50])
distances, best_source = geoalg.geodesicDistances(source_indices, target_indices)
For more detail, a Jupyter notebook is provided in the examples folder to show how to use pygeodesic to compute geodesic distances and paths.
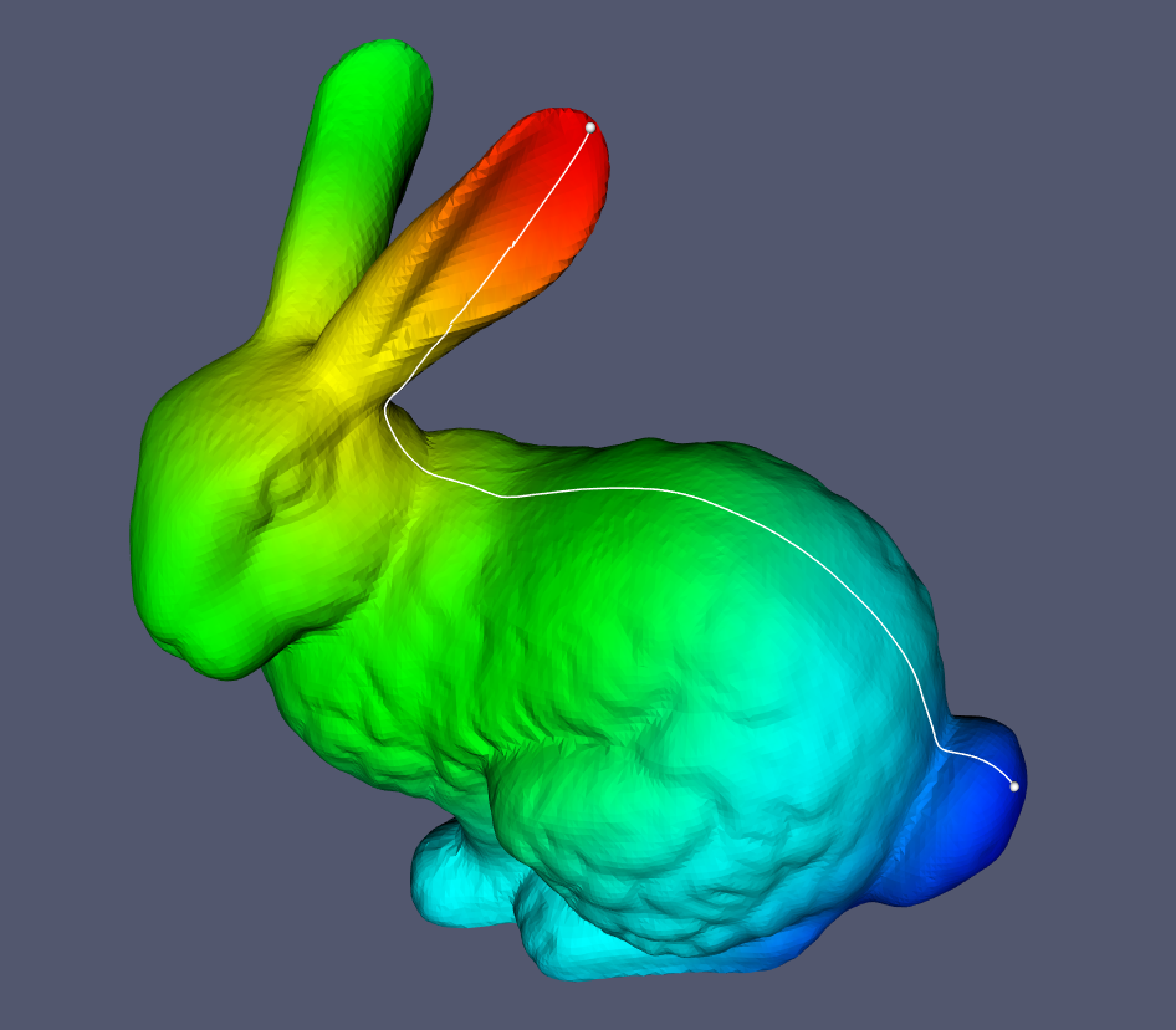
A Jupyter notebook is provided showing how to use pygeodesic to calculate the geodesic distance and path using the Stanford Bunny as an example.
FAQs
Python library for calculating geodesic distance on triangular based surface meshes
We found that pygeodesic demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Research
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.

Research
Security News
Attackers used a malicious npm package typosquatting a popular ESLint plugin to steal sensitive data, execute commands, and exploit developer systems.

Security News
The Ultralytics' PyPI Package was compromised four times in one weekend through GitHub Actions cache poisoning and failure to rotate previously compromised API tokens.