
Security News
PyPI’s New Archival Feature Closes a Major Security Gap
PyPI now allows maintainers to archive projects, improving security and helping users make informed decisions about their dependencies.
RoboDK tools for simulating and programming industrial robots (implements the RoboDK API)
The robodk package implements the RoboDK API for Python.
The RoboDK API allows creating simulations for industrial robots, specific mechanisms and generating vendor-specific programs for robots. With the RoboDK API for Python it is possible to simulate and program any industrial robot using Python programming language. The RoboDK API provides an alternative to using vendor-specific programming languages.
While RoboDK's graphical user interface can be used to create programs, it is possible to extend the robot controller limitations by using a universal programming language such as Python. The following page provides an overview of the RoboDK API using Python: https://robodk.com/offline-programming.
The robodk package is available on PyPi.
RoboDK can be used for a wide range of robot manufacturing applications, such as robot machining, 3D printing, synchronizing multiple robots, pick and place, and so on.
Important: The RoboDK API is not the same as the RoboDK Plug-In interface.
The robodk package includes the following modules:
robolink module is the link between RoboDK and Python. Any item from the RoboDK item tree can be retrieved. Items are represented by the object Item. An item can be a robot, a reference frame, a tool, an object or a specific project.robomath module is a robotics toolbox, inspired from Peter Corke's Robotics Toolbox. For instance, matrix operations, projection, timers, etc.robodialogs module is a dialogs toolbox. For instance, open and save file dialogs, message prompts, etc.robofileio module is a file operation toolbox. File properties, CSV, FTP, etc.roboapps module is a RoboDK Apps toolbox. More information can be found in our App loader documentation.You can find more information about RoboDK API in our documentation.
robodk package for PythonMac and Linux usually have Python 2 installed by default. Although it is not required, Python 3 can be installed on Linux by typing:
sudo apt-get install pip3
sudo apt-get install idle3
The RoboDK API can be used with a free RoboDK license.
By default, RoboDK automatically uses the PYTHONPATH environment variable pointing to the /RoboDK/Python/ folder to search for the robodk package. Alternatively, you can also install the robodk package for Python:
# cd path-to-python/Scripts
pip install robodk
RoboDK will automatically install external Python dependencies based on your usage. However, if you do not have an active ethernet connection or wish to install them all at once, you can specify external dependencies (see extras_require in setup.py):
# cd path-to-python/Scripts
pip install robodk[cv,apps,lint]
The Python interpreter and editor used by RoboDK can be set in:
RoboDK - Tools - Options - Python
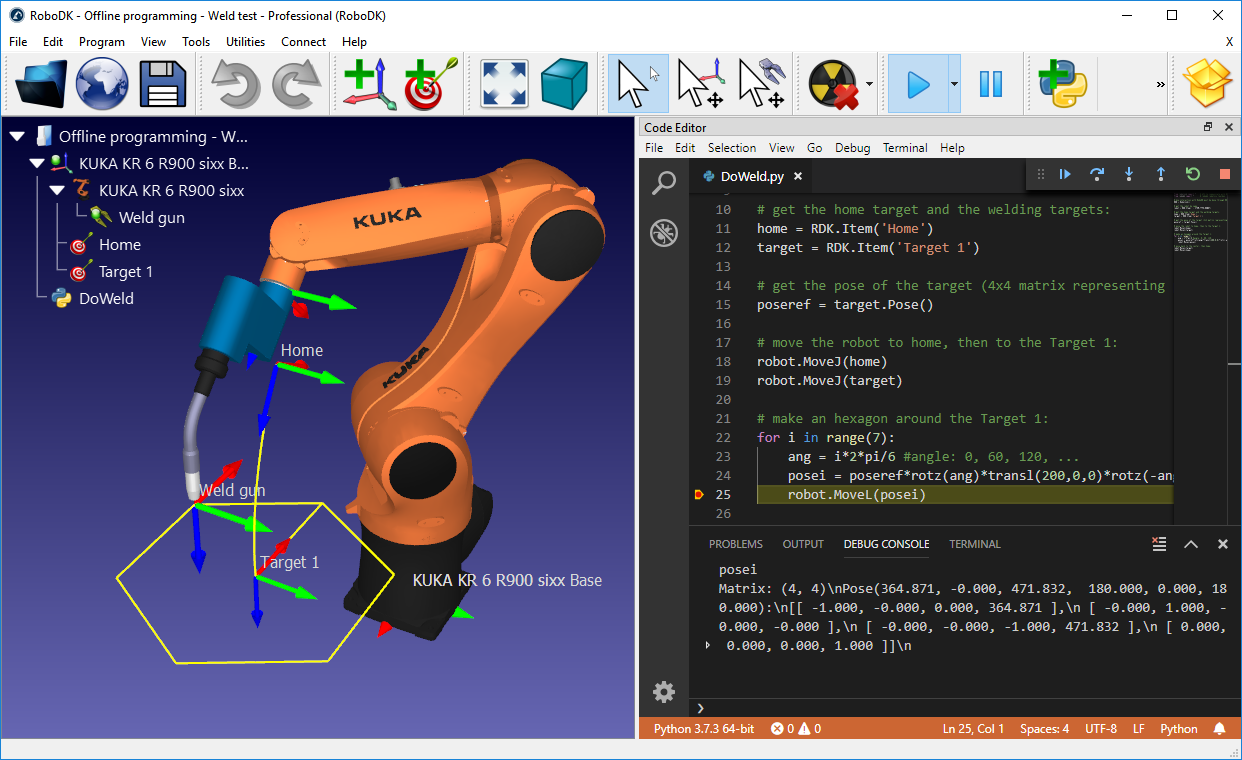
The following script shows an example that uses the robodk package for robot simulation and offline programming. For more examples using the API, see our documented examples.
from robodk.robolink import * # RoboDK's API
from robodk.robomath import * # Math toolbox for robots
# Start the RoboDK API:
RDK = Robolink()
# Get the robot item by name:
robot = RDK.Item('Fanuc LR Mate 200iD', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT)
# Get the reference target by name:
target = RDK.Item('Target 1')
target_pose = target.Pose()
xyz_ref = target_pose.Pos()
# Move the robot to the reference point:
robot.MoveJ(target)
# Draw a hexagon around the reference target:
for i in range(7):
ang = i*2*pi/6 #ang = 0, 60, 120, ..., 360
# Calculate the new position around the reference:
x = xyz_ref[0] + R*cos(ang) # new X coordinate
y = xyz_ref[1] + R*sin(ang) # new Y coordinate
z = xyz_ref[2] # new Z coordinate
target_pos.setPos([x,y,z])
# Move to the new target:
robot.MoveL(target_pos)
# Trigger a program call at the end of the movement
robot.RunCode('Program_Done')
# Move back to the reference target:
robot.MoveL(target)
The same script used for simulation can be used for robot programming offline. This means a program will be automatically generated for your robot controller to reproduce the movements on the robot. RoboDK supports a large number of robot controllers and it is easy to include compatibility for new robot controllers using Post Processors.
More information about robot post processors here:
You can find the most up to date list of supported robot controllers in our documentation for Post processors.
Once you have a script working in Python, you can easily set it up as an App using the App loader plugin. RoboDK Apps allow you to customize the RoboDK environment for simulation and offline programming. RoboDK Apps can be easily distributed for production. More information here:
Pylint is a source-code, bug and quality checker for Python programming. Pylint is integrated by default when using RoboDK's default settings (VScode/VScodium text editor).
If you prefer using other text editors you can use the pylint_robodk module with Pylint for linting. The following argument must be passed to pylint to activate this feature:
--load-plugins=pylint_robodk
FAQs
RoboDK tools for simulating and programming industrial robots (implements the RoboDK API)
We found that robodk demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
PyPI now allows maintainers to archive projects, improving security and helping users make informed decisions about their dependencies.

Research
Security News
Malicious npm package postcss-optimizer delivers BeaverTail malware, targeting developer systems; similarities to past campaigns suggest a North Korean connection.

Security News
CISA's KEV data is now on GitHub, offering easier access, API integration, commit history tracking, and automated updates for security teams and researchers.