
Security News
TypeScript is Porting Its Compiler to Go for 10x Faster Builds
TypeScript is porting its compiler to Go, delivering 10x faster builds, lower memory usage, and improved editor performance for a smoother developer experience.
traffic-light-classifier
Advanced tools
A computer vision & probabilistic approach based traffic light classifier.
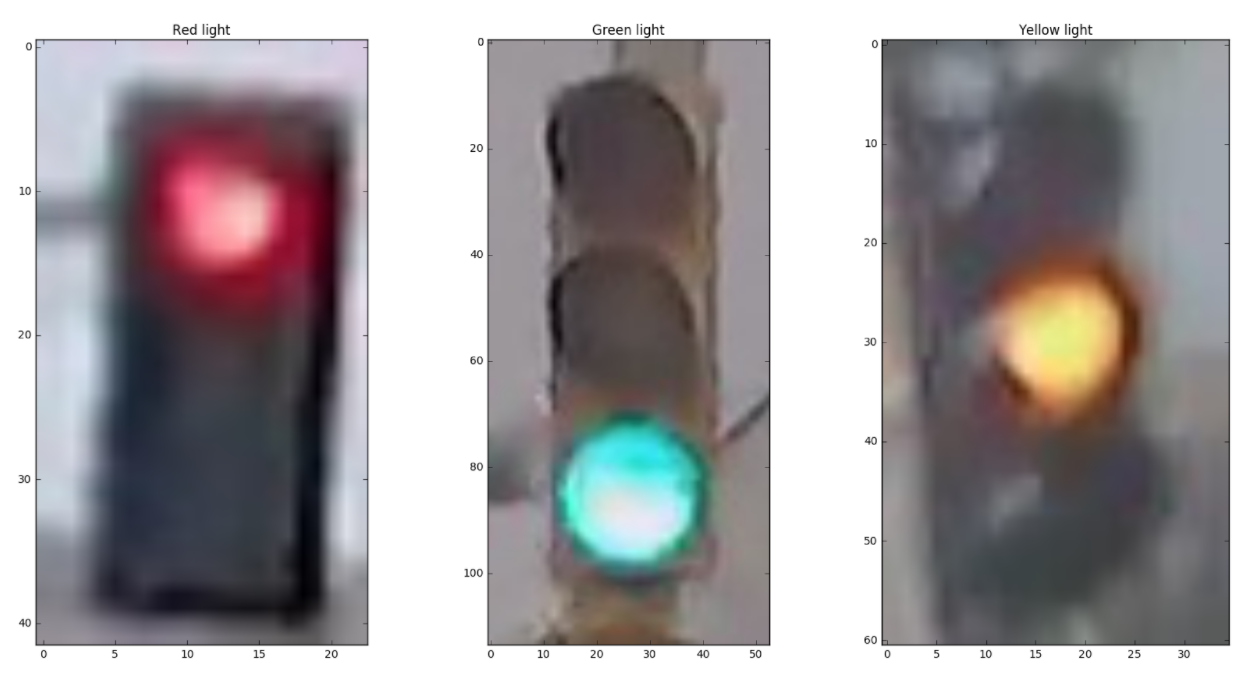
traffic_light_classifierThis traffic light dataset consists of 1484 number of color images in 3 categories - red, yellow, and green. As with most human-sourced data, the data is not evenly distributed among the types. There are:
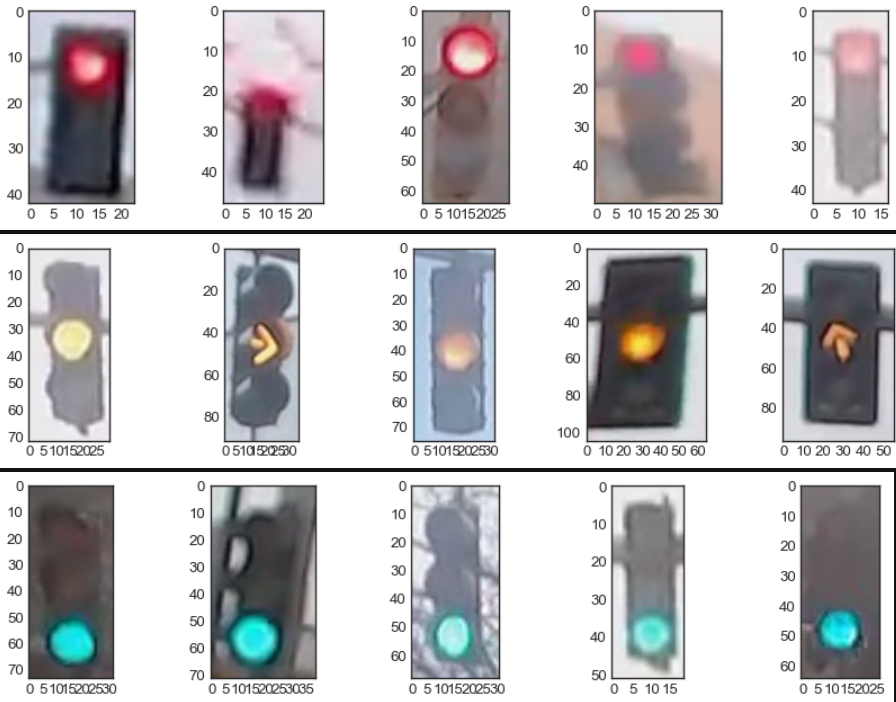

Note: All images come from this MIT self-driving car course and are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The features are in the form of either rgb values or hsv values of the pixels of the image and their locations.
For a single image, the classifier extracts the following hues from the 3 regions:
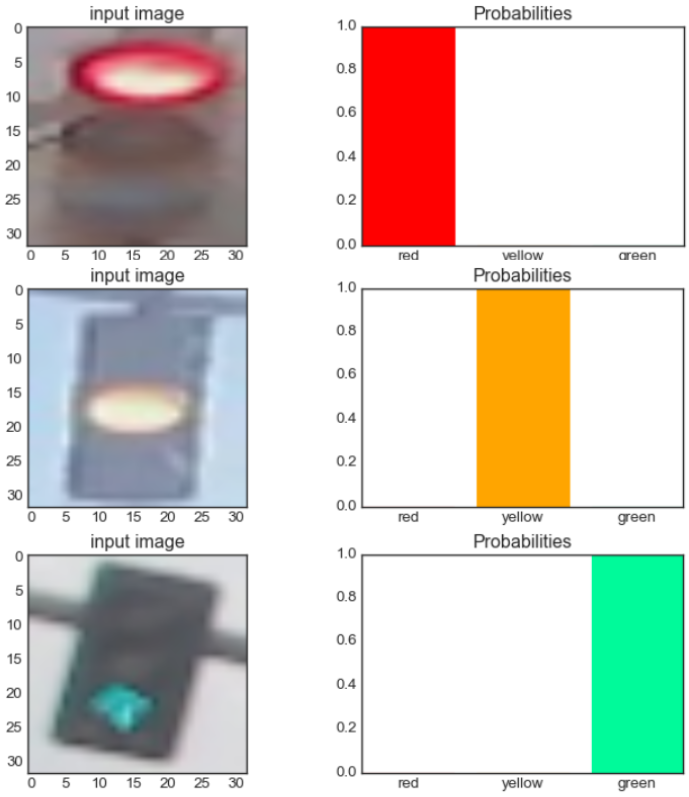
This classifier classifies an input image either red, yellow or green based on probabilities.
For a single input image, 3 lights will be located in the 3 regions (i.e. red, yellow and green light regions). Then the classifier calculates 3 probabilities:
And propobilities are calculated by,
$Probability\ of\ image\ being\ red = \dfrac {strength_{red}} {strength_{red} + strength_{yellow} + strength_{green}}$
$Probability\ of\ image\ being\ yellow = \dfrac {strength_{yellow}} {strength_{red} + strength_{yellow} + strength_{green}}$
$Probability\ of\ image\ being\ green = \dfrac {strength_{green}} {strength_{red} + strength_{yellow} + strength_{green}}$
where,
and,
Detailed analysis and visualization of each stage has been given in Notebook Traffic_Light_Classifier.
traffic_light_classifier has been implemented for this project.
traffic_light_classifiertraffic_light_classifier which contains a classifier, plotting & feature extraction functionalities, and datasets for the project.OpenCV-Python, scipy, matplotlib, numpy.# Install package from PyPI >>
!pip install traffic_light_classifier
# or
# Install package from GitHub >>
!pip install git+https://github.com/ShashankKumbhare/traffic-light-classifier.git#egg=traffic-light-classifier
traffic_light_classifier# Import package `traffic_light_classifier` >>
import traffic_light_classifier as tlc
# Create an instance of class Model provided in the package
model = tlc.Model()
# Call `compile` method of model object to train the model
# Note: Use parameter `show_analysis = True` to see the detailed process of the training/compiling stages.
model.compile()
model.compile(show_analysis = True)
# Get a random red image from the test dataset provided in the package
import random
image_red = random.choice( tlc.datasets.train.images_std.red )
tlc.plots.plot_images(image_red)
# Note: Use parameter `show_probabilities = True` to see the classification probabilities.
# Use parameter `show_analysis = True` to see the detailed process of the prediction stages.
label_predicted = model.predict( image_red )
label_predicted = model.predict( image_red, show_probabilities = True )
label_predicted = model.predict( image_red, show_analysis = True )
# For yellow and green test images
image_yellow = random.choice( tlc.datasets.train.images_std.yellow )
image_green = random.choice( tlc.datasets.train.images_std.green )
label_predicted = model.predict( image_yellow, show_analysis = True )
label_predicted = model.predict( image_green, show_analysis = True )
# Use `predict_dataset()` method to predict an entire dataset >>
images_std = tlc.datasets.test.images_std.all
labels_std = tlc.datasets.test.labels_std # optional
accuracy = model.predict_dataset(images_std, labels_std)
print(accuracy)
An ardent user might want to see what is happening in the compiling/training process. He might also want to revisit or play with them.
# After compilation/training, all the compilation stages are stored in `model.compilation` attribute >>
# To access them:
# Compilation-Stage 1: Average image for red, yellow and green training images
image1 = model.compilation.stg1_image_avg.red
image2 = model.compilation.stg1_image_avg.yellow
image3 = model.compilation.stg1_image_avg.green
tlc.plots.plot_images([image1, image2, image3])
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image1, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image2, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image3, "hsv")
# Compilation-Stage 2a: Region of high saturation in average red, yellow & green images
print(model.compilation.stg2a_region_high_s.red)
print(model.compilation.stg2a_region_high_s.yellow)
print(model.compilation.stg2a_region_high_s.green)
# Compilation-Stage 2b: Masked average images at their respective high saturation region
image1 = model.compilation.stg2b_image_avg_masked_region_high_s.red
image2 = model.compilation.stg2b_image_avg_masked_region_high_s.yellow
image3 = model.compilation.stg2b_image_avg_masked_region_high_s.green
tlc.plots.plot_images([image1, image2, image3])
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image1, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image2, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image3, "hsv")
# Compilation-Stage 3: Cropped average images at high saturation region
images1 = model.compilation.stg3_dataset_images_cropped_high_s_region.red[0:10]
images2 = model.compilation.stg3_dataset_images_cropped_high_s_region.yellow[0:10]
images3 = model.compilation.stg3_dataset_images_cropped_high_s_region.green[0:10]
tlc.plots.plot_images(images1)
tlc.plots.plot_images(images2)
tlc.plots.plot_images(images3)
# Compilation-Stage 4: Locations of lights in all training images
print(model.compilation.stg4_locations_light.red[0:5])
print(model.compilation.stg4_locations_light.yellow[0:5])
print(model.compilation.stg4_locations_light.green[0:5])
# Compilation-Stage 5: Cropped images at their respective light's position
images1 = model.compilation.stg5_dataset_images_light.red[0:10]
images2 = model.compilation.stg5_dataset_images_light.yellow[0:10]
images3 = model.compilation.stg5_dataset_images_light.green[0:10]
tlc.plots.plot_images(images1)
tlc.plots.plot_images(images2)
tlc.plots.plot_images(images3)
# Compilation-Stage 6: Average image of red lights, yellow lights & green lights
image1 = model.compilation.stg6_image_light_avg.red
image2 = model.compilation.stg6_image_light_avg.yellow
image3 = model.compilation.stg6_image_light_avg.green
tlc.plots.plot_images([image1, image2, image3])
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image1, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image2, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image3, "hsv")
# Compilation-Stage 7: Hues, saturations and brightnesses of average red light, average yellow light & average green light
print(model.compilation.stg7a_hue_avg_light.red.mu)
print(model.compilation.stg7a_hue_avg_light.red.sigma)
print(model.compilation.stg7a_hue_avg_light.red.dist)
print(model.compilation.stg7b_sat_avg_light.red.mu)
print(model.compilation.stg7b_sat_avg_light.red.sigma)
print(model.compilation.stg7b_sat_avg_light.red.dist)
print(model.compilation.stg7c_brt_avg_light.red.mu)
print(model.compilation.stg7c_brt_avg_light.red.sigma)
print(model.compilation.stg7c_brt_avg_light.red.dist)
# Compilation-Stage 8: Optimized parameters a & b for maximum accuracy
print(model.compilation.stg8_params_optimised)
# Compilation-Stage 9: Prediction analysis & accuracy of training dataset for classifier's optimized parameters
print( dir(model.compilation.stg9a_dataset_train_analysis.green[0]) )
print( dir(model.compilation.stg9a_dataset_train_analysis.green[0]) )
print( dir(model.compilation.stg9b_misclassified.green[0]) )
print( f"Accuracy red = {model.compilation.stg9c_accuracy_train.red}" )
print( f"Accuracy yellow = {model.compilation.stg9c_accuracy_train.yellow}" )
print( f"Accuracy green = {model.compilation.stg9c_accuracy_train.yellow}" )
print( f"Accuracy overall = {model.compilation.stg9c_accuracy_train.all}" )
An ardent user might want to see what is happening behind the prediction process. Analyzing misclassified images might give user the understanding of the flaws of the classifier model and help improve the algorithm.
import random
image_red = random.choice( tlc.datasets.train.images_std.red )
tlc.plots.plot_images(image_red)
label_predicted = model.predict( image_red )
# After prediction, all the compilation stages are stored in `model.prediction` attribute >>
# To access them:
# Compilation-Stage 1: Croped image at model's optimal high saturation region for red, yellow, green light's position
image1 = model.prediction.stg1_image_high_s_region.red
image2 = model.prediction.stg1_image_high_s_region.yellow
image3 = model.prediction.stg1_image_high_s_region.green
tlc.plots.plot_images([image1, image2, image3])
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image1, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image2, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image3, "hsv")
# Compilation-Stage 2: Located lights in model's optimal regions of red, yellow, green lights
model.prediction.stg2_locations_light.red
print(model.prediction.stg2_locations_light.red)
print(model.prediction.stg2_locations_light.yellow)
print(model.prediction.stg2_locations_light.green)
# Compilation-Stage 3: Cropped lights
image1 = model.prediction.stg3_image_light.red
image2 = model.prediction.stg3_image_light.yellow
image3 = model.prediction.stg3_image_light.green
tlc.plots.plot_images([image1, image2, image3])
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image1, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image2, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image3, "hsv")
# Compilation-Stage 4: Extracted model's red, yellow, green light's colors from the respective cropped parts of the input image
image1 = model.prediction.stg4_image_colors_extracted.red
image2 = model.prediction.stg4_image_colors_extracted.yellow
image3 = model.prediction.stg4_image_colors_extracted.green
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image1, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image2, "hsv")
tlc.plots.plot_channels(image3, "hsv")
# Compilation-Stage 5: Distribution of hues extracted from the model's red, yellow & green light region
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.red.mu)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.red.sigma)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.red.dist)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.yellow.mu)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.yellow.sigma)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.yellow.dist)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.green.mu)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.green.sigma)
print(model.prediction.stg5a_hue_input_light.green.dist)
# Similarly for saturation and brightness
# Compilation-Stage 6: Probabilities of image being red, yellow and green
print( model.prediction.stg6_probabilities.image_being_red )
print( model.prediction.stg6_probabilities.image_being_yellow )
print( model.prediction.stg6_probabilities.image_being_green )
# Compilation-Stage 7: Predicted label
print( model.prediction.stg7_label_predicted )
print( model.prediction.stg7_label_predicted_str )
The package usage have been clearly demonstrated in the Notebook Traffic_Light_Classifier.
FAQs
A computer vision & probabilistic approach based traffic light classifier.
We found that traffic-light-classifier demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
TypeScript is porting its compiler to Go, delivering 10x faster builds, lower memory usage, and improved editor performance for a smoother developer experience.

Research
Security News
The Socket Research Team has discovered six new malicious npm packages linked to North Korea’s Lazarus Group, designed to steal credentials and deploy backdoors.

Security News
Socket CEO Feross Aboukhadijeh discusses the open web, open source security, and how Socket tackles software supply chain attacks on The Pair Program podcast.