Python Worker Dispatcher
A flexible task dispatcher for Python with multiple threading or processing control


Features
-
Tasks Dispatching to managed workers
-
Elegant Interface for setup and use
-
Various modes to choose from
OUTLINE
DEMONSTRATION
Just write your own callback functions using the library, then run it and collect the result details:
$ python3 main.py
Worker Dispatcher Configutation:
- Local CPU core: 10
- Tasks Count: 100
- Runtime: Unlimited
- Dispatch Mode: Fixed Workers (Default)
- Workers Info:
└ Worker Type: Processing
└ Number of Workers : 10
└ Max Worker: 10
--- Start to dispatch workers at 2024-06-14T17:46:30.996685+08:00 ---
...(User-defined output)...
--- End of worker dispatch at 2024-06-14T17:46:41.420888+08:00---
Spend Time: 10.424203 sec
Completed Tasks Count: 100
Uncompleted Tasks Count: 0
Undispatched Tasks Count: 0
Use 20 theads concurrently to dispatch tasks for HTTP reqeusts
import worker_dispatcher
import requests
def each_task(id: int, config, task, log):
response = requests.get(config['my_endpoint'] + task)
return response
responses = worker_dispatcher.start({
'task': {
'list': ['ORD_AH001', 'ORD_KL502', '...' , 'ORD_GR393'],
'callback': each_task,
'config': {
'my_endpoint': 'https://your.name/order-handler/'
},
},
'worker': {
'number': 20,
}
})
Utilizes all CPU cores on the machine to compute tasks.
import worker_dispatcher
def each_task(id: int, config, task, log):
result = sum(id * i for i in range(10**9))
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
results = worker_dispatcher.start({
'task': {
'list': 10,
'callback': each_task,
},
'worker': {
'use_processing': True
}
})
INTRODUCTION
This library helps to efficiently consume tasks by using multiple threading or processing and returns all results jointly.
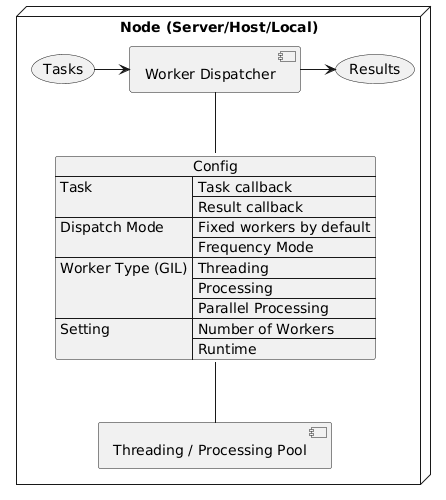
INSTALLATION
To install the current release:
$ pip install worker-dispatcher
USAGE
By calling the start() method with the configuration parameters, the package will begin dispatching tasks while managing threading or processing based on the provided settings. Once the tasks are completed, the package will return all the results.
An example configuration setting with all options is as follows:
import worker_dispatcher
results = worker_dispatcher.start({
'debug': False,
'task': {
'list': [],
'callback': callback_sample,
'config': {},
'result_callback': False
},
'worker': {
'number': 8,
'frequency_mode': {
'enabled': False,
'interval': 1,
'accumulated_workers': 0,
'max_workers': None,
},
'use_processing': False,
'parallel_processing': {
'enabled': False,
'use_queue': False,
},
},
'runtime': None,
'verbose': True
})
Options
| Option | Type | Deafult | Description |
|---|
| debug | bool | False | Debug mode |
| task.list | multitype | list | The tasks for dispatching to each worker. *
- List: Each value will be passed as a parameter to your callback function.
- Integer: The number of tasks to be generated. |
| task.callback | callable | (sample) | The callback function called by each worker runs |
| task.config | multitype | list | The custom variable to be passed to the callback function |
| task.result_callback | callable | Null | The callback function called when each task processes the result |
| worker.number | int | (auto) | The number of workers to fork.
(The default value is the number of local CPU cores) |
| worker.frequency_mode.enabled | bool | False | Changing from assigning tasks to a fixed number of workers once, to assigning tasks and workers frequently. |
| worker.frequency_mode.interval | float | 1 | The second(s) of interval. |
| worker.frequency_mode.accumulated_workers | int | 0 | Accumulate the number of workers for each interval for next dispatch. |
| worker.frequency_mode.max_workers | int | None | limit the maximum number of workers to prevent system exhaustion. |
| worker.use_processing | boolean | False | To break GIL, workers will be based on processing pool. |
| worker.parallel_processing.enabled | bool | False | worker.use_processing setting will be ignored when enabled. The actual number of workers will be adjusted to a multiple of the CPU core count. |
| worker.parallel_processing.use_queue | bool | False | Enable the use of a task queue instead of task dispatch, which allows specifying the number of workers but may be limited by your device. |
| runtime | float | None | Dispatcher max runtime in seconds. |
| verbose | bool | True | Enables or disables verbose mode for detailed output. |
task.callback
The callback function called by each worker runs
callback_function (id: int, config, task, log: dict) -> Any
| Argument | Type | Deafult | Description |
|---|
| id | int | (auto) | The sequence number generated by each task starting from 1 |
| config | multitype | {} | The custom variable to be passed to the callback function |
| task | multitype | (custom) | Each value from the task.list |
| log | dict | {} | The log from each task written by this callback function. |
The return value can be False to indicate task failure in TPS logs.
Alternatively, it can be a requests.Response, indicating failure if the status code is not 200.
task.result_callback
The callback function called when each task processes the result
result_callback_function (id: int, config, result, log: dict) -> Any
| Argument | Type | Deafult | Description |
|---|
| id | int | (auto) | The sequence number generated by each task starting from 1 |
| config | multitype | {} | The custom variable to be passed to the callback function |
| result | multitype | (custom) | Each value returned back from task.callback |
| log | dict | (auto) | Reference: get_logs() |
Other Methods
-
get_results()
Get all results in list type after completing start()
-
get_logs()
Get all logs in list type after completing start()
Each log is of type dict, containing the results of every task processed by the worker:
- task_id
- started_at
- ended_at
- duration
- result
-
get_result_info()
Get a dict with the whole spending time and started/ended timestamps after completing start()
-
get_tps()
Get TPS report in dict type after completing start() or by passing a list data.
def get_tps(logs: dict=None, debug: bool=False, interval: float=0, reverse_interval: bool = False, display_intervals: bool = False) -> dict:
The log dict matches the format of the get_logs() and refers to it by default.
Each task within a log will be validated for success according to the callback_function() result rule.
Scenarios
Stress Test
Perform a stress test scenario with 10 requests per second.
import worker_dispatcher
def each_task(id, config, task, log):
response = None
try:
response = requests.get(config['my_endpoint'], timeout=(5, 10))
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print("An error occurred:", e)
return response
responses = worker_dispatcher.start({
'task': {
'list': 600,
'callback': each_task,
'config': {
'my_endpoint': 'https://your.name/api'
},
},
'worker': {
'number': 10,
'frequency_mode': {
'enabled': True,
'interval': 1,
},
},
})
print(worker_dispatcher.get_logs())
print(worker_dispatcher.get_tps())







