
Research
/Security News
Shai Hulud Strikes Again (v2)
Another wave of Shai-Hulud campaign has hit npm with more than 500 packages and 700+ versions affected.

Sarah Gooding
September 27, 2024
The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity, ENISA, published its annual 2024 threat landscape report, providing valuable insights into the cybersecurity trends that are currently plaguing the EU. This comprehensive report highlights the most pressing challenges facing organizations today, including malware, supply chain attacks, and weaponized AI. It identifies seven primary threats that make up the bulk of the 11,079 recorded cybersecurity incidents:
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are the most commonly reported cyberthreat, accounting for more than 46% of incidents. The top sectors most affected by this type of threat include public admin (33.24%), transport (21.05%), and banking/finance (12.49%). ENISA reports that the attacks are getting larger, more complex, and less expensive to deploy.
The trend in the increasing frequency, size and complexity (e.g. multi-vector attacks) of DDoS attacks was also confirmed in 2023, with thousands of hyper-volumetric DDoS attacks at unseen rates. Akamai observed an unprecedented surge in size, with security vendors and their web sites massively attacked by DDoS. At the same time, the increasing spread of cybercrime-as-a-service ecosystem, as well as advanced tools, are reducing the cost of launching DDoS attacks at scale.
Microsoft clocked 1,700 DDoS attacks per day and 13 million worldwide last year. According to Gcore’s DDoS Attack Trends for 2023, they are growing in power, with a 100% plus increase in the peaks of attack volume in the last three years, from 300Gbps in 2021 to 1.6Tbps in 2023.
Ransomware attacks continue to be a major concern affecting the EU, with attackers targeting organizations of all sizes and industries. Manufacturing, retail, ICT service management, and other sectors are among the top targets.
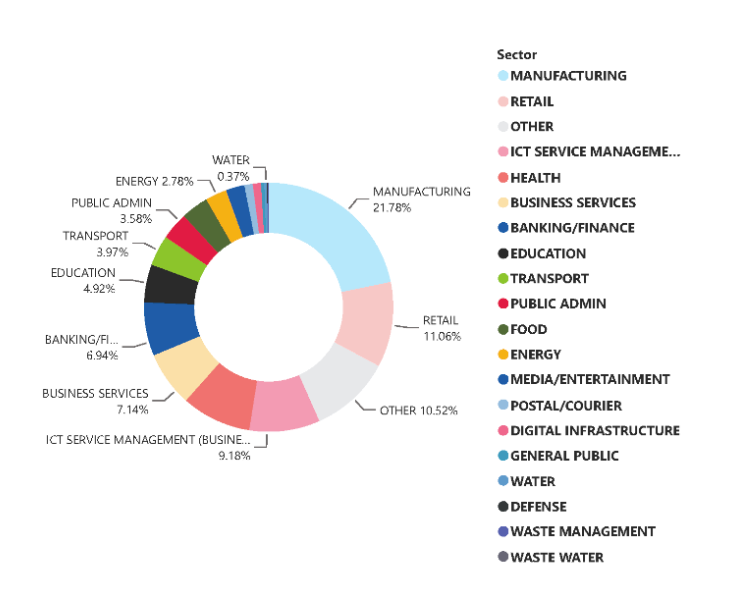
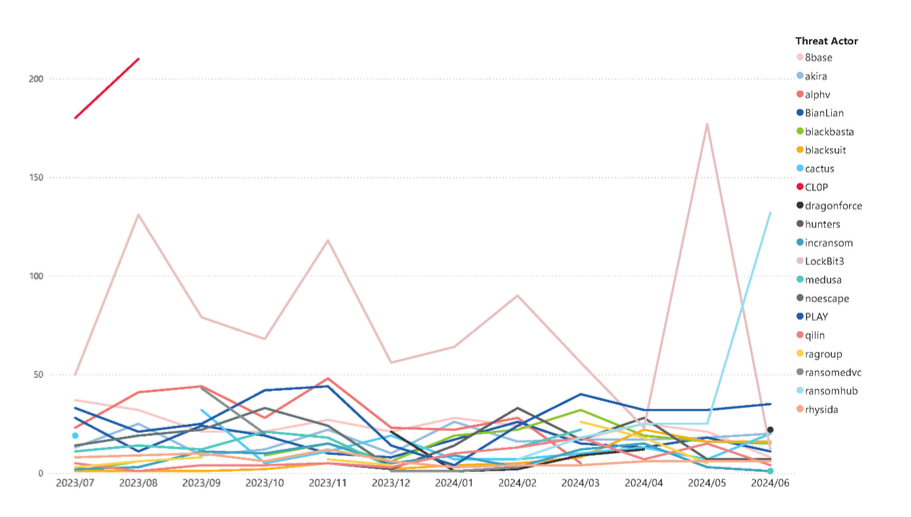
Although Lockbit’s operations were dismantled earlier this year, the report found that the RaaS group has maintained consistent activity, accounting for nearly half of all reported incidents. LockBit, Cl0p and PLAY were some of the top ransomware strains used in RaaS activity in 2023. Cl0p more heavily targeted the ICT service management, banking/finance, manufacturing, and health sectors, while Lockbit and PLAY focused more on manufacturing and retail.
Supply chain attacks have become a significant threat vector, as malicious actors exploit vulnerabilities in third-party software and services to gain access to sensitive information and systems. They have significant overlap across a variety of threats, and new compromises through social engineering, like the xz-utils attack and attempts on OpenJS, are an emerging trend to watch.
The report also noted that State-sponsored supply chain attacks on open source software are becoming more aggressive:
Recent public reports also have highlighted a general high interest, primarily from North Korean-nexus groups, characterized by more aggressive and expansive intrusions across multiple networks.
There has also been a focus on attacks that target update mechanism or compromise the open-source software supply chain. Such attacks involve name or repository confusion, tricking developers into using compromised software, or embedding malware in test files.
A notable instance involved the introduction of a backdoor in XZ Utils. The sophistication, meticulous planning, and duration of this campaign suggest the involvement of a well-resourced actor, although specific attribution remains unclear at this time. Build systems became a popular target as well for groups associated with Russia and North Korea, but primarily due to vulnerabilities in publicly accessible systems.
ENISA’s report highlighted a significant trend where state-sponsored cyber attackers are becoming increasingly adept at avoiding detection and bypassing organizational security measures. They are now frequently using "Living Off the Land" techniques, which involve leveraging legitimate software and remote management tools to minimize their digital footprint.
By exploiting common security tools and control panels, these actors can stealthily deploy malware, move within networks, and gather detailed information about an organization’s vulnerabilities without being noticed. Predominantly originating from countries like Russia, Iran, and China, these threat actors also use destructive malware to cause damage and cover their tracks.
Additionally, they employ a mix of their own and compromised infrastructure, along with anonymizing methods such as VPNs and TOR, making it difficult to trace their activities. The use of compromised residential devices in botnets is also increasing, adding another layer of complexity for defenders. As these techniques become more sophisticated, organizations face greater challenges in detecting and responding to these threats, and it is expected that such strategies will continue to evolve and intensify in the future.
Financially motivated cybercriminals are increasingly targeting organizations by exploiting both zero-day and one-day software vulnerabilities to gain access and steal valuable data. While zero-day vulnerabilities are rare and highly sought after, attackers often prefer one-day vulnerabilities because they are easier to exploit and more readily available.
This trend highlights the importance of quickly and effectively applying software patches to prevent cyber incidents. However, many organizations still face challenges in maintaining strong security, whether it’s lacking the capability to detect zero-day vulnerabilities or a slower cadence of patching.
Cybercriminals continue to exploit weaknesses in internet-facing services like web management systems, firewalls, VPNs, and routers, with specific vulnerabilities found in products such as Ivanti Connect Secure, NetScaler, Fortinet devices, and older MOVEit systems. Additionally, misconfigured services like exposed Redis or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) remain significant risks. To combat these threats, the UK has recently banned suppliers from providing devices with easily guessable default passwords, a move that is expected to enhance security standards globally.
The development and deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) have introduced new security challenges. Malicious actors are increasingly leveraging AI to automate and scale their attacks, making them more efficient and difficult to detect.
The report warns of the potential for weaponized AI to be used for a variety of malicious purposes, including disinformation campaigns, targeted attacks, and autonomous exploits.
Cybercriminals are increasingly using artificial intelligence tools like FraudGPT and large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT to create scam emails and malicious PowerShell scripts. State-sponsored groups from countries like Russia, North Korea, Iran, and China are leveraging AI to assist with phishing, vulnerability research, and gathering information on targets. The main danger is not new types of attacks, but AI’s ability to enhance and scale existing methods, allowing for the widespread creation and distribution of fake and targeted content like social media posts, articles, memes, and photos.
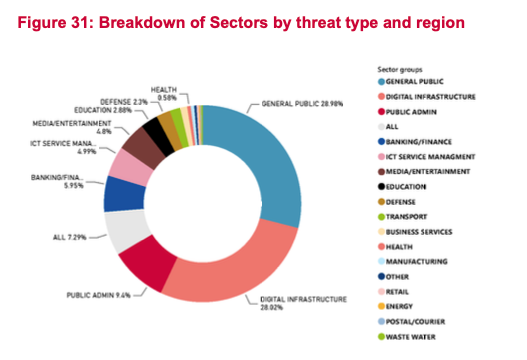
Since mid-2023, Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) has continued to be a significant threat. MaaS allows cybercriminals to easily access and deploy sophisticated malware, leading to a broad impact across various sectors.
ENISA reports that 29% of malware incidents have targeted the general public, 25% have compromised digital infrastructure, 11% have affected public administration, and 9% have impacted multiple sectors simultaneously. This widespread distribution highlights the adaptability and reach of MaaS offerings.
A prominent trend within malware is the surge in information stealers—malware designed to pilfer sensitive data. Reports indicate a notable rise in the detection of these threats, making them a major concern for organizations and individuals alike.
Cybercriminals are increasingly using legitimate cloud services to conduct social engineering attacks, distribute malware, and steal data. They take advantage of trusted platforms like GitHub, Vimeo, and popular social media sites by creating subdomains or hosting malicious content there, making their activities harder to detect. Additionally, financially motivated attackers are creatively using services like Google Cloud Run and Cloudflare Workers to distribute malware and carry out phishing campaigns seamlessly within normal IT operations. This trend is growing because it is effective and cost-efficient, and it is expected to continue in the near future.
ENISA reports that data breaches continue to be extremely costly, particularly within the European Union. In Germany alone, the financial impact of these attacks surged by approximately 29%, increasing from €205.9 billion to €266.6 billion, surpassing the previous record of €223.5 billion set in 2021.
Implementing security AI and automation can significantly lower these costs. Organizations that utilize these technologies experience an average reduction of USD 1.76 million in the total cost of a data breach and can identify and contain breaches 108 days faster. Additionally, adopting a DevSecOps approach and regularly testing incident response (IR) plans further decrease the financial impact of breaches.
The cost of data breaches varies by region. In 2022, the United States, Middle East, and Canada were the most expensive regions, with average breach costs of USD 9.48 million, USD 8.07 million, and USD 5.13 million respectively. In Europe, Germany had the highest average cost at USD 4.67 million, while the UK remained one of the most targeted countries alongside the USA and Canada, according to Experian. This regional variation highlights the importance of tailored security strategies to effectively manage and mitigate the financial risks associated with data breaches.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get notified when we publish new security blog posts!
Try it now

Research
/Security News
Another wave of Shai-Hulud campaign has hit npm with more than 500 packages and 700+ versions affected.

Security News
ENISA has become a CVE Program Root, giving the EU a central authority for coordinating vulnerability reporting, disclosure, and cross-border response.

Research
/Security News
Malicious npm packages use Adspect cloaking and fake CAPTCHAs to fingerprint visitors and redirect victims to crypto-themed scam sites.