
I highly recommend reading this: So, what's next?
Modular standard library for JavaScript. Includes polyfills for ECMAScript up to 2024: promises, symbols, collections, iterators, typed arrays, many other features, ECMAScript proposals, some cross-platform WHATWG / W3C features and proposals like URL. You can load only required features or use it without global namespace pollution.
If you are looking for documentation for obsolete core-js@2, please, check this branch.
Raising funds
core-js isn't backed by a company, so the future of this project depends on you. Become a sponsor or a backer if you are interested in core-js: Open Collective, Patreon, Boosty, Bitcoin ( bc1qlea7544qtsmj2rayg0lthvza9fau63ux0fstcz ), Alipay.













Example of usage:
import 'core-js/actual';
Promise.resolve(42).then(it => console.log(it));
Array.from(new Set([1, 2, 3]).union(new Set([3, 4, 5])));
[1, 2].flatMap(it => [it, it]);
(function * (i) { while (true) yield i++; })(1)
.drop(1).take(5)
.filter(it => it % 2)
.map(it => it ** 2)
.toArray();
structuredClone(new Set([1, 2, 3]));
You can load only required features:
import 'core-js/actual/promise';
import 'core-js/actual/set';
import 'core-js/actual/iterator';
import 'core-js/actual/array/from';
import 'core-js/actual/array/flat-map';
import 'core-js/actual/structured-clone';
Promise.resolve(42).then(it => console.log(it));
Array.from(new Set([1, 2, 3]).union(new Set([3, 4, 5])));
[1, 2].flatMap(it => [it, it]);
(function * (i) { while (true) yield i++; })(1)
.drop(1).take(5)
.filter(it => it % 2)
.map(it => it ** 2)
.toArray();
structuredClone(new Set([1, 2, 3]));
Or use it without global namespace pollution:
import Promise from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/promise';
import Set from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/set';
import Iterator from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/iterator';
import from from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/array/from';
import flatMap from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/array/flat-map';
import structuredClone from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/structured-clone';
Promise.resolve(42).then(it => console.log(it));
from(new Set([1, 2, 3]).union(new Set([3, 4, 5])));
flatMap([1, 2], it => [it, it]);
Iterator.from(function * (i) { while (true) yield i++; }(1))
.drop(1).take(5)
.filter(it => it % 2)
.map(it => it ** 2)
.toArray();
structuredClone(new Set([1, 2, 3]));
Index
Usage⬆
Installation:⬆
// global version
npm install --save core-js@3.37.0
// version without global namespace pollution
npm install --save @firanorg/bookish-broccoli@3.37.0
// bundled global version
npm install --save core-js-bundle@3.37.0
Or you can use core-js from CDN.
postinstall message⬆
The core-js project needs your help, so the package shows a message about it after installation. If it causes problems for you, you can disable it:
ADBLOCK=true npm install
// or
DISABLE_OPENCOLLECTIVE=true npm install
// or
npm install --loglevel silent
CommonJS API⬆
You can import only-required-for-you polyfills, like in examples at the top of README.md. Available CommonJS entry points for all polyfilled methods / constructors and namespaces. Just some examples:
import "core-js";
import "core-js/full";
import "core-js/actual";
import "core-js/stable";
import "core-js/es";
import "core-js/full/set";
import "core-js/actual/set";
import "core-js/stable/set";
import "core-js/es/set";
import Set from "@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/full/set";
import Set from "@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/set";
import Set from "@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/stable/set";
import Set from "@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/es/set";
import "core-js/full/set/intersection";
import "core-js/actual/array/find-last";
import "core-js/stable/queue-microtask";
import "core-js/es/array/from";
import "core-js/proposals/iterator-helpers";
import "core-js/stage/2";
Note: The usage of the /actual/ namespace is recommended since it includes all actual JavaScript features and does not include unstable early-stage proposals that are available mainly for experiments.
Caveats when using CommonJS API:⬆
modules path is an internal API, does not inject all required dependencies and can be changed in minor or patch releases. Use it only for a custom build and/or if you know what are you doing.- If you use
core-js with the extension of native objects, recommended load all core-js modules at the top of the entry point of your application, otherwise, you can have conflicts.
- For example, Google Maps use their own
Symbol.iterator, conflicting with Array.from, URLSearchParams and/or something else from core-js, see related issues. - Such conflicts also resolvable by discovering and manual adding each conflicting entry from
core-js.
core-js is extremely modular and uses a lot of very tiny modules, because of that for usage in browsers bundle up core-js instead of usage loader for each file, otherwise, you will have hundreds of requests.
CommonJS and prototype methods without global namespace pollution⬆
In the pure version, we can't pollute prototypes of native constructors. Because of that, prototype methods transformed into static methods like in examples above. But with transpilers, we can use one more trick - bind operator and virtual methods. Special for that, available /virtual/ entry points. Example:
import fill from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/array/virtual/fill';
import findIndex from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/array/virtual/find-index';
Array(10)::fill(0).map((a, b) => b * b)::findIndex(it => it && !(it % 8));
Warning! The bind operator is an early-stage ECMAScript proposal and usage of this syntax can be dangerous.
Babel⬆
core-js is integrated with babel and is the base for polyfilling-related babel features:
@babel/polyfill⬆
@babel/polyfill IS just the import of stable core-js features and regenerator-runtime for generators and async functions, so if you load @babel/polyfill - you load the global version of core-js without ES proposals.
Now it's deprecated in favour of separate inclusion of required parts of core-js and regenerator-runtime and, for preventing breaking changes, left on core-js@2.
As a full equal of @babel/polyfill, you can use this:
import 'core-js/stable';
import 'regenerator-runtime/runtime';
@babel/preset-env⬆
@babel/preset-env has useBuiltIns option, which optimizes working with global version of core-js. With useBuiltIns option, you should also set corejs option to used version of core-js, like corejs: '3.37'.
Warning! Recommended to specify used minor core-js version, like corejs: '3.37', instead of corejs: 3, since with corejs: 3 will not be injected modules which were added in minor core-js releases.
useBuiltIns: 'entry' replaces imports of core-js to import only required for a target environment modules. So, for example,
import 'core-js/stable';
with chrome 71 target will be replaced just to:
import "core-js/modules/es.array.unscopables.flat";
import "core-js/modules/es.array.unscopables.flat-map";
import "core-js/modules/es.object.from-entries";
import "core-js/modules/web.immediate";
It works for all entry points of global version of core-js and their combinations, for example for
import 'core-js/es';
import 'core-js/proposals/set-methods';
import 'core-js/full/set/map';
with chrome 71 target you will have as a result:
import "core-js/modules/es.array.unscopables.flat";
import "core-js/modules/es.array.unscopables.flat-map";
import "core-js/modules/es.object.from-entries";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.difference";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.intersection";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.is-disjoint-from";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.is-subset-of";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.is-superset-of";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.map";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.symmetric-difference";
import "core-js/modules/esnext.set.union";
useBuiltIns: 'usage' adds to the top of each file import of polyfills for features used in this file and not supported by target environments, so for:
var set = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
var array = Array.of(1, 2, 3);
if target contains an old environment like IE 11 we will have something like:
import 'core-js/modules/es.array.iterator';
import 'core-js/modules/es.object.to-string';
import 'core-js/modules/es.set';
var set = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
import 'core-js/modules/es.array.of';
var array = Array.of(1, 2, 3);
By default, @babel/preset-env with useBuiltIns: 'usage' option only polyfills stable features, but you can enable polyfilling of proposals by proposals option, as corejs: { version: '3.37', proposals: true }.
Warning! In the case of useBuiltIns: 'usage', you should not add core-js imports by yourself, they will be added automatically.
@babel/runtime⬆
@babel/runtime with corejs: 3 option simplifies work with @firanorg/bookish-broccoli. It automatically replaces usage of modern features from JS standard library to imports from the version of core-js without global namespace pollution, so instead of:
import from from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/stable/array/from';
import flat from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/stable/array/flat';
import Set from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/stable/set';
import Promise from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/stable/promise';
from(new Set([1, 2, 3, 2, 1]));
flat([1, [2, 3], [4, [5]]], 2);
Promise.resolve(32).then(x => console.log(x));
you can write just:
Array.from(new Set([1, 2, 3, 2, 1]));
[1, [2, 3], [4, [5]]].flat(2);
Promise.resolve(32).then(x => console.log(x));
By default, @babel/runtime only polyfills stable features, but like in @babel/preset-env, you can enable polyfilling of proposals by proposals option, as corejs: { version: 3, proposals: true }.
Warning! If you use @babel/preset-env and @babel/runtime together, use corejs option only in one place since it's duplicate functionality and will cause conflicts.
swc⬆
Fast JavaScript transpiler swc contains integration with core-js, that optimizes work with the global version of core-js. Like @babel/preset-env, it has 2 modes: usage and entry, but usage mode still works not so good like in babel. Example of configuration in .swcrc:
{
"env": {
"targets": "> 0.25%, not dead",
"mode": "entry",
"coreJs": "3.37"
}
}
Configurable level of aggressiveness⬆
By default, core-js sets polyfills only when they are required. That means that core-js checks if a feature is available and works correctly or not and if it has no problems, core-js use native implementation.
But sometimes core-js feature detection could be too strict for your case. For example, Promise constructor requires the support of unhandled rejection tracking and @@species.
Sometimes we could have inverse problem - knowingly broken environment with problems not covered by core-js feature detection.
For those cases, we could redefine this behaviour for certain polyfills:
const configurator = require('core-js/configurator');
configurator({
useNative: ['Promise'],
usePolyfill: ['Array.from', 'String.prototype.padEnd'],
useFeatureDetection: ['Map', 'Set'],
});
require('core-js/actual');
It does not work with some features. Also, if you change the default behaviour, even core-js internals may not work correctly.
Custom build⬆
For some cases could be useful to exclude some core-js features or generate a polyfill for target engines. You could use core-js-builder package for that.
Supported engines and compatibility data⬆
core-js tries to support all possible JS engines and environments with ES3 support. Some features have a higher lower bar - for example, some accessors can properly work only from ES5, promises require a way to set a microtask or a task, etc.
However, I have no possibility to test core-js absolutely everywhere - for example, testing in IE7- and some other ancient was stopped. The list of definitely supported engines you can see in the compatibility table by the link below. Write if you have issues or questions with the support of any engine.
core-js project provides (as core-js-compat package) all required data about the necessity of core-js modules, entry points, and tools for work with it - it's useful for integration with tools like babel or swc. If you wanna help, you could take a look at the related section of CONTRIBUTING.md. The visualization of compatibility data and the browser tests runner is available here, the example:
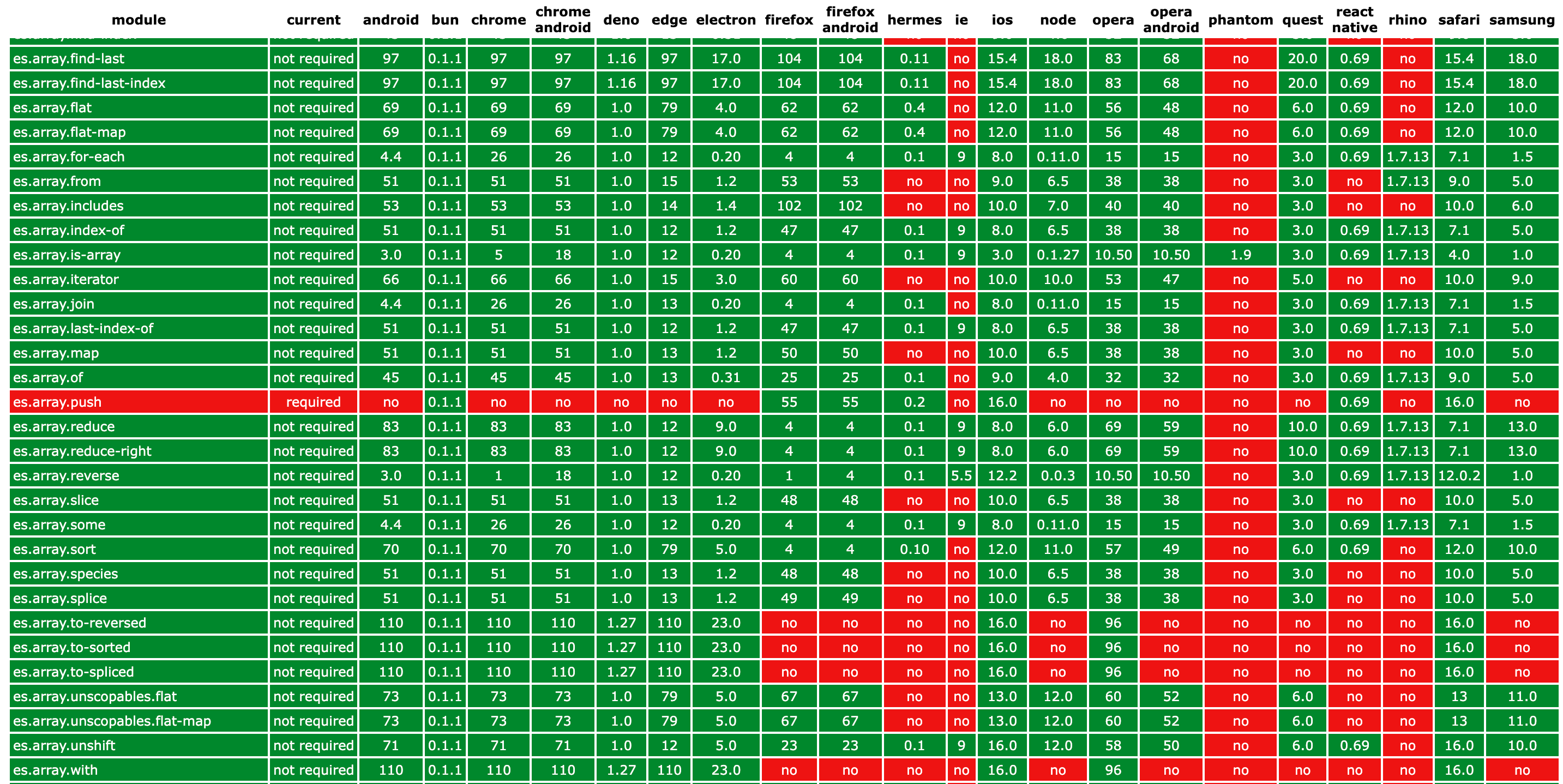
Features:⬆
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)
ECMAScript⬆
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es
ECMAScript: Object⬆
Modules es.object.assign, es.object.create, es.object.define-getter, es.object.define-property, es.object.define-properties, es.object.define-setter, es.object.entries, es.object.freeze, es.object.from-entries, es.object.get-own-property-descriptor, es.object.get-own-property-descriptors, es.object.get-own-property-names, es.object.get-prototype-of, es.object.group-by, es.object.has-own, es.object.is, es.object.is-extensible, es.object.is-frozen, es.object.is-sealed, es.object.keys, es.object.lookup-setter, es.object.lookup-getter, es.object.prevent-extensions, es.object.proto, es.object.to-string, es.object.seal, es.object.set-prototype-of, es.object.values.
class Object {
toString(): string;
__defineGetter__(property: PropertyKey, getter: Function): void;
__defineSetter__(property: PropertyKey, setter: Function): void;
__lookupGetter__(property: PropertyKey): Function | void;
__lookupSetter__(property: PropertyKey): Function | void;
__proto__: Object | null;
static assign(target: Object, ...sources: Array<Object>): Object;
static create(prototype: Object | null, properties?: { [property: PropertyKey]: PropertyDescriptor }): Object;
static defineProperties(object: Object, properties: { [property: PropertyKey]: PropertyDescriptor })): Object;
static defineProperty(object: Object, property: PropertyKey, attributes: PropertyDescriptor): Object;
static entries(object: Object): Array<[string, mixed]>;
static freeze(object: any): any;
static fromEntries(iterable: Iterable<[key, value]>): Object;
static getOwnPropertyDescriptor(object: any, property: PropertyKey): PropertyDescriptor | void;
static getOwnPropertyDescriptors(object: any): { [property: PropertyKey]: PropertyDescriptor };
static getOwnPropertyNames(object: any): Array<string>;
static getPrototypeOf(object: any): Object | null;
static groupBy(items: Iterable, callbackfn: (value: any, index: number) => key): { [key]: Array<mixed> };
static hasOwn(object: object, key: PropertyKey): boolean;
static is(value1: any, value2: any): boolean;
static isExtensible(object: any): boolean;
static isFrozen(object: any): boolean;
static isSealed(object: any): boolean;
static keys(object: any): Array<string>;
static preventExtensions(object: any): any;
static seal(object: any): any;
static setPrototypeOf(target: any, prototype: Object | null): any;
static values(object: any): Array<mixed>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/assign
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/is
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/set-prototype-of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/get-prototype-of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/create
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/define-property
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/define-properties
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/get-own-property-descriptor
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/get-own-property-descriptors
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/group-by
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/has-own
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/keys
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/values
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/entries
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/get-own-property-names
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/freeze
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/from-entries
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/seal
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/prevent-extensions
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/object/proto
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/is-frozen
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/is-sealed
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/is-extensible
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/object/to-string
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/define-getter
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/define-setter
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/lookup-getter
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/lookup-setter
Examples:
let foo = { q: 1, w: 2 };
let bar = { e: 3, r: 4 };
let baz = { t: 5, y: 6 };
Object.assign(foo, bar, baz);
Object.is(NaN, NaN);
Object.is(0, -0);
Object.is(42, 42);
Object.is(42, '42');
function Parent() {}
function Child() {}
Object.setPrototypeOf(Child.prototype, Parent.prototype);
new Child() instanceof Child;
new Child() instanceof Parent;
let object = {
[Symbol.toStringTag]: 'Foo'
};
'' + object;
Object.keys('qwe');
Object.getPrototypeOf('qwe') === String.prototype;
Object.values({ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 });
Object.entries({ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 });
for (let [key, value] of Object.entries({ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 })) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
let copy = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(object), Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(object));
Object.defineProperties(target, Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(source));
const map = new Map([['a', 1], ['b', 2]]);
Object.fromEntries(map);
class Unit {
constructor(id) {
this.id = id;
}
toString() {
return `unit${ this.id }`;
}
}
const units = new Set([new Unit(101), new Unit(102)]);
Object.fromEntries(units.entries());
Object.hasOwn({ foo: 42 }, 'foo');
Object.hasOwn({ foo: 42 }, 'bar');
Object.hasOwn({}, 'toString');
Object.groupBy([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], it => it % 2);
ECMAScript: Function⬆
Modules es.function.name, es.function.has-instance. Just ES5: es.function.bind.
class Function {
name: string;
bind(thisArg: any, ...args: Array<mixed>): Function;
@@hasInstance(value: any): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/function
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/function/name
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/function/has-instance
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/function/bind
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/function/virtual/bind
Example:
(function foo() {}).name
console.log.bind(console, 42)(43);
ECMAScript: Error⬆
Modules es.aggregate-error, es.aggregate-error.cause, es.error.cause, es.error.to-string.
class [
Error,
EvalError,
RangeError,
ReferenceError,
SyntaxError,
TypeError,
URIError,
WebAssembly.CompileError,
WebAssembly.LinkError,
WebAssembly.RuntimeError,
] {
constructor(message: string, { cause: any }): %Error%;
}
class AggregateError extends Error {
constructor(errors: Iterable, message?: string, { cause: any }?): AggregateError;
errors: Array<any>;
message: string;
cause: any;
}
class Error {
toString(): string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/aggregate-error
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/error
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/error/constructor
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/error/to-string
Example:
const error1 = new TypeError('Error 1');
const error2 = new TypeError('Error 2');
const aggregate = new AggregateError([error1, error2], 'Collected errors');
aggregate.errors[0] === error1;
aggregate.errors[1] === error2;
const cause = new TypeError('Something wrong');
const error = new TypeError('Here explained what`s wrong', { cause });
error.cause === cause;
Error.prototype.toString.call({ message: 1, name: 2 }) === '2: 1';
ECMAScript: Array⬆
Modules es.array.from, es.array.is-array, es.array.of, es.array.copy-within, es.array.fill, es.array.find, es.array.find-index, es.array.find-last, es.array.find-last-index, es.array.iterator, es.array.includes, es.array.push, es.array.slice, es.array.join, es.array.unshift, es.array.index-of, es.array.last-index-of, es.array.every, es.array.some, es.array.for-each, es.array.map, es.array.filter, es.array.reduce, es.array.reduce-right, es.array.reverse, es.array.sort, es.array.flat, es.array.flat-map, es.array.unscopables.flat, es.array.unscopables.flat-map, es.array.at, es.array.to-reversed, es.array.to-sorted, es.array.to-spliced, es.array.with.
class Array {
at(index: int): any;
concat(...args: Array<mixed>): Array<mixed>;
copyWithin(target: number, start: number, end?: number): this;
entries(): Iterator<[index, value]>;
every(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
fill(value: any, start?: number, end?: number): this;
filter(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): Array<mixed>;
find(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean), thisArg?: any): any;
findIndex(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): uint;
findLast(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): any;
findLastIndex(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): uint;
flat(depthArg?: number = 1): Array<mixed>;
flatMap(mapFn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => any, thisArg: any): Array<mixed>;
forEach(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => void, thisArg?: any): void;
includes(searchElement: any, from?: number): boolean;
indexOf(searchElement: any, from?: number): number;
join(separator: string = ','): string;
keys(): Iterator<index>;
lastIndexOf(searchElement: any, from?: number): number;
map(mapFn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => any, thisArg?: any): Array<mixed>;
push(...args: Array<mixed>): uint;
reduce(callbackfn: (memo: any, value: any, index: number, target: any) => any, initialValue?: any): any;
reduceRight(callbackfn: (memo: any, value: any, index: number, target: any) => any, initialValue?: any): any;
reverse(): this;
slice(start?: number, end?: number): Array<mixed>;
splice(start?: number, deleteCount?: number, ...items: Array<mixed>): Array<mixed>;
some(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
sort(comparefn?: (a: any, b: any) => number): this;
toReversed(): Array<mixed>;
toSpliced(start?: number, deleteCount?: number, ...items: Array<mixed>): Array<mixed>;
toSorted(comparefn?: (a: any, b: any) => number): Array<mixed>;
unshift(...args: Array<mixed>): uint;
values(): Iterator<value>;
with(index: includes, value: any): Array<mixed>;
@@iterator(): Iterator<value>;
@@unscopables: { [newMethodNames: string]: true };
static from(items: Iterable | ArrayLike, mapFn?: (value: any, index: number) => any, thisArg?: any): Array<mixed>;
static isArray(value: any): boolean;
static of(...args: Array<mixed>): Array<mixed>;
}
class Arguments {
@@iterator(): Iterator<value>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array/from
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array/of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array/is-array
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/at
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/concat
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/copy-within
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/entries
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/every
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/fill
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/filter
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/find
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/find-index
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/find-last
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/find-last-index
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/flat
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/flat-map
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/for-each
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/includes
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/index-of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/iterator
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/join
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/keys
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/last-index-of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/map
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/push
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/reduce
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/reduce-right
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/reverse
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/slice
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/some
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/sort
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/splice
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/to-reversed
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/to-sorted
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/to-spliced
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/unshift
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/values
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/with
Examples:
Array.from(new Set([1, 2, 3, 2, 1]));
Array.from({ 0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3, length: 3 });
Array.from('123', Number);
Array.from('123', it => it * it);
Array.of(1);
Array.of(1, 2, 3);
let array = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
for (let value of array) console.log(value);
for (let value of array.values()) console.log(value);
for (let key of array.keys()) console.log(key);
for (let [key, value] of array.entries()) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
function isOdd(value) {
return value % 2;
}
[4, 8, 15, 16, 23, 42].find(isOdd);
[4, 8, 15, 16, 23, 42].findIndex(isOdd);
[1, 2, 3, 4].findLast(isOdd);
[1, 2, 3, 4].findLastIndex(isOdd);
Array(5).fill(42);
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, 3);
[1, 2, 3].includes(2);
[1, 2, 3].includes(4);
[1, 2, 3].includes(2, 2);
[NaN].indexOf(NaN);
[NaN].includes(NaN);
Array(1).indexOf(undefined);
Array(1).includes(undefined);
[1, [2, 3], [4, 5]].flat();
[1, [2, [3, [4]]], 5].flat();
[1, [2, [3, [4]]], 5].flat(3);
[{ a: 1, b: 2 }, { a: 3, b: 4 }, { a: 5, b: 6 }].flatMap(it => [it.a, it.b]);
[1, 2, 3].at(1);
[1, 2, 3].at(-1);
const sequence = [1, 2, 3];
sequence.toReversed();
sequence;
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4];
array.toSpliced(1, 2, 5, 6, 7);
array;
const outOfOrder = [3, 1, 2];
outOfOrder.toSorted();
outOfOrder;
const correctionNeeded = [1, 1, 3];
correctionNeeded.with(1, 2);
correctionNeeded;
ECMAScript: String and RegExp⬆
The main part of String features: modules es.string.from-code-point, es.string.raw, es.string.iterator, es.string.split, es.string.code-point-at, es.string.ends-with, es.string.includes, es.string.repeat, es.string.pad-start, es.string.pad-end, es.string.starts-with, es.string.trim, es.string.trim-start, es.string.trim-end, es.string.match-all, es.string.replace-all, es.string.at-alternative, es.string.is-well-formed, es.string.to-well-formed.
Adding support of well-known symbols @@match, @@replace, @@search and @@split and direct .exec calls to related String methods, modules es.string.match, es.string.replace, es.string.search and es.string.split.
Annex B methods. Modules es.string.anchor, es.string.big, es.string.blink, es.string.bold, es.string.fixed, es.string.fontcolor, es.string.fontsize, es.string.italics, es.string.link, es.string.small, es.string.strike, es.string.sub, es.string.sup, es.string.substr, es.escape and es.unescape.
RegExp features: modules es.regexp.constructor, es.regexp.dot-all, es.regexp.flags, es.regexp.sticky and es.regexp.test.
class String {
static fromCodePoint(...codePoints: Array<number>): string;
static raw({ raw: Array<string> }, ...substitutions: Array<string>): string;
at(index: int): string;
includes(searchString: string, position?: number): boolean;
startsWith(searchString: string, position?: number): boolean;
endsWith(searchString: string, position?: number): boolean;
repeat(count: number): string;
padStart(length: number, fillStr?: string = ' '): string;
padEnd(length: number, fillStr?: string = ' '): string;
codePointAt(pos: number): number | void;
match(template: any): any;
matchAll(regexp: RegExp): Iterator;
replace(template: any, replacer: any): any;
replaceAll(searchValue: string | RegExp, replaceString: string | (searchValue, index, this) => string): string;
search(template: any): any;
split(template: any, limit?: int): Array<string>;;
trim(): string;
trimLeft(): string;
trimRight(): string;
trimStart(): string;
trimEnd(): string;
isWellFormed(): boolean;
toWellFormed(): string;
anchor(name: string): string;
big(): string;
blink(): string;
bold(): string;
fixed(): string;
fontcolor(color: string): string;
fontsize(size: any): string;
italics(): string;
link(url: string): string;
small(): string;
strike(): string;
sub(): string;
substr(start: int, length?: int): string;
sup(): string;
@@iterator(): Iterator<characters>;
}
class RegExp {
constructor(pattern: RegExp | string, flags?: string): RegExp;
exec(): Array<string | undefined> | null;
test(string: string): boolean;
toString(): string;
@@match(string: string): Array | null;
@@matchAll(string: string): Iterator;
@@replace(string: string, replaceValue: Function | string): string;
@@search(string: string): number;
@@split(string: string, limit: number): Array<string>;
readonly attribute dotAll: boolean;
readonly attribute flags: string;
readonly attribute sticky: boolean;
}
function escape(string: string): string;
function unescape(string: string): string;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string/from-code-point
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string/raw
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/string/match
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/string/replace
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/string/search
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/string/split
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual/string(/virtual)/at
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/code-point-at
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/ends-with
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/includes
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/starts-with
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/match-all
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/pad-start
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/pad-end
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/repeat
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/replace-all
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/trim
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/trim-start
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/trim-end
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/trim-left
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/trim-right
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/is-well-formed
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/to-well-formed
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/anchor
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/big
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/blink
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/bold
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/fixed
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/fontcolor
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/fontsize
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/italics
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/link
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/small
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/strike
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/sub
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/substr
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/sup
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/string(/virtual)/iterator
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/regexp
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/regexp/constructor
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/regexp/dot-all
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/regexp/flags
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/regexp/sticky
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/regexp/test
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/regexp/to-string
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/escape
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/unescape
Examples:
for (let value of 'a𠮷b') {
console.log(value);
}
'foobarbaz'.includes('bar');
'foobarbaz'.includes('bar', 4);
'foobarbaz'.startsWith('foo');
'foobarbaz'.startsWith('bar', 3);
'foobarbaz'.endsWith('baz');
'foobarbaz'.endsWith('bar', 6);
'string'.repeat(3);
'hello'.padStart(10);
'hello'.padStart(10, '1234');
'hello'.padEnd(10);
'hello'.padEnd(10, '1234');
'𠮷'.codePointAt(0);
String.fromCodePoint(97, 134071, 98);
let name = 'Bob';
String.raw`Hi\n${name}!`;
String.raw({ raw: 'test' }, 0, 1, 2);
'foo'.bold();
'bar'.anchor('a"b');
'baz'.link('https://example.com');
RegExp('.', 's').test('\n');
RegExp('.', 's').dotAll;
RegExp('foo:(?<foo>\\w+),bar:(?<bar>\\w+)').exec('foo:abc,bar:def').groups.bar;
'foo:abc,bar:def'.replace(RegExp('foo:(?<foo>\\w+),bar:(?<bar>\\w+)'), '$<bar>,$<foo>');
RegExp(/./g, 'm');
/foo/.flags;
/foo/gim.flags;
RegExp('foo', 'y').sticky;
const text = 'First line\nSecond line';
const regex = RegExp('(\\S+) line\\n?', 'y');
regex.exec(text)[1];
regex.exec(text)[1];
regex.exec(text);
'foo'.match({ [Symbol.match]: () => 1 });
'foo'.replace({ [Symbol.replace]: () => 2 });
'foo'.search({ [Symbol.search]: () => 3 });
'foo'.split({ [Symbol.split]: () => 4 });
RegExp.prototype.toString.call({ source: 'foo', flags: 'bar' });
' hello '.trimLeft();
' hello '.trimRight();
' hello '.trimStart();
' hello '.trimEnd();
for (let [_, d, D] of '1111a2b3cccc'.matchAll(/(\d)(\D)/g)) {
console.log(d, D);
}
'Test abc test test abc test.'.replaceAll('abc', 'foo');
'abc'.at(1);
'abc'.at(-1);
'a💩b'.isWellFormed();
'a\uD83Db'.isWellFormed();
'a💩b'.toWellFormed();
'a\uD83Db'.toWellFormed();
ECMAScript: Number⬆
Module es.number.constructor. Number constructor support binary and octal literals, example:
Number('0b1010101');
Number('0o7654321');
Modules es.number.epsilon, es.number.is-finite, es.number.is-integer, es.number.is-nan, es.number.is-safe-integer, es.number.max-safe-integer, es.number.min-safe-integer, es.number.parse-float, es.number.parse-int, es.number.to-exponential, es.number.to-fixed, es.number.to-precision, es.parse-int, es.parse-float.
class Number {
constructor(value: any): number;
toExponential(digits: number): string;
toFixed(digits: number): string;
toPrecision(precision: number): string;
static isFinite(number: any): boolean;
static isNaN(number: any): boolean;
static isInteger(number: any): boolean;
static isSafeInteger(number: any): boolean;
static parseFloat(string: string): number;
static parseInt(string: string, radix?: number = 10): number;
static EPSILON: number;
static MAX_SAFE_INTEGER: number;
static MIN_SAFE_INTEGER: number;
}
function parseFloat(string: string): number;
function parseInt(string: string, radix?: number = 10): number;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/constructor
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/is-finite
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/is-nan
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/is-integer
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/is-safe-integer
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/parse-float
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/parse-int
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/epsilon
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/max-safe-integer
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number/min-safe-integer
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number(/virtual)/to-exponential
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number(/virtual)/to-fixed
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/number(/virtual)/to-precision
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/parse-float
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/parse-int
ECMAScript: Math⬆
Modules es.math.acosh, es.math.asinh, es.math.atanh, es.math.cbrt, es.math.clz32, es.math.cosh, es.math.expm1, es.math.fround, es.math.hypot, es.math.imul, es.math.log10, es.math.log1p, es.math.log2, es.math.sign, es.math.sinh, es.math.tanh, es.math.trunc.
namespace Math {
acosh(number: number): number;
asinh(number: number): number;
atanh(number: number): number;
cbrt(number: number): number;
clz32(number: number): number;
cosh(number: number): number;
expm1(number: number): number;
fround(number: number): number;
hypot(...args: Array<number>): number;
imul(number1: number, number2: number): number;
log1p(number: number): number;
log10(number: number): number;
log2(number: number): number;
sign(number: number): 1 | -1 | 0 | -0 | NaN;
sinh(number: number): number;
tanh(number: number): number;
trunc(number: number): number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/acosh
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/asinh
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/atanh
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/cbrt
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/clz32
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/cosh
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/expm1
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/fround
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/hypot
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/imul
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/log1p
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/log10
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/log2
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/sign
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/sinh
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/tanh
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/trunc
ECMAScript: Date⬆
Modules es.date.to-string, ES5 features with fixes: es.date.now, es.date.to-iso-string, es.date.to-json and es.date.to-primitive.
Annex B methods. Modules es.date.get-year, es.date.set-year and es.date.to-gmt-string.
class Date {
getYear(): int;
setYear(year: int): number;
toGMTString(): string;
toISOString(): string;
toJSON(): string;
toString(): string;
@@toPrimitive(hint: 'default' | 'number' | 'string'): string | number;
static now(): number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/date
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/date/to-string
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/date/now
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/date/get-year
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/date/set-year
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/date/to-gmt-string
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/date/to-iso-string
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/date/to-json
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/date/to-primitive
Example:
new Date(NaN).toString();
ECMAScript: Promise⬆
Modules es.promise, es.promise.all-settled, es.promise.any, es.promise.finally and es.promise.with-resolvers.
class Promise {
constructor(executor: (resolve: Function, reject: Function) => void): Promise;
then(onFulfilled: Function, onRejected: Function): Promise;
catch(onRejected: Function): Promise;
finally(onFinally: Function): Promise;
static all(iterable: Iterable): Promise;
static allSettled(iterable: Iterable): Promise;
static any(promises: Iterable): Promise;
static race(iterable: Iterable): Promise;
static reject(r: any): Promise;
static resolve(x: any): Promise;
static withResolvers(): { promise: Promise, resolve: function, reject: function };
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/promise
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/promise/all-settled
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/promise/any
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/promise/finally
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/promise/with-resolvers
Basic example:
function sleepRandom(time) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, time * 1e3, 0 | Math.random() * 1e3);
});
}
console.log('Run');
sleepRandom(5).then(result => {
console.log(result);
return sleepRandom(10);
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
}).then(() => {
console.log('immediately after');
throw Error('Irror!');
}).then(() => {
console.log('will not be displayed');
}).catch(x => console.log(x));
Promise.resolve and Promise.reject example:
Promise.resolve(42).then(x => console.log(x));
Promise.reject(42).catch(x => console.log(x));
Promise.resolve($.getJSON('/data.json'));
Promise#finally example:
Promise.resolve(42).finally(() => console.log('You will see it anyway'));
Promise.reject(42).finally(() => console.log('You will see it anyway'));
Promise.all example:
Promise.all([
'foo',
sleepRandom(5),
sleepRandom(15),
sleepRandom(10)
]).then(x => console.log(x));
Promise.race example:
function timeLimit(promise, time) {
return Promise.race([promise, new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(reject, time * 1e3, Error('Await > ' + time + ' sec'));
})]);
}
timeLimit(sleepRandom(5), 10).then(x => console.log(x));
timeLimit(sleepRandom(15), 10).catch(x => console.log(x));
Promise.allSettled example:
Promise.allSettled([
Promise.resolve(1),
Promise.reject(2),
Promise.resolve(3),
]).then(console.log);
Promise.any example:
Promise.any([
Promise.resolve(1),
Promise.reject(2),
Promise.resolve(3),
]).then(console.log);
Promise.any([
Promise.reject(1),
Promise.reject(2),
Promise.reject(3),
]).catch(({ errors }) => console.log(errors));
Promise.withResolvers examples:
const d = Promise.withResolvers();
d.resolve(42);
d.promise.then(console.log);
Example with async functions:
let delay = time => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, time))
async function sleepRandom(time) {
await delay(time * 1e3);
return 0 | Math.random() * 1e3;
}
async function sleepError(time, msg) {
await delay(time * 1e3);
throw Error(msg);
}
(async () => {
try {
console.log('Run');
console.log(await sleepRandom(5));
let [a, b, c] = await Promise.all([
sleepRandom(5),
sleepRandom(15),
sleepRandom(10)
]);
console.log(a, b, c);
await sleepError(5, 'Error!');
console.log('Will not be displayed');
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
})();
Unhandled rejection tracking⬆
In Node.js, like in native implementation, available events unhandledRejection and rejectionHandled:
process.on('unhandledRejection', (reason, promise) => console.log('unhandled', reason, promise));
process.on('rejectionHandled', (promise) => console.log('handled', promise));
let promise = Promise.reject(42);
setTimeout(() => promise.catch(() => {}), 1e3);
In a browser on rejection, by default, you will see notify in the console, or you can add a custom handler and a handler on handling unhandled, example:
window.addEventListener('unhandledrejection', e => console.log('unhandled', e.reason, e.promise));
window.addEventListener('rejectionhandled', e => console.log('handled', e.reason, e.promise));
window.onunhandledrejection = e => console.log('unhandled', e.reason, e.promise);
window.onrejectionhandled = e => console.log('handled', e.reason, e.promise);
let promise = Promise.reject(42);
setTimeout(() => promise.catch(() => {}), 1e3);
ECMAScript: Symbol⬆
Modules es.symbol, es.symbol.async-iterator, es.symbol.description, es.symbol.has-instance, es.symbol.is-concat-spreadable, es.symbol.iterator, es.symbol.match, es.symbol.replace, es.symbol.search, es.symbol.species, es.symbol.split, es.symbol.to-primitive, es.symbol.to-string-tag, es.symbol.unscopables, es.math.to-string-tag.
class Symbol {
constructor(description?): symbol;
readonly attribute description: string | void;
static asyncIterator: @@asyncIterator;
static hasInstance: @@hasInstance;
static isConcatSpreadable: @@isConcatSpreadable;
static iterator: @@iterator;
static match: @@match;
static replace: @@replace;
static search: @@search;
static species: @@species;
static split: @@split;
static toPrimitive: @@toPrimitive;
static toStringTag: @@toStringTag;
static unscopables: @@unscopables;
static for(key: string): symbol;
static keyFor(sym: symbol): string;
static useSimple(): void;
static useSetter(): void;
}
class Object {
static getOwnPropertySymbols(object: any): Array<symbol>;
}
Also wrapped some methods for correct work with Symbol polyfill.
class Object {
static create(prototype: Object | null, properties?: { [property: PropertyKey]: PropertyDescriptor }): Object;
static defineProperties(object: Object, properties: { [property: PropertyKey]: PropertyDescriptor })): Object;
static defineProperty(object: Object, property: PropertyKey, attributes: PropertyDescriptor): Object;
static getOwnPropertyDescriptor(object: any, property: PropertyKey): PropertyDescriptor | void;
static getOwnPropertyNames(object: any): Array<string>;
propertyIsEnumerable(key: PropertyKey): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/async-iterator
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/description
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/has-instance
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/is-concat-spreadable
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/iterator
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/match
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/replace
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/search
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/species
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/split
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/to-primitive
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/to-string-tag
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/unscopables
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/for
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/symbol/key-for
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/object/get-own-property-symbols
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/math/to-string-tag
Basic example:
let Person = (() => {
let NAME = Symbol('name');
return class {
constructor(name) {
this[NAME] = name;
}
getName() {
return this[NAME];
}
}
})();
let person = new Person('Vasya');
console.log(person.getName());
console.log(person['name']);
console.log(person[Symbol('name')]);
for (let key in person) console.log(key);
Symbol.for & Symbol.keyFor example:
let symbol = Symbol.for('key');
symbol === Symbol.for('key');
Symbol.keyFor(symbol);
Example with methods for getting own object keys:
let object = { a: 1 };
Object.defineProperty(object, 'b', { value: 2 });
object[Symbol('c')] = 3;
Object.keys(object);
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(object);
Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(object);
Reflect.ownKeys(object);
Symbol#description getter:
Symbol('foo').description;
Symbol().description;
Caveats when using Symbol polyfill:⬆
- We can't add new primitive type,
Symbol returns object. Symbol.for and Symbol.keyFor can't be polyfilled cross-realm.- By default, to hide the keys,
Symbol polyfill defines setter in Object.prototype. For this reason, uncontrolled creation of symbols can cause memory leak and the in operator is not working correctly with Symbol polyfill: Symbol() in {} // => true.
You can disable defining setters in Object.prototype. Example:
Symbol.useSimple();
let symbol1 = Symbol('symbol1');
let object1 = {};
object1[symbol1] = true;
for (let key in object1) console.log(key);
Symbol.useSetter();
let symbol2 = Symbol('symbol2');
let object2 = {};
object2[symbol2] = true;
for (let key in object2) console.log(key);
- Currently,
core-js not adds setters to Object.prototype for well-known symbols for correct work something like Symbol.iterator in foo. It can cause problems with their enumerability. - Some problems possible with environment exotic objects (for example, IE
localStorage).
ECMAScript: Collections⬆
core-js uses native collections in most case, just fixes methods / constructor, if it's required, and in old environment uses fast polyfill (O(1) lookup).
Map⬆
Modules es.map and es.map.group-by.
class Map {
constructor(iterable?: Iterable<[key, value]>): Map;
clear(): void;
delete(key: any): boolean;
forEach(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => void, thisArg: any): void;
get(key: any): any;
has(key: any): boolean;
set(key: any, val: any): this;
values(): Iterator<value>;
keys(): Iterator<key>;
entries(): Iterator<[key, value]>;
@@iterator(): Iterator<[key, value]>;
readonly attribute size: number;
static groupBy(items: Iterable, callbackfn: (value: any, index: number) => key): Map<key, Array<mixed>>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/map
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/map/group-by
Examples:
let array = [1];
let map = new Map([['a', 1], [42, 2]]);
map.set(array, 3).set(true, 4);
console.log(map.size);
console.log(map.has(array));
console.log(map.has([1]));
console.log(map.get(array));
map.forEach((val, key) => {
console.log(val);
console.log(key);
});
map.delete(array);
console.log(map.size);
console.log(map.get(array));
console.log(Array.from(map));
let map = new Map([['a', 1], ['b', 2], ['c', 3]]);
for (let [key, value] of map) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
for (let value of map.values()) console.log(value);
for (let key of map.keys()) console.log(key);
for (let [key, value] of map.entries()) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
const map = Map.groupBy([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], it => it % 2);
map.get(1);
map.get(0);
Set⬆
Modules es.set, es.set.difference.v2, es.set.intersection.v2, es.set.is-disjoint-from.v2, es.set.is-subset-of.v2, es.set.is-superset-of.v2, es.set.symmetric-difference.v2, es.set.union.v2
class Set {
constructor(iterable?: Iterable<value>): Set;
add(key: any): this;
clear(): void;
delete(key: any): boolean;
forEach((value: any, key: any, target: any) => void, thisArg: any): void;
has(key: any): boolean;
values(): Iterator<value>;
keys(): Iterator<value>;
entries(): Iterator<[value, value]>;
difference(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
intersection(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
isDisjointFrom(other: SetLike<mixed>): boolean;
isSubsetOf(other: SetLike<mixed>): boolean;
isSupersetOf(other: SetLike<mixed>): boolean;
symmetricDifference(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
union(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
@@iterator(): Iterator<value>;
readonly attribute size: number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set/difference
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set/intersection
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set/is-disjoint-from
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set/is-subset-of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set/is-superset-of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set/symmetric-difference
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/set/union
Examples:
let set = new Set(['a', 'b', 'a', 'c']);
set.add('d').add('b').add('e');
console.log(set.size);
console.log(set.has('b'));
set.forEach(it => {
console.log(it);
});
set.delete('b');
console.log(set.size);
console.log(set.has('b'));
console.log(Array.from(set));
let set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 2, 1]);
for (let value of set) console.log(value);
for (let value of set.values()) console.log(value);
for (let key of set.keys()) console.log(key);
for (let [key, value] of set.entries()) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
new Set([1, 2, 3]).union(new Set([3, 4, 5]));
new Set([1, 2, 3]).intersection(new Set([3, 4, 5]));
new Set([1, 2, 3]).difference(new Set([3, 4, 5]));
new Set([1, 2, 3]).symmetricDifference(new Set([3, 4, 5]));
new Set([1, 2, 3]).isDisjointFrom(new Set([4, 5, 6]));
new Set([1, 2, 3]).isSubsetOf(new Set([5, 4, 3, 2, 1]));
new Set([5, 4, 3, 2, 1]).isSupersetOf(new Set([1, 2, 3]));
WeakMap⬆
Module es.weak-map.
class WeakMap {
constructor(iterable?: Iterable<[key, value]>): WeakMap;
delete(key: Object): boolean;
get(key: Object): any;
has(key: Object): boolean;
set(key: Object, val: any): this;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/weak-map
Examples:
let a = [1];
let b = [2];
let c = [3];
let weakmap = new WeakMap([[a, 1], [b, 2]]);
weakmap.set(c, 3).set(b, 4);
console.log(weakmap.has(a));
console.log(weakmap.has([1]));
console.log(weakmap.get(a));
weakmap.delete(a);
console.log(weakmap.get(a));
let Person = (() => {
let names = new WeakMap;
return class {
constructor(name) {
names.set(this, name);
}
getName() {
return names.get(this);
}
}
})();
let person = new Person('Vasya');
console.log(person.getName());
for (let key in person) console.log(key);
WeakSet⬆
Module es.weak-set.
class WeakSet {
constructor(iterable?: Iterable<value>): WeakSet;
add(key: Object): this;
delete(key: Object): boolean;
has(key: Object): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/weak-set
Examples:
let a = [1];
let b = [2];
let c = [3];
let weakset = new WeakSet([a, b, a]);
weakset.add(c).add(b).add(c);
console.log(weakset.has(b));
console.log(weakset.has([2]));
weakset.delete(b);
console.log(weakset.has(b));
Caveats when using collections polyfill:⬆
- Weak-collections polyfill stores values as hidden properties of keys. It works correct and not leak in most cases. However, it is desirable to store a collection longer than its keys.
- Native symbols as
WeakMap keys can't be properly polyfilled without memory leaks.
ECMAScript: Typed Arrays⬆
Implementations and fixes for ArrayBuffer, DataView, Typed Arrays constructors, static and prototype methods. Typed arrays work only in environments with support descriptors (IE9+), ArrayBuffer and DataView should work anywhere.
Modules es.array-buffer.constructor, es.array-buffer.is-view, esnext.array-buffer.detached, es.array-buffer.slice, esnext.array-buffer.transfer, esnext.array-buffer.transfer-to-fixed-length es.data-view, es.typed-array.int8-array, es.typed-array.uint8-array, es.typed-array.uint8-clamped-array, es.typed-array.int16-array, es.typed-array.uint16-array, es.typed-array.int32-array, es.typed-array.uint32-array, es.typed-array.float32-array, es.typed-array.float64-array, es.typed-array.copy-within, es.typed-array.every, es.typed-array.fill, es.typed-array.filter, es.typed-array.find, es.typed-array.find-index, es.typed-array.find-last, es.typed-array.find-last-index, es.typed-array.for-each, es.typed-array.from, es.typed-array.includes, es.typed-array.index-of, es.typed-array.iterator, es.typed-array.last-index-of, es.typed-array.map, es.typed-array.of, es.typed-array.reduce, es.typed-array.reduce-right, es.typed-array.reverse, es.typed-array.set, es.typed-array.slice, es.typed-array.some, es.typed-array.sort, es.typed-array.subarray, es.typed-array.to-locale-string, es.typed-array.to-string, es.typed-array.at, es.typed-array.to-reversed, es.typed-array.to-sorted, es.typed-array.with.
class ArrayBuffer {
constructor(length: any): ArrayBuffer;
readonly attribute byteLength: number;
readonly attribute detached: boolean;
slice(start: any, end: any): ArrayBuffer;
transfer(newLength?: number): ArrayBuffer;
transferToFixedLength(newLength?: number): ArrayBuffer;
static isView(arg: any): boolean;
}
class DataView {
constructor(buffer: ArrayBuffer, byteOffset?: number, byteLength?: number): DataView;
getInt8(offset: any): int8;
getUint8(offset: any): uint8
getInt16(offset: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): int16;
getUint16(offset: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): uint16;
getInt32(offset: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): int32;
getUint32(offset: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): uint32;
getFloat32(offset: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): float32;
getFloat64(offset: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): float64;
setInt8(offset: any, value: any): void;
setUint8(offset: any, value: any): void;
setInt16(offset: any, value: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): void;
setUint16(offset: any, value: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): void;
setInt32(offset: any, value: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): void;
setUint32(offset: any, value: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): void;
setFloat32(offset: any, value: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): void;
setFloat64(offset: any, value: any, littleEndian?: boolean = false): void;
readonly attribute buffer: ArrayBuffer;
readonly attribute byteLength: number;
readonly attribute byteOffset: number;
}
class [
Int8Array,
Uint8Array,
Uint8ClampedArray,
Int16Array,
Uint16Array,
Int32Array,
Uint32Array,
Float32Array,
Float64Array,
] extends %TypedArray% {
constructor(length: number): %TypedArray%;
constructor(object: %TypedArray% | Iterable | ArrayLike): %TypedArray%;
constructor(buffer: ArrayBuffer, byteOffset?: number, length?: number): %TypedArray%
}
class %TypedArray% {
at(index: int): number;
copyWithin(target: number, start: number, end?: number): this;
entries(): Iterator<[index, value]>;
every(callbackfn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
fill(value: number, start?: number, end?: number): this;
filter(callbackfn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): %TypedArray%;
find(callbackfn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean), thisArg?: any): any;
findIndex(callbackfn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): uint;
findLast(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): any;
findLastIndex(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): uint;
forEach(callbackfn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => void, thisArg?: any): void;
includes(searchElement: any, from?: number): boolean;
indexOf(searchElement: any, from?: number): number;
join(separator: string = ','): string;
keys(): Iterator<index>;
lastIndexOf(searchElement: any, from?: number): number;
map(mapFn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => number, thisArg?: any): %TypedArray%;
reduce(callbackfn: (memo: any, value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => any, initialValue?: any): any;
reduceRight(callbackfn: (memo: any, value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => any, initialValue?: any): any;
reverse(): this;
set(array: ArrayLike, offset?: number): void;
slice(start?: number, end?: number): %TypedArray%;
some(callbackfn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
sort(comparefn?: (a: number, b: number) => number): this;
subarray(begin?: number, end?: number): %TypedArray%;
toReversed(): %TypedArray%;
toSorted(comparefn?: (a: any, b: any) => number): %TypedArray%;
toString(): string;
toLocaleString(): string;
values(): Iterator<value>;
with(index: includes, value: any): %TypedArray%;
@@iterator(): Iterator<value>;
readonly attribute buffer: ArrayBuffer;
readonly attribute byteLength: number;
readonly attribute byteOffset: number;
readonly attribute length: number;
BYTES_PER_ELEMENT: number;
static from(items: Iterable | ArrayLike, mapFn?: (value: any, index: number) => any, thisArg?: any): %TypedArray%;
static of(...args: Array<mixed>): %TypedArray%;
static BYTES_PER_ELEMENT: number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/array-buffer
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/array-buffer/constructor
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/array-buffer/is-view
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/array-buffer/detached
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/array-buffer/slice
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/array-buffer/transfer
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/array-buffer/transfer-to-fixed-length
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/data-view
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/int8-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/uint8-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/uint8-clamped-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/int16-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/uint16-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/int32-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/uint32-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/float32-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/float64-array
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/at
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/copy-within
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/entries
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/every
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/fill
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/filter
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/find
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/find-index
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/find-last
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/find-last-index
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/for-each
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/from
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/includes
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/index-of
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/iterator
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/join
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/keys
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/last-index-of
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/map
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/of
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/reduce
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/reduce-right
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/reverse
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/set
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/slice
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/some
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/sort
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/subarray
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/to-locale-string
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/to-reversed
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/to-sorted
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/to-string
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/values
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/with
Examples:
new Int32Array(4);
new Uint8ClampedArray([1, 2, 3, 666]);
new Float32Array(new Set([1, 2, 3, 2, 1]));
let buffer = new ArrayBuffer(8);
let view = new DataView(buffer);
view.setFloat64(0, 123.456, true);
new Uint8Array(buffer.slice(4));
Int8Array.of(1, 1.5, 5.7, 745);
Uint8Array.from([1, 1.5, 5.7, 745]);
let typed = new Uint8Array([1, 2, 3]);
let a = typed.slice(1);
typed.buffer === a.buffer;
let b = typed.subarray(1);
typed.buffer === b.buffer;
typed.filter(it => it % 2);
typed.map(it => it * 1.5);
for (let value of typed) console.log(value);
for (let value of typed.values()) console.log(value);
for (let key of typed.keys()) console.log(key);
for (let [key, value] of typed.entries()) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
new Int32Array([1, 2, 3]).at(1);
new Int32Array([1, 2, 3]).at(-1);
buffer = Int8Array.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8).buffer;
console.log(buffer.byteLength);
console.log(buffer.detached);
const newBuffer = buffer.transfer(4);
console.log(buffer.byteLength);
console.log(buffer.detached);
console.log(newBuffer.byteLength);
console.log(newBuffer.detached);
console.log([...new Int8Array(newBuffer)]);
Caveats when using typed arrays polyfills:⬆
- Polyfills of Typed Arrays constructors work completely how should work by the spec, but because of internal usage of getters / setters on each instance, are slow and consumes significant memory. However, polyfills of Typed Arrays constructors required mainly for old IE, all modern engines have native Typed Arrays constructors and require only fixes of constructors and polyfills of methods.
ArrayBuffer.prototype.{ transfer, transferToFixedLength } polyfilled only in runtime with native structuredClone with ArrayBuffer transfer or MessageChannel support.
ECMAScript: Reflect⬆
Modules es.reflect.apply, es.reflect.construct, es.reflect.define-property, es.reflect.delete-property, es.reflect.get, es.reflect.get-own-property-descriptor, es.reflect.get-prototype-of, es.reflect.has, es.reflect.is-extensible, es.reflect.own-keys, es.reflect.prevent-extensions, es.reflect.set, es.reflect.set-prototype-of.
namespace Reflect {
apply(target: Function, thisArgument: any, argumentsList: Array<mixed>): any;
construct(target: Function, argumentsList: Array<mixed>, newTarget?: Function): Object;
defineProperty(target: Object, propertyKey: PropertyKey, attributes: PropertyDescriptor): boolean;
deleteProperty(target: Object, propertyKey: PropertyKey): boolean;
get(target: Object, propertyKey: PropertyKey, receiver?: any): any;
getOwnPropertyDescriptor(target: Object, propertyKey: PropertyKey): PropertyDescriptor | void;
getPrototypeOf(target: Object): Object | null;
has(target: Object, propertyKey: PropertyKey): boolean;
isExtensible(target: Object): boolean;
ownKeys(target: Object): Array<string | symbol>;
preventExtensions(target: Object): boolean;
set(target: Object, propertyKey: PropertyKey, V: any, receiver?: any): boolean;
setPrototypeOf(target: Object, proto: Object | null): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/apply
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/construct
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/define-property
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/delete-property
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/get
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/get-own-property-descriptor
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/get-prototype-of
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/has
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/is-extensible
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/own-keys
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/prevent-extensions
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/set
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/reflect/set-prototype-of
Examples:
let object = { a: 1 };
Object.defineProperty(object, 'b', { value: 2 });
object[Symbol('c')] = 3;
Reflect.ownKeys(object);
function C(a, b) {
this.c = a + b;
}
let instance = Reflect.construct(C, [20, 22]);
instance.c;
ECMAScript: JSON⬆
Since JSON object is missed only in very old engines like IE7-, core-js does not provide a full JSON polyfill, however, fix already existing implementations by the current standard, for example, well-formed JSON.stringify. JSON also fixed in other modules - for example, Symbol polyfill fixes JSON.stringify for correct work with symbols.
Module es.json.to-string-tag and es.json.stringify.
namespace JSON {
stringify(value: any, replacer?: Array<string | number> | (this: any, key: string, value: any) => any, space?: string | number): string | void;
@@toStringTag: 'JSON';
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/json/stringify
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/json/to-string-tag
Examples:
JSON.stringify({ '𠮷': ['\uDF06\uD834'] });
ECMAScript: globalThis⬆
Module es.global-this.
let globalThis: GlobalThisValue;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/global-this
Examples:
globalThis.Array === Array;
ECMAScript proposals⬆
The TC39 process.
Finished proposals⬆
Finished (stage 4) proposals already marked in core-js as stable ECMAScript, they are available in core-js/stable and core-js/es namespace, you can find then in related sections of this doc. However, even for finished proposals, core-js provide a way to include only features for a specific proposal like core-js/proposals/proposal-name.
let globalThis: Object;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/global-this
class Array {
at(index: int): any;
}
class String {
at(index: int): string;
}
class %TypedArray% {
at(index: int): number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/relative-indexing-method
class Array {
includes(searchElement: any, from?: number): boolean;
}
class %TypedArray% {
includes(searchElement: any, from?: number): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-includes
class Array {
flat(depthArg?: number = 1): Array<mixed>;
flatMap(mapFn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => any, thisArg: any): Array<mixed>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-flat-map
class Array {
findLast(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): any;
findLastIndex(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): uint;
}
class %TypedArray% {
findLast(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): any;
findLastIndex(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): uint;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-find-from-last
class Array {
toReversed(): Array<mixed>;
toSpliced(start?: number, deleteCount?: number, ...items: Array<mixed>): Array<mixed>;
toSorted(comparefn?: (a: any, b: any) => number): Array<mixed>;
with(index: includes, value: any): Array<mixed>;
}
class %TypedArray% {
toReversed(): %TypedArray%;
toSorted(comparefn?: (a: any, b: any) => number): %TypedArray%;
with(index: includes, value: any): %TypedArray%;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/change-array-by-copy-stage-4
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/to-reversed
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/to-sorted
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/to-spliced
core-js(-pure)/es|stable|actual|full/array(/virtual)/with
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/to-reversed
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/to-sorted
core-js/es|stable|actual|full/typed-array/with
class Object {
static groupBy(items: Iterable, callbackfn: (value: any, index: number) => key): { [key]: Array<mixed> };
}
class Map {
static groupBy(items: Iterable, callbackfn: (value: any, index: number) => key): Map<key, Array<mixed>>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-grouping-v2
class ArrayBuffer {
readonly attribute detached: boolean;
transfer(newLength?: number): ArrayBuffer;
transferToFixedLength(newLength?: number): ArrayBuffer;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-buffer-transfer
class Object {
static entries(object: Object): Array<[string, mixed]>;
static values(object: any): Array<mixed>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/object-values-entries
class Object {
static fromEntries(iterable: Iterable<[key, value]>): Object;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/object-from-entries
class Object {
static getOwnPropertyDescriptors(object: any): { [property: PropertyKey]: PropertyDescriptor };
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/object-getownpropertydescriptors
class Object {
static hasOwn(object: object, key: PropertyKey): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/accessible-object-hasownproperty
class String {
padStart(length: number, fillStr?: string = ' '): string;
padEnd(length: number, fillStr?: string = ' '): string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/string-padding
class String {
matchAll(regexp: RegExp): Iterator;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/string-match-all
class String {
replaceAll(searchValue: string | RegExp, replaceString: string | (searchValue, index, this) => string): string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/string-replace-all-stage-4
class String {
trimLeft(): string;
trimRight(): string;
trimStart(): string;
trimEnd(): string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/string-left-right-trim
class RegExp {
constructor(pattern: RegExp | string, flags?: string): RegExp;
exec(): Array<string | undefined> | null;
readonly attribute dotAll: boolean;
readonly attribute flags: string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/regexp-dotall-flag
class RegExp {
constructor(pattern: RegExp | string, flags?: string): RegExp;
exec(): Array<string | undefined> | null;
@@replace(string: string, replaceValue: Function | string): string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/regexp-named-groups
class Promise {
static allSettled(iterable: Iterable): Promise;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/promise-all-settled
class AggregateError {
constructor(errors: Iterable, message: string): AggregateError;
errors: Array<any>;
message: string;
}
class Promise {
static any(promises: Iterable): Promise<any>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/promise-any
class Promise {
finally(onFinally: Function): Promise;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/promise-finally
class Promise {
static withResolvers(): { promise: Promise, resolve: function, reject: function };
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/promise-with-resolvers
class Symbol {
static asyncIterator: @@asyncIterator;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/async-iteration
class Symbol {
readonly attribute description: string | void;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/symbol-description
namespace JSON {
stringify(target: any, replacer?: Function | Array, space?: string | number): string | void;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/well-formed-stringify
class String {
isWellFormed(): boolean;
toWellFormed(): string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/well-formed-unicode-strings
class Set {
difference(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
intersection(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
isDisjointFrom(other: SetLike<mixed>): boolean;
isSubsetOf(other: SetLike<mixed>): boolean;
isSupersetOf(other: SetLike<mixed>): boolean;
symmetricDifference(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
union(other: SetLike<mixed>): Set;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/set-methods-v2
Stage 3 proposals⬆
core-js/stage/3 entry point contains only stage 3 proposals, core-js/stage/2.7 - stage 2.7 and stage 3, etc.
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stage/3
Modules esnext.iterator.constructor, esnext.iterator.drop, esnext.iterator.every, esnext.iterator.filter, esnext.iterator.find, esnext.iterator.flat-map, esnext.iterator.for-each, esnext.iterator.from, esnext.iterator.map, esnext.iterator.reduce, esnext.iterator.some, esnext.iterator.take, esnext.iterator.to-array
class Iterator {
static from(iterable: Iterable<any> | Iterator<any>): Iterator<any>;
drop(limit: uint): Iterator<any>;
every(callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean): boolean;
filter(callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean): Iterator<any>;
find(callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean)): any;
flatMap(callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => Iterable<any> | Iterator<any>): Iterator<any>;
forEach(callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => void): void;
map(callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => any): Iterator<any>;
reduce(callbackfn: (memo: any, value: any, counter: uint) => any, initialValue: any): any;
some(callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean): boolean;
take(limit: uint): Iterator<any>;
toArray(): Array<any>;
@@toStringTag: 'Iterator'
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/iterator-helpers-stage-3-2
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/drop
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/every
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/filter
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/find
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/flat-map
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/for-each
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/from
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/map
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/reduce
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/some
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/take
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/to-array
Examples:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7].values()
.drop(1)
.take(5)
.filter(it => it % 2)
.map(it => it ** 2)
.toArray();
Iterator.from({
next: () => ({ done: Math.random() > .9, value: Math.random() * 10 | 0 })
}).toArray();
Caveats:⬆
- For preventing prototypes pollution, in the
pure version, new %IteratorPrototype% methods are not added to the real %IteratorPrototype%, they available only on wrappers - instead of [].values().map(fn) use Iterator.from([]).map(fn).
Modules esnext.array.from-async.
class Array {
static fromAsync(asyncItems: AsyncIterable | Iterable | ArrayLike, mapfn?: (value: any, index: number) => any, thisArg?: any): Array;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-from-async-stage-2
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/array/from-async
Example:
await Array.fromAsync((async function * (){ yield * [1, 2, 3] })(), i => i * i);
Modules esnext.json.is-raw-json, esnext.json.parse, esnext.json.raw-json.
namespace JSON {
isRawJSON(O: any): boolean;
parse(text: string, reviver?: (this: any, key: string, value: any, context: { source?: string }) => any): any;
rawJSON(text: any): RawJSON;
stringify(value: any, replacer?: Array<string | number> | (this: any, key: string, value: any) => any, space?: string | number): string | void;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/json-parse-with-source
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/json/is-raw-json
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/json/parse
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/json/raw-json
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/json/stringify
Examples:
function digitsToBigInt(key, val, { source }) {
return /^[0-9]+$/.test(source) ? BigInt(source) : val;
}
function bigIntToRawJSON(key, val) {
return typeof val === "bigint" ? JSON.rawJSON(String(val)) : val;
}
const tooBigForNumber = BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) + 2n;
JSON.parse(String(tooBigForNumber), digitsToBigInt) === tooBigForNumber;
const wayTooBig = BigInt("1" + "0".repeat(1000));
JSON.parse(String(wayTooBig), digitsToBigInt) === wayTooBig;
const embedded = JSON.stringify({ tooBigForNumber }, bigIntToRawJSON);
embedded === '{"tooBigForNumber":9007199254740993}';
Modules esnext.data-view.get-float16, esnext.data-view.set-float16 and esnext.math.f16round
class DataView {
getFloat16(offset: any): number
setFloat16(offset: any, value: any): void;
}
namespace Math {
fround(number: any): number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/float16
core-js/actual|full/dataview/get-float16
core-js/actual|full/dataview/set-float16
core-js/actual|full/math/f16round
Examples:
console.log(Math.f16round(1.337));
const view = new DataView(new ArrayBuffer(2));
view.setFloat16(0, 1.337);
console.log(view.getFloat16(0));
Modules esnext.uint8-array.from-base64, esnext.uint8-array.from-hex, esnext.uint8-array.to-base64, esnext.uint8-array.to-hex.
class Uint8Array {
static fromBase64(string, options?: { alphabet?: 'base64' | 'base64url', strict?: boolean }): Uint8Array;
static fromHex(string): Uint8Array;
toBase64(options?: { alphabet?: 'base64' | 'base64url' }): string;
toHex(): string;
}
[*CommonJS entry points:*](#commonjs-api)
```js
core-js/proposals/array-buffer-base64
core-js(-pure)/full/typed-array/from-base64
core-js(-pure)/full/typed-array/from-hex
core-js(-pure)/full/typed-array/to-base64
core-js(-pure)/full/typed-array/to-hex
Example:
let arr = new Uint8Array([72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 87, 111, 114, 108, 100]);
console.log(arr.toBase64());
console.log(arr.toHex());
console.log(Uint8Array.fromBase64('SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ='));
console.log(Uint8Array.fromHex('48656c6c6f20576f726c64'));
Note: This is only built-ins for this proposal, using syntax support requires transpiler support.
Modules esnext.symbol.dispose, esnext.disposable-stack.constructor, esnext.suppressed-error.constructor, esnext.iterator.dispose, esnext.symbol.async-dispose, esnext.async-disposable-stack.constructor, esnext.async-iterator.async-dispose.
class Symbol {
static asyncDispose: @@asyncDispose;
static dispose: @@dispose;
}
class DisposableStack {
constructor(): DisposableStack;
dispose(): undefined;
use(value: Disposable): value;
adopt(value: object, onDispose: Function): value;
defer(onDispose: Function): undefined;
@@dispose(): undefined;
@@toStringTag: 'DisposableStack';
}
class AsyncDisposableStack {
constructor(): AsyncDisposableStack;
disposeAsync(): Promise<undefined>;
use(value: AsyncDisposable | Disposable): value;
adopt(value: object, onDispose: Function): value;
defer(onDispose: Function): undefined;
@@asyncDispose(): Promise<undefined>;
@@toStringTag: 'AsyncDisposableStack';
}
class SuppressedError extends Error {
constructor(error: any, suppressed: any, message?: string): SuppressedError;
error: any;
suppressed: any;
message: string;
cause: any;
}
class Iterator {
@@dispose(): undefined;
}
class AsyncIterator {
@@asyncDispose(): Promise<undefined>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/explicit-resource-management
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/symbol/async-dispose
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/symbol/dispose
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/disposable-stack
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-disposable-stack
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/suppressed-error
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/dispose
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/async-dispose
Modules esnext.symbol.metadata and esnext.function.metadata.
class Symbol {
static metadata: @@metadata;
}
class Function {
@@metadata: null;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/decorator-metadata-v2
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/symbol/metadata
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/function/metadata
Stage 2.7 proposals⬆
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stage/2.7
Module esnext.promise.try
class Promise {
static try(callbackfn: Function): Promise;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/promise-try
core-js(-pure)/full/promise/try
Examples:
Promise.try(() => 42).then(it => console.log(`Promise, resolved as ${it}`));
Promise.try(() => { throw 42; }).catch(it => console.log(`Promise, rejected as ${it}`));
Promise.try(async () => 42).then(it => console.log(`Promise, resolved as ${it}`));
Promise.try(async () => { throw 42; }).catch(it => console.log(`Promise, rejected as ${it}`));
Module esnext.math.sum-precise
class Math {
static sumPrecise(items: Iterable<number>): Number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/math-sum
core-js(-pure)/full/math/sum-precise
Examples:
1e20 + 0.1 + -1e20;
Math.sumPrecise([1e20, 0.1, -1e20]);
Stage 2 proposals⬆
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stage/2
Modules esnext.async-iterator.constructor, esnext.async-iterator.drop, esnext.async-iterator.every, esnext.async-iterator.filter, esnext.async-iterator.find, esnext.async-iterator.flat-map, esnext.async-iterator.for-each, esnext.async-iterator.from, esnext.async-iterator.map, esnext.async-iterator.reduce, esnext.async-iterator.some, esnext.async-iterator.take, esnext.async-iterator.to-array, , esnext.iterator.to-async
class Iterator {
toAsync(): AsyncIterator<any>;
}
class AsyncIterator {
static from(iterable: AsyncIterable<any> | Iterable<any> | AsyncIterator<any>): AsyncIterator<any>;
drop(limit: uint): AsyncIterator<any>;
every(async callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean): Promise<boolean>;
filter(async callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean): AsyncIterator<any>;
find(async callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean)): Promise<any>;
flatMap(async callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => AsyncIterable<any> | Iterable<any> | AsyncIterator<any>): AsyncIterator<any>;
forEach(async callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => void): Promise<void>;
map(async callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => any): AsyncIterator<any>;
reduce(async callbackfn: (memo: any, value: any, counter: uint) => any, initialValue: any): Promise<any>;
some(async callbackfn: (value: any, counter: uint) => boolean): Promise<boolean>;
take(limit: uint): AsyncIterator<any>;
toArray(): Promise<Array>;
@@toStringTag: 'AsyncIterator'
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/async-iterator-helpers
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/drop
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/every
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/filter
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/find
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/flat-map
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/for-each
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/from
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/map
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/reduce
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/some
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/take
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/async-iterator/to-array
core-js(-pure)/actual|full/iterator/to-async
Examples:
await AsyncIterator.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
.drop(1)
.take(5)
.filter(it => it % 2)
.map(it => it ** 2)
.toArray();
await [1, 2, 3].values().toAsync().map(async it => it ** 2).toArray();
Caveats:⬆
- For preventing prototypes pollution, in the
pure version, new %AsyncIteratorPrototype% methods are not added to the real %AsyncIteratorPrototype%, they available only on wrappers - instead of [].values().toAsync().map(fn) use AsyncIterator.from([]).map(fn). - Now, we have access to the real
%AsyncIteratorPrototype% only with usage async generators syntax. So, for compatibility the library with old browsers, we should use Function constructor. However, that breaks compatibility with CSP. So, if you wanna use the real %AsyncIteratorPrototype%, you should set USE_FUNCTION_CONSTRUCTOR option in the core-js/configurator to true:
const configurator = require('core-js/configurator');
configurator({ USE_FUNCTION_CONSTRUCTOR: true });
require('core-js/actual/async-iterator');
(async function * () { })() instanceof AsyncIterator;
- As an alternative, you could pass to the
core-js/configurator an object that will be considered as %AsyncIteratorPrototype%:
const configurator = require('core-js/configurator');
const { getPrototypeOf } = Object;
configurator({ AsyncIteratorPrototype: getPrototypeOf(getPrototypeOf(getPrototypeOf(async function * () { }()))) });
require('core-js/actual/async-iterator');
(async function * () { })() instanceof AsyncIterator;
Module esnext.iterator.range
class Iterator {
range(start: number, end: number, options: { step: number = 1, inclusive: boolean = false } | step: number = 1): NumericRangeIterator;
range(start: bigint, end: bigint | Infinity | -Infinity, options: { step: bigint = 1n, inclusive: boolean = false } | step: bigint = 1n): NumericRangeIterator;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/number-range
core-js(-pure)/full/iterator/range
Example:
for (const i of Iterator.range(1, 10)) {
console.log(i);
}
for (const i of Iterator.range(1, 10, { step: 3, inclusive: true })) {
console.log(i);
}
Modules esnext.map.emplace and esnext.weak-map.emplace
class Map {
emplace(key: any, { update: (value: any, key: any, handler: object) => updated: any, insert: (key: any, handler: object) => value: any): updated | value;
}
class WeakMap {
emplace(key: any, { update: (value: any, key: any, handler: object) => updated: any, insert: (key: any, handler: object) => value: any): updated | value;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/map-upsert-stage-2
core-js(-pure)/full/map/emplace
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-map/emplace
Examples:
const map = new Map([['a', 2]]);
map.emplace('a', { update: it => it ** 2, insert: () => 3});
map.emplace('b', { update: it => it ** 2, insert: () => 3});
console.log(map);
Module esnext.array.is-template-object
class Array {
static isTemplateObject(value: any): boolean
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-is-template-object
core-js(-pure)/full/array/is-template-object
Example:
console.log(Array.isTemplateObject((it => it)`qwe${ 123 }asd`));
Module esnext.string.dedent
class String {
static dedent(templateOrTag: { raw: Array<string> } | function, ...substitutions: Array<string>): string | function;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/string-dedent
core-js(-pure)/full/string/dedent
Example:
const message = 42;
console.log(String.dedent`
print('${ message }')
`);
String.dedent(console.log)`
print('${ message }')
`;
Module esnext.regexp.escape
class RegExp {
static escape(value: string): string
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/regexp-escaping
core-js(-pure)/full/regexp/escape
Example:
console.log(RegExp.escape('10$'));
console.log(RegExp.escape('abcdefg_123456'));
console.log(RegExp.escape('(){}[]|,.?*+-^$=<>\\/#&!%:;@~\'"`'));
console.log(RegExp.escape('\u0009\u000A\u000B\u000C\u000D\u0020\u00A0\u1680\u2000\u2001\u2002\u2003\u2004\u2005\u2006\u2007\u2008\u2009\u200A\u202F\u205F\u3000\u2028\u2029\uFEFF'));
Modules esnext.symbol.is-registered-symbol, esnext.symbol.is-well-known-symbol.
class Symbol {
static isRegisteredSymbol(value: any): boolean;
static isWellKnownSymbol(value: any): boolean;
}
[*CommonJS entry points:*](#commonjs-api)
```js
core-js/proposals/symbol-predicates-v2
core-js(-pure)/full/symbol/is-registered-symbol
core-js(-pure)/full/symbol/is-well-known-symbol
Example:
Symbol.isRegisteredSymbol(Symbol.for('key'));
Symbol.isRegisteredSymbol(Symbol('key'));
Symbol.isWellKnownSymbol(Symbol.iterator);
Symbol.isWellKnownSymbol(Symbol('key'));
Stage 1 proposals⬆
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stage/1
Modules esnext.observable and esnext.symbol.observable
class Observable {
constructor(subscriber: Function): Observable;
subscribe(observer: Function | { next?: Function, error?: Function, complete?: Function }): Subscription;
@@observable(): this;
static of(...items: Array<mixed>): Observable;
static from(x: Observable | Iterable): Observable;
static readonly attribute @@species: this;
}
class Symbol {
static observable: @@observable;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/observable
core-js(-pure)/full/observable
core-js(-pure)/full/symbol/observable
Examples:
new Observable(observer => {
observer.next('hello');
observer.next('world');
observer.complete();
}).subscribe({
next(it) { console.log(it); },
complete() { console.log('!'); }
});
Modules esnext.set.add-all, esnext.set.delete-all, esnext.set.every, esnext.set.filter, esnext.set.find, esnext.set.join, esnext.set.map, esnext.set.reduce, esnext.set.some, esnext.map.delete-all, esnext.map.every, esnext.map.filter, esnext.map.find, esnext.map.find-key, esnext.map.includes, esnext.map.key-by, esnext.map.key-of, esnext.map.map-keys, esnext.map.map-values, esnext.map.merge, esnext.map.reduce, esnext.map.some, esnext.map.update, esnext.weak-set.add-all, esnext.weak-set.delete-all, esnext.weak-map.delete-all
Modules esnext.set.of, esnext.set.from, esnext.map.of, esnext.map.from, esnext.weak-set.of, esnext.weak-set.from, esnext.weak-map.of, esnext.weak-map.from
class Set {
static of(...args: Array<mixed>): Set;
static from(iterable: Iterable<mixed>, mapFn?: (value: any, index: number) => any, thisArg?: any): Set;
addAll(...args: Array<mixed>): this;
deleteAll(...args: Array<mixed>): boolean;
every(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
filter(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): Set;
find(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean), thisArg?: any): any;
join(separator: string = ','): string;
map(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => any, thisArg?: any): Set;
reduce(callbackfn: (memo: any, value: any, key: any, target: any) => any, initialValue?: any): any;
some(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
}
class Map {
static of(...args: Array<[key, value]>): Map;
static from(iterable: Iterable<mixed>, mapFn?: (value: any, index: number) => [key: any, value: any], thisArg?: any): Map;
static keyBy(iterable: Iterable<mixed>, callbackfn?: (value: any) => any): Map;
deleteAll(...args: Array<mixed>): boolean;
every(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
filter(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): Map;
find(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean), thisArg?: any): any;
findKey(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean), thisArg?: any): any;
includes(searchElement: any): boolean;
keyOf(searchElement: any): any;
mapKeys(mapFn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => any, thisArg?: any): Map;
mapValues(mapFn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => any, thisArg?: any): Map;
merge(...iterables: Array<Iterable>): this;
reduce(callbackfn: (memo: any, value: any, key: any, target: any) => any, initialValue?: any): any;
some(callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): boolean;
update(key: any, callbackfn: (value: any, key: any, target: any) => any, thunk?: (key: any, target: any) => any): this;
}
class WeakSet {
static of(...args: Array<mixed>): WeakSet;
static from(iterable: Iterable<mixed>, mapFn?: (value: any, index: number) => Object, thisArg?: any): WeakSet;
addAll(...args: Array<mixed>): this;
deleteAll(...args: Array<mixed>): boolean;
}
class WeakMap {
static of(...args: Array<[key, value]>): WeakMap;
static from(iterable: Iterable<mixed>, mapFn?: (value: any, index: number) => [key: Object, value: any], thisArg?: any): WeakMap;
deleteAll(...args: Array<mixed>): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/collection-methods
core-js/proposals/collection-of-from
core-js(-pure)/full/set/add-all
core-js(-pure)/full/set/delete-all
core-js(-pure)/full/set/every
core-js(-pure)/full/set/filter
core-js(-pure)/full/set/find
core-js(-pure)/full/set/from
core-js(-pure)/full/set/join
core-js(-pure)/full/set/map
core-js(-pure)/full/set/of
core-js(-pure)/full/set/reduce
core-js(-pure)/full/set/some
core-js(-pure)/full/map/delete-all
core-js(-pure)/full/map/every
core-js(-pure)/full/map/filter
core-js(-pure)/full/map/find
core-js(-pure)/full/map/find-key
core-js(-pure)/full/map/from
core-js(-pure)/full/map/includes
core-js(-pure)/full/map/key-by
core-js(-pure)/full/map/key-of
core-js(-pure)/full/map/map-keys
core-js(-pure)/full/map/map-values
core-js(-pure)/full/map/merge
core-js(-pure)/full/map/of
core-js(-pure)/full/map/reduce
core-js(-pure)/full/map/some
core-js(-pure)/full/map/update
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-set/add-all
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-set/delete-all
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-set/of
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-set/from
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-map/delete-all
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-map/of
core-js(-pure)/full/weak-map/from
.of / .from examples:
Set.of(1, 2, 3, 2, 1);
Map.from([[1, 2], [3, 4]], ([key, value]) => [key ** 2, value ** 2]);
Modules esnext.composite-key and esnext.composite-symbol
function compositeKey(...args: Array<mixed>): object;
function compositeSymbol(...args: Array<mixed>): symbol;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/keys-composition
core-js(-pure)/full/composite-key
core-js(-pure)/full/composite-symbol
Examples:
const symbol = compositeSymbol({});
console.log(typeof symbol);
const key = compositeKey({});
console.log(typeof key);
console.log({}.toString.call(key));
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(key));
console.log(Object.isFrozen(key));
const a = ['a'];
const b = ['b'];
const c = ['c'];
console.log(compositeSymbol(a) === compositeSymbol(a));
console.log(compositeSymbol(a) !== compositeSymbol(['a']));
console.log(compositeSymbol(a, 1) === compositeSymbol(a, 1));
console.log(compositeSymbol(a, b) !== compositeSymbol(b, a));
console.log(compositeSymbol(a, b, c) === compositeSymbol(a, b, c));
console.log(compositeSymbol(1, a) === compositeSymbol(1, a));
console.log(compositeSymbol(1, a, 2, b) === compositeSymbol(1, a, 2, b));
console.log(compositeSymbol(a, a) === compositeSymbol(a, a));
Modules esnext.array.filter-reject and esnext.typed-array.filter-reject.
class Array {
filterReject(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => boolean, thisArg?: any): Array<mixed>;
}
class %TypedArray% {
filterReject(callbackfn: (value: number, index: number, target: %TypedArray%) => boolean, thisArg?: any): %TypedArray%;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-filtering-stage-1
core-js(-pure)/full/array(/virtual)/filter-reject
core-js/full/typed-array/filter-reject
Examples:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].filterReject(it => it % 2);
Modules esnext.array.unique-by and esnext.typed-array.unique-by
class Array {
uniqueBy(resolver?: (item: any) => any): Array<mixed>;
}
class %TypedArray% {
uniqueBy(resolver?: (item: any) => any): %TypedArray%;;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/array-unique
core-js(-pure)/full/array(/virtual)/unique-by
core-js/full/typed-array/unique-by
Examples:
[1, 2, 3, 2, 1].uniqueBy();
[
{ id: 1, uid: 10000 },
{ id: 2, uid: 10000 },
{ id: 3, uid: 10001 }
].uniqueBy(it => it.uid);
Modules esnext.data-view.get-uint8-clamped and esnext.data-view.set-uint8-clamped
class DataView {
getUint8Clamped(offset: any): uint8
setUint8Clamped(offset: any, value: any): void;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/data-view-get-set-uint8-clamped
core-js/full/dataview/get-uint8-clamped
core-js/full/dataview/set-uint8-clamped
Examples:
const view = new DataView(new ArrayBuffer(1));
view.setUint8Clamped(0, 100500);
console.log(view.getUint8Clamped(0));
Module esnext.number.from-string
class Number {
fromString(string: string, radix: number): number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/number-from-string
core-js(-pure)/full/number/from-string
Module esnext.string.cooked
class String {
static cooked(template: Array<string>, ...substitutions: Array<string>): string;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/string-cooked
core-js(-pure)/full/string/cooked
Example:
function safePath(strings, ...subs) {
return String.cooked(strings, ...subs.map(sub => encodeURIComponent(sub)));
}
let id = 'spottie?';
safePath`/cats/${ id }`;
Module esnext.string.code-points
class String {
codePoints(): Iterator<{ codePoint, position }>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/string-code-points
core-js(-pure)/full/string/code-points
Example:
for (let { codePoint, position } of 'qwe'.codePoints()) {
console.log(codePoint);
console.log(position);
}
Module esnext.symbol.custom-matcher.
class Symbol {
static customMatcher: @@customMatcher;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/pattern-matching-v2
core-js(-pure)/full/symbol/custom-matcher
Module esnext.symbol.custom-matcher.
class Symbol {
static customMatcher: @@customMatcher;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/pattern-extractors
core-js(-pure)/full/symbol/custom-matcher
Stage 0 proposals⬆
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stage/0
Module esnext.function.demethodize
class Function {
demethodize(): Function;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/function-demethodize
core-js(-pure)/full/function/demethodize
core-js(-pure)/full/function/virtual/demethodize
Examples:
const slice = Array.prototype.slice.demethodize();
slice([1, 2, 3], 1);
Modules esnext.function.is-callable, esnext.function.is-constructor
class Function {
static isCallable(value: any): boolean;
static isConstructor(value: any): boolean;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/function-is-callable-is-constructor
core-js(-pure)/full/function/is-callable
core-js(-pure)/full/function/is-constructor
Examples:
Function.isCallable(null);
Function.isCallable({});
Function.isCallable(function () {});
Function.isCallable(() => {});
Function.isCallable(class {});
Function.isConstructor(null);
Function.isConstructor({});
Function.isConstructor(function () {});
Function.isConstructor(() => {});
Function.isConstructor(class {});
Pre-stage 0 proposals⬆
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stage/pre
Modules esnext.reflect.define-metadata, esnext.reflect.delete-metadata, esnext.reflect.get-metadata, esnext.reflect.get-metadata-keys, esnext.reflect.get-own-metadata, esnext.reflect.get-own-metadata-keys, esnext.reflect.has-metadata, esnext.reflect.has-own-metadata and esnext.reflect.metadata.
namespace Reflect {
defineMetadata(metadataKey: any, metadataValue: any, target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): void;
getMetadata(metadataKey: any, target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): any;
getOwnMetadata(metadataKey: any, target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): any;
hasMetadata(metadataKey: any, target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): boolean;
hasOwnMetadata(metadataKey: any, target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): boolean;
deleteMetadata(metadataKey: any, target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): boolean;
getMetadataKeys(target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): Array<mixed>;
getOwnMetadataKeys(target: Object, propertyKey?: PropertyKey): Array<mixed>;
metadata(metadataKey: any, metadataValue: any): decorator(target: Object, targetKey?: PropertyKey) => void;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/reflect-metadata
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/define-metadata
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/delete-metadata
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/get-metadata
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/get-metadata-keys
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/get-own-metadata
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/get-own-metadata-keys
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/has-metadata
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/has-own-metadata
core-js(-pure)/full/reflect/metadata
Examples:
let object = {};
Reflect.defineMetadata('foo', 'bar', object);
Reflect.ownKeys(object);
Reflect.getOwnMetadataKeys(object);
Reflect.getOwnMetadata('foo', object);
Web standards⬆
self⬆
Spec, module web.self
getter self: GlobalThisValue;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/self
Examples:
self.Array === Array;
structuredClone⬆
Spec, module web.structured-clone
function structuredClone(value: Serializable, { transfer?: Sequence<Transferable> }): any;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/structured-clone
Examples:
const structured = [{ a: 42 }];
const sclone = structuredClone(structured);
console.log(sclone);
console.log(structured !== sclone);
console.log(structured[0] !== sclone[0]);
const circular = {};
circular.circular = circular;
const cclone = structuredClone(circular);
console.log(cclone.circular === cclone);
structuredClone(42);
structuredClone({ x: 42 });
structuredClone([1, 2, 3]);
structuredClone(new Set([1, 2, 3]));
structuredClone(new Map([['a', 1], ['b', 2]]));
structuredClone(new Int8Array([1, 2, 3]));
structuredClone(new AggregateError([1, 2, 3], 'message'));
structuredClone(new TypeError('message', { cause: 42 }));
structuredClone(new DOMException('message', 'DataCloneError'));
structuredClone(document.getElementById('myfileinput'));
structuredClone(new DOMPoint(1, 2, 3, 4));
structuredClone(new Blob(['test']));
structuredClone(new ImageData(8, 8));
structuredClone(new WeakMap());
Caveats when using structuredClone polyfill:⬆
- Many platform types cannot be transferred in most engines since we have no way to polyfill this behavior, however
.transfer option works for some platform types. I recommend avoiding this option. - Some specific platform types can't be cloned in old engines. Mainly it's very specific types or very old engines, but here are some exceptions. For example, we have no sync way to clone
ImageBitmap in Safari 14.0- or Firefox 83-, so it's recommended to look to the polyfill source if you wanna clone something specific.
Base64 utility methods⬆
Specification, MDN. Modules web.atob, web.btoa.
function atob(data: string): string;
function btoa(data: string): string;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/atob
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/btoa
Examples:
btoa('hi, core-js');
atob('aGksIGNvcmUtanM=');
setTimeout and setInterval⬆
Module web.timers. Additional arguments fix for IE9-.
function setTimeout(callback: any, time: any, ...args: Array<mixed>): number;
function setInterval(callback: any, time: any, ...args: Array<mixed>): number;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/set-timeout
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/set-interval
setTimeout(log.bind(null, 42), 1000);
setTimeout(log, 1000, 42);
setImmediate⬆
Module web.immediate. setImmediate polyfill.
function setImmediate(callback: any, ...args: Array<mixed>): number;
function clearImmediate(id: number): void;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/set-immediate
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/clear-immediate
Examples:
setImmediate((arg1, arg2) => {
console.log(arg1, arg2);
}, 'Message will be displayed', 'with minimum delay');
clearImmediate(setImmediate(() => {
console.log('Message will not be displayed');
}));
queueMicrotask⬆
Spec, module web.queue-microtask
function queueMicrotask(fn: Function): void;
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/queue-microtask
Examples:
queueMicrotask(() => console.log('called as microtask'));
URL and URLSearchParams⬆
URL standard implementation. Modules web.url, web.url.can-parse, web.url.parse, web.url.to-json, web.url-search-params, web.url-search-params.delete, web.url-search-params.has, web.url-search-params.size.
class URL {
constructor(url: string, base?: string);
attribute href: string;
readonly attribute origin: string;
attribute protocol: string;
attribute username: string;
attribute password: string;
attribute host: string;
attribute hostname: string;
attribute port: string;
attribute pathname: string;
attribute search: string;
readonly attribute searchParams: URLSearchParams;
attribute hash: string;
toJSON(): string;
toString(): string;
static canParse(url: string, base?: string): boolean;
static parse(url: string, base?: string): URL | null;
}
class URLSearchParams {
constructor(params?: string | Iterable<[key, value]> | Object);
append(name: string, value: string): void;
delete(name: string, value?: string): void;
get(name: string): string | void;
getAll(name: string): Array<string>;
has(name: string, value?: string): boolean;
set(name: string, value: string): void;
sort(): void;
toString(): string;
forEach(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => void, thisArg: any): void;
entries(): Iterator<[key, value]>;
keys(): Iterator<key>;
values(): Iterator<value>;
@@iterator(): Iterator<[key, value]>;
readonly attribute size: number;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js/proposals/url
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/url
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/url/can-parse
core-js/stable|actual|full/url/to-json
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/url-search-params
Examples:
URL.canParse('https://login:password@example.com:8080/?a=1&b=2&a=3&c=4#fragment');
URL.canParse('https');
URL.parse('https://login:password@example.com:8080/?a=1&b=2&a=3&c=4#fragment');
URL.parse('https');
const url = new URL('https://login:password@example.com:8080/foo/bar?a=1&b=2&a=3#fragment');
console.log(url.href);
console.log(url.origin);
console.log(url.protocol);
console.log(url.username);
console.log(url.password);
console.log(url.host);
console.log(url.hostname);
console.log(url.port);
console.log(url.pathname);
console.log(url.search);
console.log(url.hash);
console.log(url.toJSON());
console.log(url.toString());
for (let [key, value] of url.searchParams) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
url.pathname = '';
url.searchParams.append('c', 4);
console.log(url.search);
console.log(url.href);
const params = new URLSearchParams('?a=1&b=2&a=3');
params.append('c', 4);
params.append('a', 2);
params.delete('a', 1);
params.sort();
console.log(params.size);
for (let [key, value] of params) {
console.log(key);
console.log(value);
}
console.log(params.has('a'));
console.log(params.has('a', 3));
console.log(params.has('a', 4));
console.log(params.toString());
Caveats when using URL and URLSearchParams:⬆
- IE8 does not support setters, so they do not work on
URL instances. However, URL constructor can be used for basic URL parsing. - Legacy encodings in a search query are not supported. Also,
core-js implementation has some other encoding-related issues. URL implementations from all of the popular browsers have much more problems than core-js, however, replacing all of them does not looks like a good idea. You can customize the aggressiveness of polyfill by your requirements.
DOMException:⬆
The specification. Modules web.dom-exception.constructor, web.dom-exception.stack, web.dom-exception.to-string-tag.
class DOMException {
constructor(message: string, name?: string);
readonly attribute name: string;
readonly attribute message: string;
readonly attribute code: string;
attribute stack: string;
@@toStringTag: 'DOMException';
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/dom-exception
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/dom-exception/constructor
core-js/stable|actual|full/dom-exception/to-string-tag
Examples:
const exception = new DOMException('error', 'DataCloneError');
console.log(exception.name);
console.log(exception.message);
console.log(exception.code);
console.log(typeof exception.stack);
console.log(exception instanceof DOMException);
console.log(exception instanceof Error);
console.log(exception.toString());
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(exception));
Iterable DOM collections⬆
Some DOM collections should have iterable interface or should be inherited from Array. That means they should have forEach, keys, values, entries and @@iterator methods for iteration. So add them. Modules web.dom-collections.iterator and web.dom-collections.for-each.
class [
CSSRuleList,
CSSStyleDeclaration,
CSSValueList,
ClientRectList,
DOMRectList,
DOMStringList,
DataTransferItemList,
FileList,
HTMLAllCollection,
HTMLCollection,
HTMLFormElement,
HTMLSelectElement,
MediaList,
MimeTypeArray,
NamedNodeMap,
PaintRequestList,
Plugin,
PluginArray,
SVGLengthList,
SVGNumberList,
SVGPathSegList,
SVGPointList,
SVGStringList,
SVGTransformList,
SourceBufferList,
StyleSheetList,
TextTrackCueList,
TextTrackList,
TouchList,
] {
@@iterator(): Iterator<value>;
}
class [DOMTokenList, NodeList] {
forEach(callbackfn: (value: any, index: number, target: any) => void, thisArg: any): void;
entries(): Iterator<[key, value]>;
keys(): Iterator<key>;
values(): Iterator<value>;
@@iterator(): Iterator<value>;
}
CommonJS entry points:
core-js(-pure)/stable|actual|full/dom-collections/iterator
core-js/stable|actual|full/dom-collections/for-each
Examples:
for (let { id } of document.querySelectorAll('*')) {
if (id) console.log(id);
}
for (let [index, { id }] of document.querySelectorAll('*').entries()) {
if (id) console.log(index, id);
}
document.querySelectorAll('*').forEach(it => console.log(it.id));
Iteration helpers⬆
Helpers for check iterability / get iterator in the pure version or, for example, for arguments object:
function isIterable(value: any): boolean;
function getIterator(value: any): Object;
function getIteratorMethod(value: any): Function | void;
CommonJS entry points:
@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/es|stable|actual|full/is-iterable
@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/es|stable|actual|full/get-iterator
@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/es|stable|actual|full/get-iterator-method
Examples:
import isIterable from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/is-iterable';
import getIterator from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/get-iterator';
import getIteratorMethod from '@firanorg/bookish-broccoli/actual/get-iterator-method';
let list = (function () {
return arguments;
})(1, 2, 3);
console.log(isIterable(list));
let iterator = getIterator(list);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
getIterator({});
let method = getIteratorMethod(list);
console.log(typeof method);
let iterator = method.call(list);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
console.log(iterator.next().value);
console.log(getIteratorMethod({}));
Missing polyfills⬆
- ES
BigInt can't be polyfilled since it requires changes in the behavior of operators, you could find more info here. You could try to use JSBI. - ES
Proxy can't be polyfilled, you can try to use proxy-polyfill which provides a very little subset of features. - ES
String#normalize is not a very useful feature, but this polyfill will be very large. If you need it, you can use unorm. - ECMA-402
Intl is missed because of the size. You can use those polyfills. window.fetch is not a cross-platform feature, in some environments, it makes no sense. For this reason, I don't think it should be in core-js. Looking at a large number of requests it might be added in the future. Now you can use, for example, this polyfill.









