
Research
Security News
Quasar RAT Disguised as an npm Package for Detecting Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.
@ideditor/location-conflation
Advanced tools
Define complex geographic regions by including and excluding country codes and geojson shapes
🧩 Define complex geographic regions by including and excluding country codes and GeoJSON shapes.
Location-conflation is a tool for generating GeoJSON features by including and excluding other locations and shapes.
⚡️ Try it now!: https://ideditor.github.io/location-conflation/
You can define a locationSet as an Object with include and exclude properties:
let locationSet = {
include: [ Array of locations ],
exclude: [ Array of locations ]
};
The "locations" can be any of the following:
"de".geojson features. If you want to use your own features, pass them to the LocationConflation constructor in a FeatureCollection - each Feature must have an id that ends in .geojson."de-hamburg.geojson"[longitude, latitude] coordinate pairs. A 25km radius circle will be computed around the point.[8.67039, 49.41882]To install location-conflation as a dependency in your project:
$ npm install --save @ideditor/location-conflation
location-conflation is distributed in both UMD and ES6 module formats for maxmimum compatibility. (Read more about Javascript module formats)
index.mjs - ES6 moduledist/index.js - UMD module, ES6 syntaxdist/index.es5.js - UMD module, ES5 syntaxWhether you require or import it, it should just work.
const LocationConflation = require('@ideditor/location-conflation'); // UMD import all
// or
import * as LocationConflation from '@ideditor/location-conflation'; // ES6 import all
You can also use location-conflation directly in a web browser. A good way to do this is to fetch the file from the jsDelivr CDN, which can even deliver minified versions.
The latest versions of many web browsers now support ES6 modules in script tags like this:
<script type="module" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@ideditor/location-conflation@0.5/index.min.mjs"></script>
Older versions of modern ES6-capable browsers can still load the UMD build:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@ideditor/location-conflation@0.5/dist/index.min.js"></script>
Or if you need to support even older browsers like Internet Explorer, fetch the ES5 version:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@ideditor/location-conflation@0.5/dist/index.es5.min.js"></script>
const LocationConflation = require('@ideditor/location-conflation');
const myFeatures = require('./path/to/FeatureCollection.json'); // optional
const loco = new LocationConflation(myFeatures);
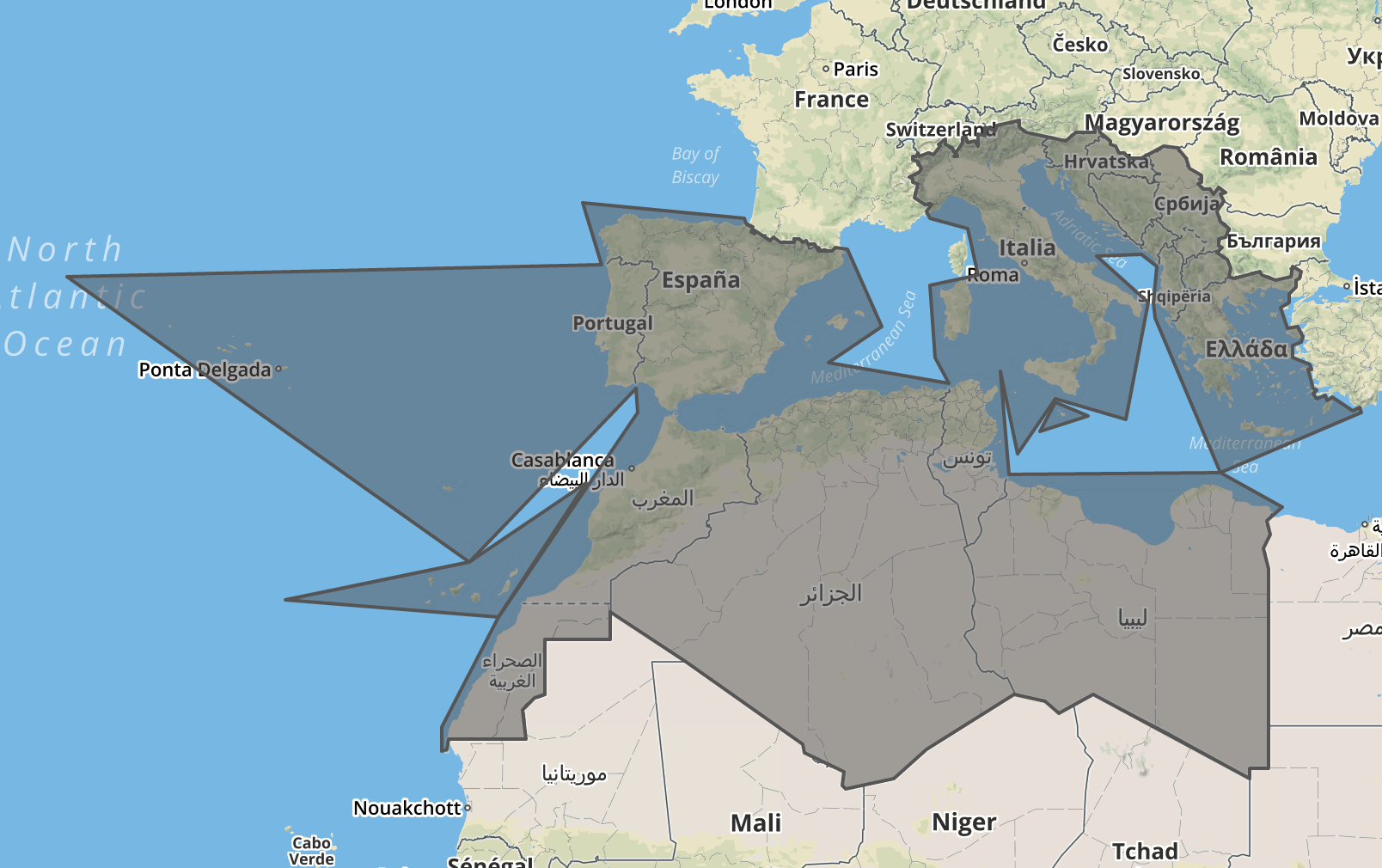
let locationSet = { include: ['039'] }; // 039 = Southern Europe
let result = loco.resolveLocationSet(locationSet);
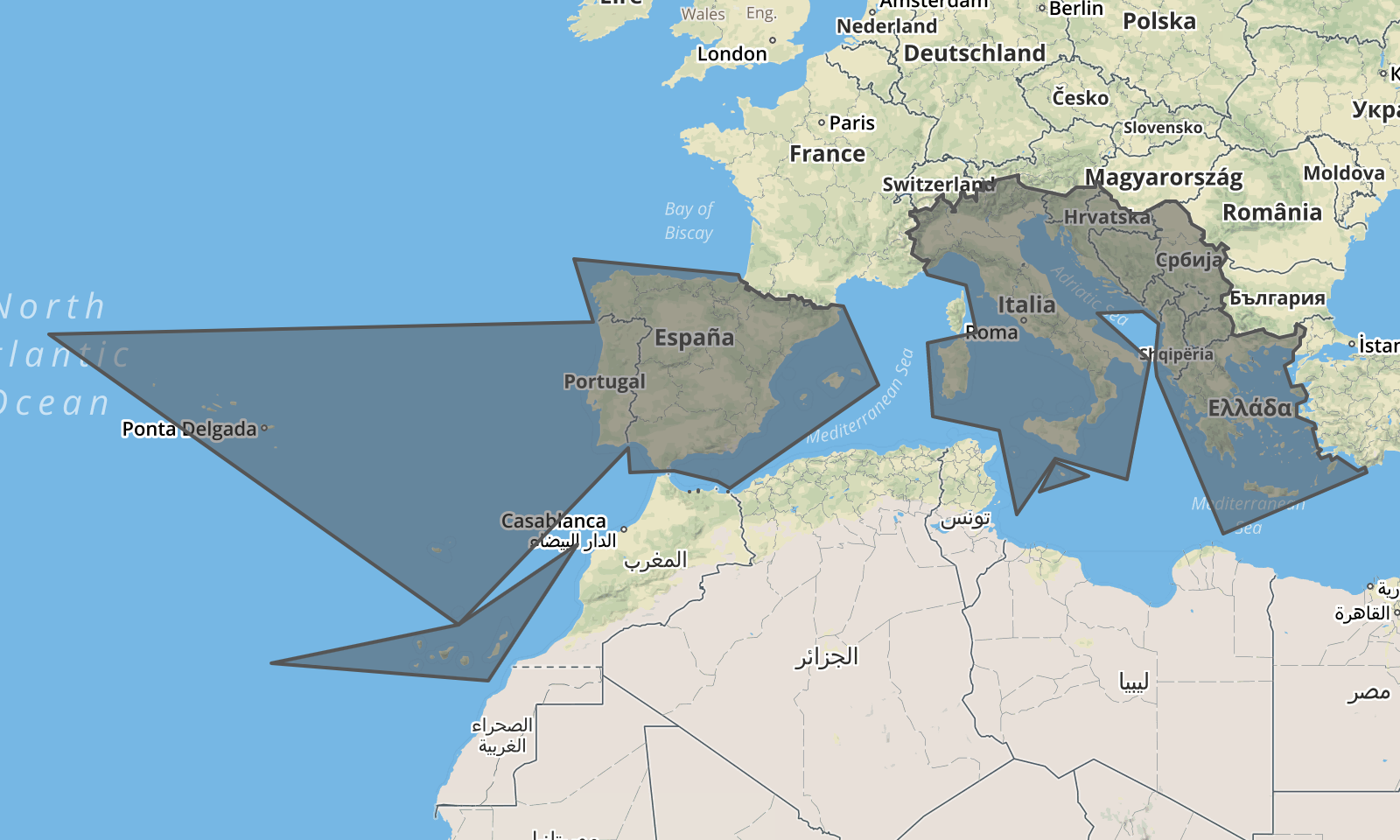
let locationSet = { include: ['039','015'] }; // 015 = Northern Africa
let result = loco.resolveLocationSet(locationSet);
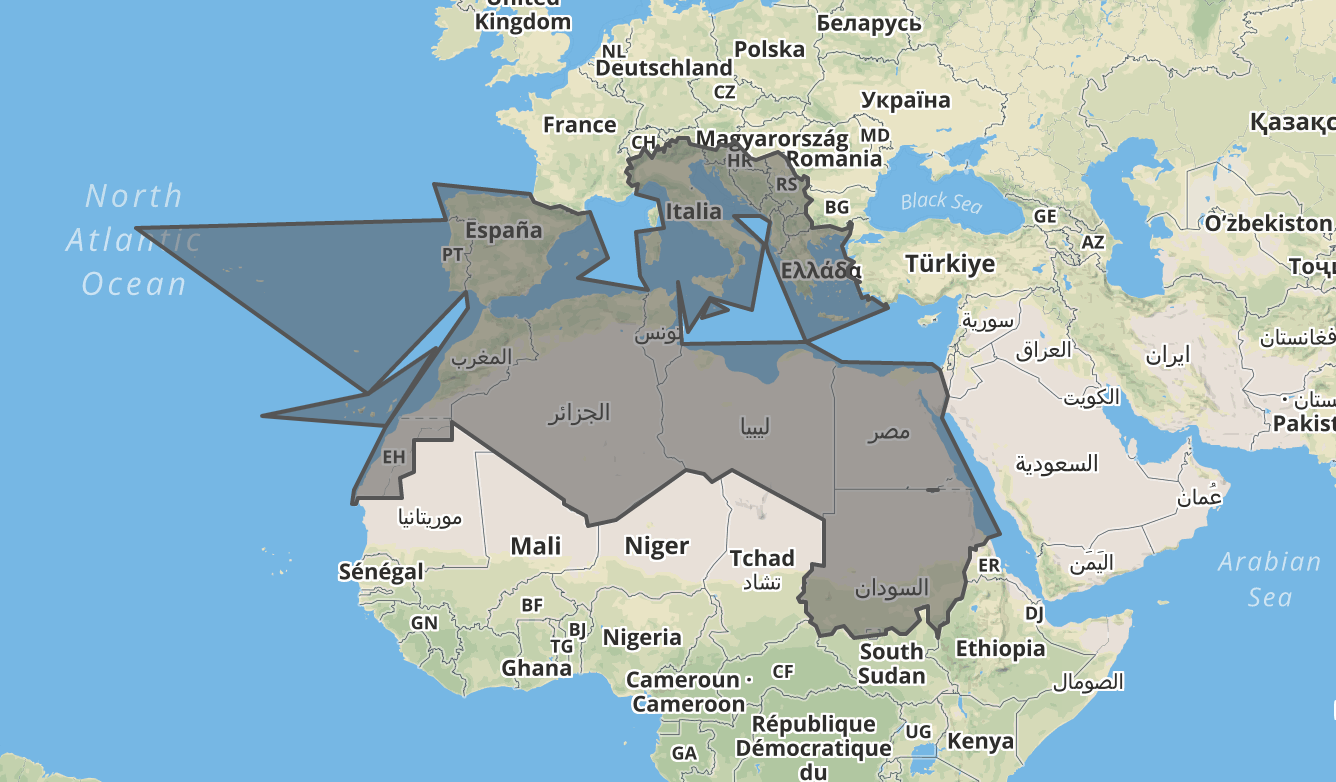
let locationSet = { include: ['039','015'], exclude: ['eg','sd'] };
let result = loco.resolveLocationSet(locationSet);
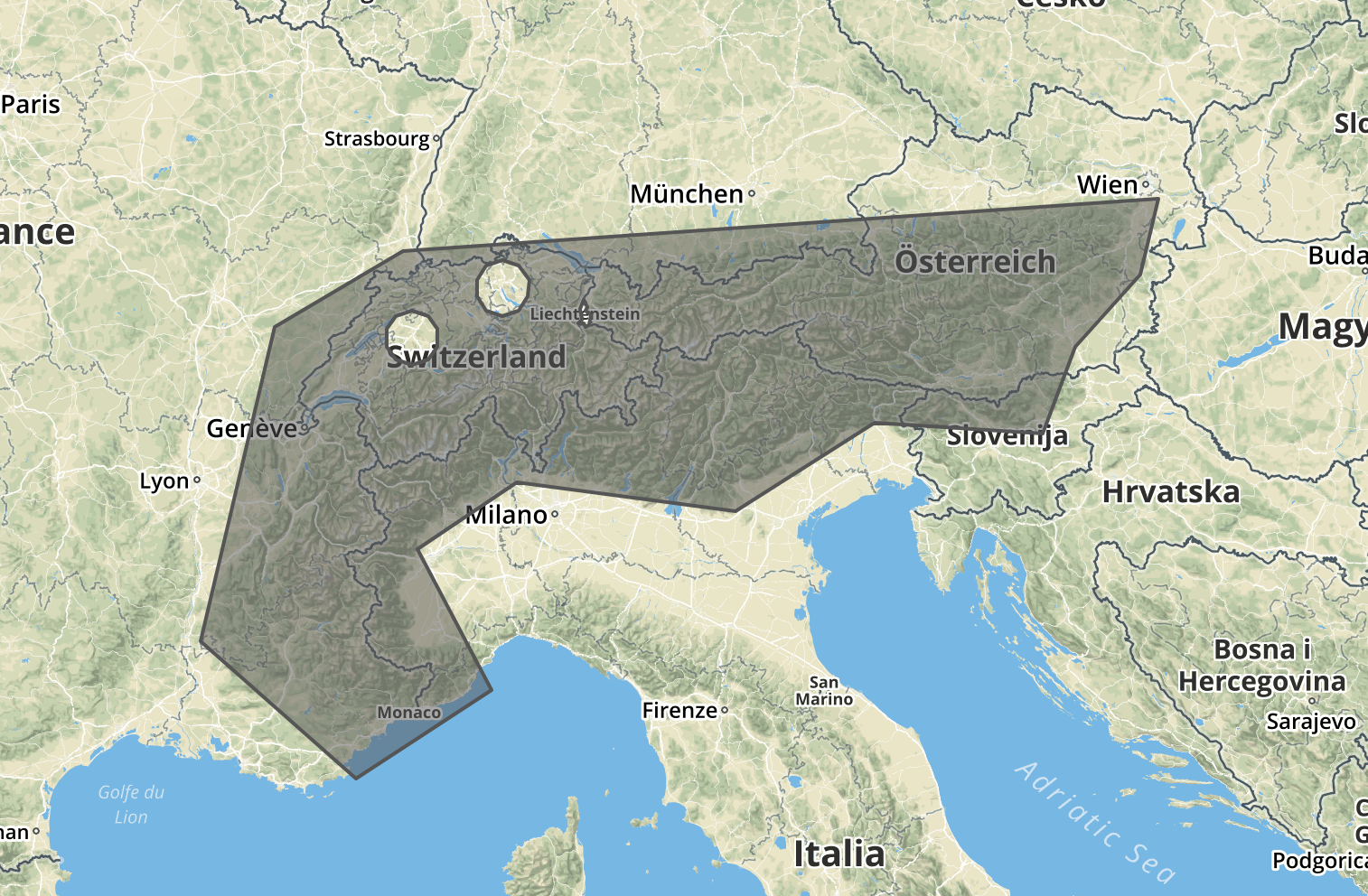
let result = loco.resolveLocationSet({ include: ['alps.geojson'], exclude: ['li', [8.55,47.36], [7.45,46.95]] });
# const loco = new LocationConflation(featureCollection)
Constructs a new LocationConflation instance.
Optionally pass a GeoJSON FeatureCollection of known features which can be used later as locations.
Each feature must have a filename-like id, for example: example.geojson
{
"type": "FeatureCollection"
"features": [
{
"type": "Feature",
"id": "example.geojson",
"properties": { … },
"geometry": { … }
}
]
}
# loco.validateLocation(location)
Validates a given location. The "locations" can be:
[longitude, latitude] coordinate pairs. Example: [8.67039, 49.41882].geojson features. Example: "de-hamburg.geojson""de"If the location is valid, returns a result Object like:
{
type: 'point', 'geojson', or 'countrycoder'
location: the queried location
id: the stable identifier for the feature
}
If the location is invalid,
null
# loco.validateLocationSet(locationSet)
Validates a given locationSet. Pass a locationSet Object like:
{
include: [ Array of locations ],
exclude: [ Array of locations ]
}
If the locationSet is valid, returns a result Object like:
{
type: 'locationset'
locationSet: the queried locationSet
id: the stable identifier for the feature
}
If the locationSet is invalid or contains any invalid locations,
{ type: 'locationset', locationSet: ['Q2'], id: +[Q2] }
# loco.resolveLocation(location)
Resolves a given location into a GeoJSON feature. This is similar to validateLocation, but runs slower and includes the actual GeoJSON in the result. Results are cached, so if you ask for the same thing multiple times we don't repeat the expensive clipping operations.
The returned GeoJSON feature will also have an area property containing the approximate size of the feature in km². (This is helpful for sorting features)
If the location is valid, returns a result Object like:
{
type: 'point', 'geojson', or 'countrycoder'
location: the queried location
id: the stable identifier for the feature
feature: the resolved GeoJSON feature
}
If the location is invalid,
null
# loco.resolveLocationSet(locationSet)
Resolves a given locationSet into a GeoJSON feature. This is similar to validateLocationSet, but runs slower and includes the actual GeoJSON in the result. Results are cached, so if you ask for the same thing multiple times we don't repeat the expensive clipping operations.
The returned GeoJSON feature will also have an area property containing the approximate size of the feature in km². (This is helpful for sorting features)
If the locationSet is valid, returns a result Object like:
{
type: 'locationset'
locationSet: the queried locationSet
id: the stable identifier for the feature
feature: the resolved GeoJSON feature
}
If the locationSet is invalid or contains any invalid locations,
{ type: 'locationset', locationSet: ['Q2'], id: +[Q2] }
# loco.strict(val)
Get/set "strict mode". New instances of LocationConflation start out in strict mode by default.
loco.strict(false); // pass a true/false value to set the strict mode
const isStrict = loco.strict(); // pass no value to return the current value
# loco.stringify(object, options)
Convenience method that wraps json-stringify-pretty-compact to stringify the given object. Optional options parameter gets passed through to json-stringify-pretty-compact.
loco.stringify(someGeoJson, { maxLength: 100 }); // Make it pretty!
# loco.cache()
Convenience method to access the internal feature _cache. You probably shouldn't use it except for debugging.
git clone git@github.com:ideditor/location-conflation.gitcd into the project folder,npm install to install librariesnpm run buildlocation-conflation is really just a wrapper around these other great projects:
This project is available under the ISC License. See the LICENSE.md file for more details.
0.5.0
validateLocation / validateLocationSet - fast, return stable idsresolveLocation / resolveLocationSet - slower, resolve GeoJSON features.strict(val), for example:<br/>
const loco = new LocationConflation(features).strict(false); // not strictFAQs
Define complex geographic regions by including and excluding country codes and geojson shapes
We found that @ideditor/location-conflation demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 6 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.

Security News
Research
A supply chain attack on Rspack's npm packages injected cryptomining malware, potentially impacting thousands of developers.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers discovered a malware campaign on npm delivering the Skuld infostealer via typosquatted packages, exposing sensitive data.