



This project is part of the
@thi.ng/umbrella monorepo.
About
Typedarray integer & float pixel buffers w/ customizable formats, blitting, dithering, convolution.

- Buffer creation from HTML image elements w/ opt resize & format
conversion (browser only)
- Buffer-to-buffer blitting w/ automatic format conversion
- Buffer-to-canvas blitting
- Buffer-to-buffer blending w/ Porter-Duff
operators
- Pre/post-multiply alpha
- Region / sub-image extraction
- Single-channel manipulation / extraction / replacement / conversion
- k-means based dominant color extraction (float buffers only)
- Accessors for normalized channel value
- Image sampling, resizing, pooling
- Filters: nearest neighbor, bilinear, bicubic
- Wrap behaviors: clamp, wrap, repeat
- Pooling: mean/min/max
- Invert image
- Convolution w/ arbitrary shaped/sized kernels, pooling, striding
- Convolution kernel & pooling kernels presets
- Higher order kernel generators (Gaussian, Lanczos)
- Image pyramid generation (w/ customizable kernels)
- Customizable normal map generation (i.e. X/Y gradients plus static Z component)
- XY full pixel & channel-only accessors
- 12 packed integer and 6 floating point preset formats (see table below)
- Ordered dithering w/ customizable Bayer matrix size and target color
steps (int formats only)
- Declarative custom format & optimized code generation
- HTML canvas creation &
ImageData utilities
Packed integer pixel formats
All packed integer formats use the canvas native ABGR 32bit format as
common intermediate for conversions. During conversion to ABGR, channels
with sizes smaller than 8 bits will be scaled appropriately to ensure an
as full-range and as linear as possible mapping. E.g. a 4 bit channel
will be scaled by 255 / 15 = 17.
Format specs can freely control channel layout within current limits:
- Channel sizes: 1 - 32 bits.
- Storage: 8, 16 or 32 bits per pixel
New formats can be defined via defPackedFormat().
| Format ID | Bits per pixel | Description |
|---|
ALPHA8 | 8 | 8 bit channel (alpha only) |
GRAY8 | 8 | 8 bit single channel (grayscale conv) |
GRAY_ALPHA8 | 16 | 8 bit single channel (grayscale conv), 8 bit alpha |
GRAY16 | 16 | 16 bit single channel (grayscale conv) |
GRAY_ALPHA16 | 32 | 16 bit single channel (grayscale conv), 16 bit alpha |
ARGB4444 | 16 | 4 channels @ 4 bits each |
ARGB1555 | 16 | 5 bits each for RGB, 1 bit alpha |
RGB565 | 16 | 5 bits red, 6 bits green, 5 bits blue |
RGB888 | 32 (24 effective) | 3 channels @ 8 bits each |
ARGB8888 | 32 | 4 channels @ 8 bits each |
BGR888 | 32 (24 effective) | 3 channels @ 8 bits each |
ABGR8888 | 32 | 4 channels @ 8 bits each |
ALPHA8 is mapped from/to ABGR alpha channelGRAY8/16, GRAY_ALPHA8/16 compute grayscale/luminance when
converting from ABGR and in return produce grayscale ABGR- In all built-in formats supporting it, the alpha channel always
occupies the most-significant bits (up to format size)
Floating point pixel formats
Strided floating point format presets for use with floatBuffer(). New
formats can be defined via defFloatFormat().
| Format ID | Channel count | Description |
|---|
FLOAT_GRAY | 1 | Single channel / grayscale |
FLOAT_GRAY_ALPHA | 2 | Grayscale and alpha channel |
FLOAT_NORMAL | 3 | Normal map (signed values) |
FLOAT_RGB | 3 | Red, Green, Blue |
FLOAT_RGBA | 4 | Red, Green, Blue, Alpha |
- All color channels are unclamped (but can be clamped via
buf.clamp()). For
conversion to packed int formats assumed to contain normalized data (i.e.
[0..1] interval, with exception of FLOAT_NORMAL which uses [-1..1] range) - Conversion between float formats is currently unsupported
Filtered image sampling and resizing
Available (and optimized) for both integer & floating point formats, image
samplers can be created with the following filters & wrap modes:
Filters
"nearest" - nearest neighbor"linear" - bilinear interpolation"cubic" - bicubic interpolation
Wrap mode
"clamp" - outside values return 0"wrap" - infinite tiling"repeat" - edge pixels are repeated
const src = packedBuffer(4, 4, ABGR8888);
src.forEach((_,i) => 0xff000000 | Math.random() * 0xffffff);
const sampler = defSampler(src, "linear", "repeat");
sampler(-1.1, 0.5).toString(16)
const img = src.resize(1024, 256, "cubic");
| Filter | |
|---|
"nearest" |  |
"linear" |  |
"cubic" |  |
Strided convolution & pooling
Floating point buffers can be processed using arbitrary convolution kernels. The
following convolution kernel presets are provided for convenience:
| Kernel | Size |
|---|
BOX_BLUR3 | 3x3 |
BOX_BLUR5 | 5x5 |
GAUSSIAN_BLUR3 | 3x3 |
GAUSSIAN_BLUR5 | 5x5 |
GAUSSIAN(n) | 2n+1 x 2n+1 |
HIGHPASS3 | 3x3 |
LANCZOS(a,s) | as+1 x as+1 |
SHARPEN3 | 3x3 |
SOBEL_X | 3x3 |
SOBEL_Y | 3x3 |
UNSHARP_MASK5 | 5x5 |
Custom kernels can be defined (and code generated) using an array of
coefficients and a given kernel size. See above presets and
defKernel() for
reference.
Furthermore, convolution supports striding (i.e. only processing & keeping every
nth pixel column/row, aka downscaling) and pixel pooling (e.g. for ML
applications). Available pooling kernel presets (kernel sizes must be configured
independently):
| Kernel | Description |
|---|
POOL_MEAN | Moving average |
POOL_MAX | Local maximum |
POOL_MIN | Local minimum |
POOL_NEAREST | Nearest neighbor |
POOL_THRESHOLD(bias) | Adaptive threshold |
Convolution can be applied to single, multiple or all channels of a
FloatBuffer. See
convolveChannel()
and
convolveImage().
See
ConvolveOpts
for config options.
src = floatBuffer(read("test.ppm"), FLOAT_RGB);
convolveImage(src, { kernel: SOBEL_X, stride: 2, scale: 4 });
Normal map generation
Normal maps can be created via normalMap(). This function uses an adjustable
convolution kernel size to control gradient smoothness & details. Result X/Y
gradients can also be scaled (uniform or anisotropic) and the Z component can be
customized to (default: 1.0). The resulting image is in FLOAT_NORMAL format,
using signed channel values. This channel format is auto-translating these into
unsigned values when the image is converted into an integer format.
| Step | Scale = 1 | Scale = 2 | Scale = 4 | Scale = 8 |
|---|
| 0 |  |  |  |  |
| 1 |  |  |  |  |
| 2 |  |  |  |  |
| 3 |  |  | 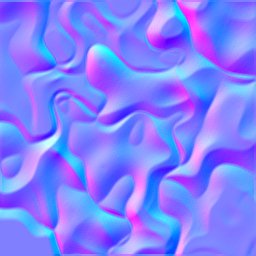 | 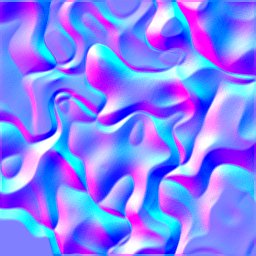 |
import { floatBuffer, normalMap, FLOAT_GRAY, RGB888 } from "@thi.ng/pixel";
import { asPPM, read } from "@thi.ng/pixel-io-netpbm";
const src = floatBuffer(read(readFileSync("noise.pgm")), FLOAT_GRAY);
const nmap = normalMap(src, { step: 0, scale: 1 });
nmap.getAt(10, 10);
writeFileSync("noise-normal.ppm", asPPM(nmap.as(RGB888)));
The dominantColors() function applies k-means
clustering to
extract the dominant colors from the given image. The clustering can be
configured. The function returns an array of { color, area } objects (sorted
by descending area), where color is a cluster's dominant color (in the format
of the source image) and area the normalized cluster size (number of selected
pixels over total number of pixels in the image).
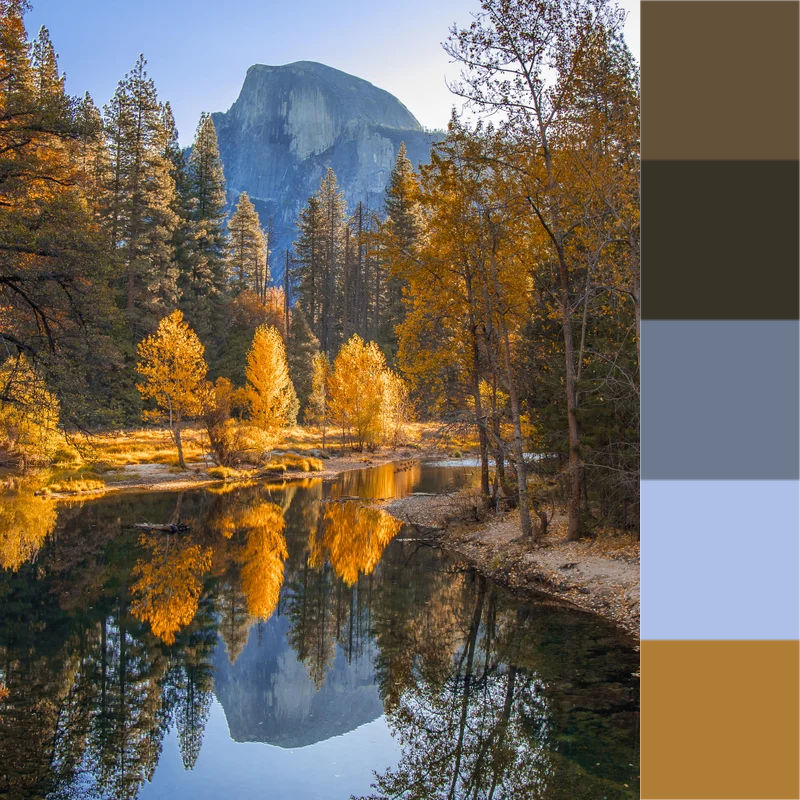

Picture credit: /u/kristophershinn
const img = floatBuffer(read(readFileSync(`test.ppm`)), FLOAT_RGB);
const clusters = dominantColors(img, 5);
console.log(clusters);
Status
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
Support packages
Related packages
Installation
yarn add @thi.ng/pixel
// ES module
<script type="module" src="https://unpkg.com/@thi.ng/pixel?module" crossorigin></script>
// UMD
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@thi.ng/pixel/lib/index.umd.js" crossorigin></script>
Package sizes (gzipped, pre-treeshake): ESM: 9.22 KB / CJS: 9.52 KB / UMD: 9.23 KB
Dependencies
Usage examples
Several demos in this repo's
/examples
directory are using this package.
A selection:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|---|
 | Interactive image processing (adaptive threshold) | Demo | Source |
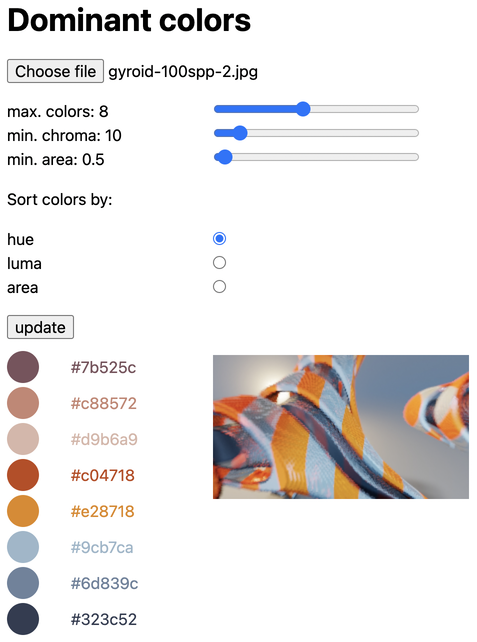 | Color palette generation via dominant color extraction from uploaded images | Demo | Source |
 | Pixel buffer manipulations | Demo | Source |
 | Interactive pixel sorting tool using thi.ng/color & thi.ng/pixel | Demo | Source |
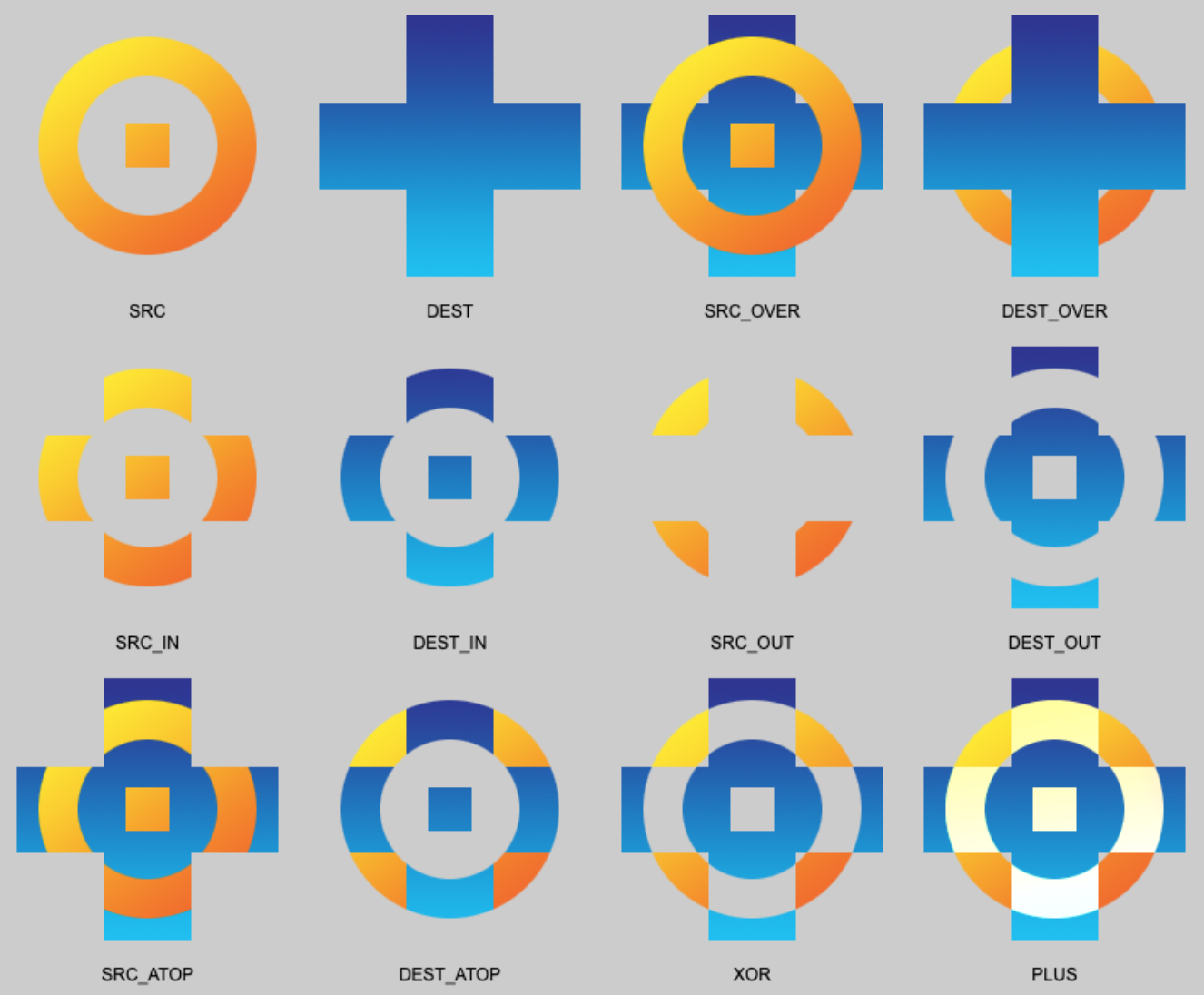 | Port-Duff image compositing / alpha blending | Demo | Source |
 | Fork-join worker-based raymarch renderer | Demo | Source |
 | Textmode image warping w/ 16bit color output | Demo | Source |
| Minimal multi-pass / GPGPU example | Demo | Source |
API
Generated API docs
import * as pix from "@thi.ng/pixel";
import { SRC_OVER_I } from "@thi.ng/porter-duff";
import IMG from "../assets/haystack.jpg";
import LOGO from "../assets/logo-64.png";
Promise
.all([IMG, LOGO].map(pix.imagePromise))
.then(([img, logo]) => {
const buf = pix.PackedBuffer.fromImage(img, pix.RGB565, 256, 256);
pix.PackedBuffer.fromImage(logo, pix.GRAY_ALPHA88)
.premultiply()
.blend(SRC_OVER_I, buf, {
dx: 10,
dy: 10
});
const region = buf.getRegion(32, 96, 128, 64);
region.blit(buf, { dx: 96, dy: 32 });
const ctx = pix.canvas2d(buf.width, buf.height * 3);
buf.blitCanvas(ctx.canvas);
const id = 0;
const ch = buf.getChannel(id).invert();
for (let y = 0; y < ch.height; y += 2) {
for (let x = (y >> 1) & 1; x < ch.width; x += 2) {
ch.setAt(x, y, 0xff);
}
}
buf.setChannel(id, ch);
buf.blitCanvas(ctx.canvas, 0, buf.height);
buf.as(GRAY8).blitCanvas(ctx.canvas, 0, buf.height * 2);
document.body.appendChild(ctx.canvas);
});
TODO see examples & source comments for now
Authors
Karsten Schmidt
If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-pixel,
title = "@thi.ng/pixel",
author = "Karsten Schmidt",
note = "https://thi.ng/pixel",
year = 2019
}
License
© 2019 - 2021 Karsten Schmidt // Apache Software License 2.0









